Rectus Capitis Posterior Major: Difference between revisions
Evan Thomas (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Evan Thomas (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
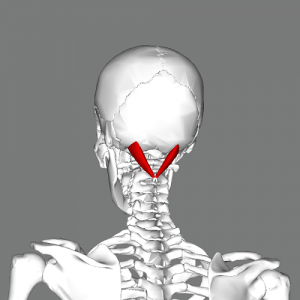
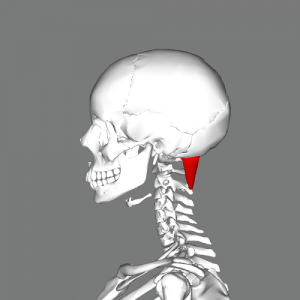
The fibers of this muscle skips C1 as it runs from C2 to the occiput, lateral to the rectus capitis posterior minor. It is also known as the Greater Posterior Rectus Capitis, and comprises the posterosuperior boarder of the suboccipital triangle. | The fibers of this muscle skips C1 as it runs from C2 to the occiput, lateral to the rectus capitis posterior minor. It is also known as the Greater Posterior Rectus Capitis, and comprises the posterosuperior boarder of the suboccipital triangle.<ref name="T&S">Travell JG, Simons DG, Simons LS (1998). Travell and Simons' Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: The Trigger Point Manual, Volume 1: Upper Half of Body (2nd ed). Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins.</ref> | ||
{| cellpadding="2" border="0;" | {| cellpadding="2" border="0;" | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
== Proximal Attachment (Origin) == | == Proximal Attachment (Origin) == | ||
Tip of the spinous process of the axis (C2). | Tip of the spinous process of the axis (C2).<ref name="AE">http://www.anatomyexpert.com/structure_detail/5210/</ref> | ||
== Distal Attachment (Insertion) == | == Distal Attachment (Insertion) == | ||
Lateral aspect of the inferior nuchal line of the occiput, as well as to the bone inferior to this line. | Lateral aspect of the inferior nuchal line of the occiput,<ref name="AE" /> as well as to the bone inferior to this line.<ref name="T&S" /> | ||
== Nerve Supply == | == Nerve Supply == | ||
Suboccipital nerve or dorsal ramus of cervical spinal nerve (C1). | Suboccipital nerve or dorsal ramus of cervical spinal nerve (C1).<ref name="AE" /> | ||
== Blood Supply == | == Blood Supply == | ||
Vertebral artery and the deep descending branch of the occipital artery. | Vertebral artery and the deep descending branch of the occipital artery.<ref name="AE" /> | ||
== Action == | == Action == | ||
Ipsilateral rotation of the atlantoaxial joint. | Ipsilateral rotation of the atlantoaxial joint.<ref name="Grants">Agur AMR, Dalley AF (2012). Grant's Atlas of Anatomy (13th ed). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.</ref> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Likely a postural muscle that monitors the position of the head. | Likely a postural muscle that monitors the position of the head.<ref name="AE" /> | ||
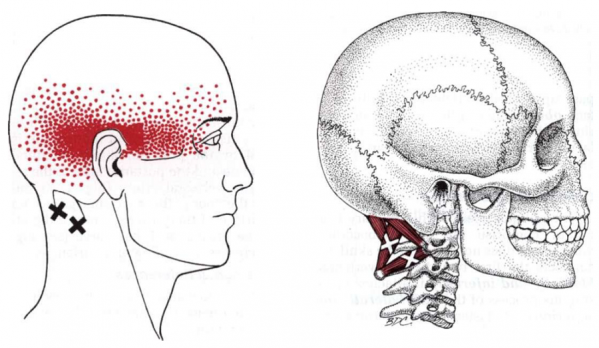
== Trigger Point Referral Pattern == | == Trigger Point Referral Pattern<ref name="T&S" /> == | ||
[[Image:OCI RCPM TrP Referral.png|center|600x348px|OCI_post_view]] | [[Image:OCI RCPM TrP Referral.png|center|600x348px|OCI_post_view]] | ||
== Recent Related Research (from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ Pubmed]) == | == Recent Related Research (from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ Pubmed]) == | ||
Revision as of 17:37, 21 February 2014
Original Editor - Evan Thomas
Lead Editors - Evan Thomas, Vidya Acharya, Tarina van der Stockt, WikiSysop and Kim Jackson
Description[edit | edit source]
The fibers of this muscle skips C1 as it runs from C2 to the occiput, lateral to the rectus capitis posterior minor. It is also known as the Greater Posterior Rectus Capitis, and comprises the posterosuperior boarder of the suboccipital triangle.[1]
Proximal Attachment (Origin)[edit | edit source]
Tip of the spinous process of the axis (C2).[2]
Distal Attachment (Insertion)[edit | edit source]
Lateral aspect of the inferior nuchal line of the occiput,[2] as well as to the bone inferior to this line.[1]
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Suboccipital nerve or dorsal ramus of cervical spinal nerve (C1).[2]
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
Vertebral artery and the deep descending branch of the occipital artery.[2]
Action[edit | edit source]
Ipsilateral rotation of the atlantoaxial joint.[3]
Function[edit | edit source]
Likely a postural muscle that monitors the position of the head.[2]
Trigger Point Referral Pattern[1][edit | edit source]
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Failed to load RSS feed from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=18E289OhM5uzk8xMY7ztSOekXlsSF11IjLHoEXe0G3R1uaJcNN|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10: Error parsing XML for RSS
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Travell JG, Simons DG, Simons LS (1998). Travell and Simons' Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: The Trigger Point Manual, Volume 1: Upper Half of Body (2nd ed). Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 http://www.anatomyexpert.com/structure_detail/5210/
- ↑ Agur AMR, Dalley AF (2012). Grant's Atlas of Anatomy (13th ed). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.