Femoral Neck Fractures, Garden Classification: Difference between revisions
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
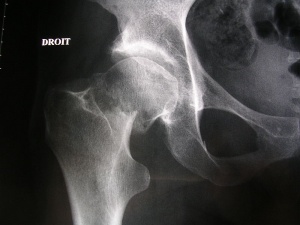
[[File:Neck of femur fracture (garden IV).jpeg|thumb|NOF fracture, Garden 4]] | [[File:Neck of femur fracture (garden IV).jpeg|thumb|NOF fracture, Garden 4]] | ||
'''The Garden classification''' is the most commonly used | '''The Garden classification''' is the most commonly used to classify intracapsular [[Femoral Neck Fractures|femoral neck fractures]]<ref>Garden RS. Low-angle fixation in fractures of the femoral neck. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. British Volume. 1961 Nov;43(4):647-63.</ref>. It is simple and predicts the development of [[Avascular necrosis of the femoral head]]. Garden splits into four categories depending on the severity of the fracture and the degree of displacement. | ||
==Classification of Hip Fractures== | ==Classification of Hip Fractures== | ||
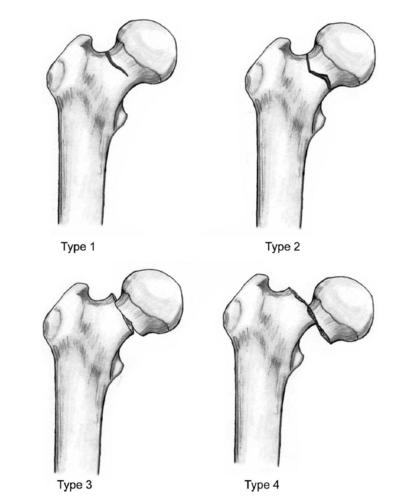
The categories are graded, depending on the type of fracture: | |||
# Type I is an incomplete fracture or valgus impacted [[fracture]]. | # Type I is an incomplete fracture or valgus impacted [[fracture]]. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
== Surgical Treatment == | == Surgical Treatment == | ||
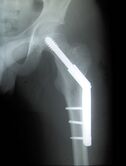
[[File:DHS.jpg|thumb|166x166px|DHS]] | [[File:DHS.jpg|thumb|166x166px|DHS]] | ||
In general: | Surgery may be indicated depending on the type of fracture. In general: | ||
# Garden stage I and II are stable fractures and can be treated with internal fixation (head-preservation) eg [[Dynamic Hip Screw - DHS|Dynamic hip screw DHS]] | # Garden stage I and II are stable fractures and can be treated with internal fixation (head-preservation) eg [[Dynamic Hip Screw - DHS|Dynamic hip screw DHS]] | ||
Revision as of 12:48, 13 December 2022
Original Editor - Lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton and Kim Jackson
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The Garden classification is the most commonly used to classify intracapsular femoral neck fractures[1]. It is simple and predicts the development of Avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Garden splits into four categories depending on the severity of the fracture and the degree of displacement.
Classification of Hip Fractures[edit | edit source]
The categories are graded, depending on the type of fracture:
- Type I is an incomplete fracture or valgus impacted fracture.
- Type II is a complete fracture without displacement.
- Type III is a complete fracture with partial displacement of fracture fragments.
- Type IV is a complete fracture with total displacement of fracture fragments, allowing the femoral head to rotate back to its anatomical position within the acetabulum.[2]
Surgical Treatment[edit | edit source]
Surgery may be indicated depending on the type of fracture. In general:
- Garden stage I and II are stable fractures and can be treated with internal fixation (head-preservation) eg Dynamic hip screw DHS
- Garden stage III and IV are unstable fractures and hence treated with hemi or total hip replacement.[3]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Garden RS. Low-angle fixation in fractures of the femoral neck. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. British Volume. 1961 Nov;43(4):647-63.
- ↑ Florschutz AV, Langford JR, Haidukewych GJ, Koval KJ. Femoral neck fractures: current management. Journal of orthopaedic trauma. 2015 Mar 1;29(3):121-9.
- ↑ Radiopedia Classification Garden Available: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/garden-classification-of-hip-fractures?lang=gb(accessed 13.12.2022)