Joint Range of Motion During Gait: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Stance Versus Swing Phase == | == Stance Versus Swing Phase == | ||
The | The typical forward stride consists of two phases: stance phase and swing phase.<ref>Cicirelli G, Impedovo D, Dentamaro V, Marani R, Pirlo G, D’Orazio TR. [https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9466394 Human gait analysis in neurodegenerative diseases: a review.] IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics. 2021 Jun 28;26(1):229-42.</ref> | ||
* The stance phase occupies 0-60% of the gait cycle, | * The stance phase occupies 0-60% of the gait cycle. During stance phase, one leg and foot bear most or all of the body weight.<ref name=":4">Magee DJ, Manske RC. Orthopedic physical assessment-E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2020 Dec 11.</ref> | ||
* The swing phase occupies 60-100% (total<span class="reference" id="cite_ref-Loudon_4-3"></span> 40%) of the gait cycle, | * The swing phase occupies 60-100% (total<span class="reference" id="cite_ref-Loudon_4-3"></span> 40%) of the gait cycle. During swing phase, the foot does not touch the walking surface and the body weight is borne by the other leg and foot.<ref name=":1">Loudon J, et al. The clinical orthopedic assessment guide. 2nd ed. Kansas: Human Kinetics, 2008. p.395-408.</ref> | ||
* In a complete two-step cycle, both feet are in contact with the floor at the same time for about 25% of the time. This part of the cycle is called the double-support phase.<ref name=":4" /> | * In a complete two-step cycle, both feet are in contact with the floor at the same time for about 25% of the time. This part of the cycle is called the double-support phase.<ref name=":4" /> | ||
* Gait cycle phases: the stance phase and the swing phase | * Gait cycle phases: the stance phase and the swing phase involve a combination of open and close chain activities.<ref name=":2">Shultz SJ et al. Examination of musculoskeletal injuries. 2nd ed, North Carolina: Human Kinetics, 2005. p55-60.</ref><ref name=":3">Hazari A, Maiya AG, Nagda TV. Kinematics and Kinetics of Gait. InConceptual Biomechanics and Kinesiology 2021 (pp. 181-196). Springer, Singapore.</ref> | ||
Read more: [[The Gait Cycle]] | Read more here: [[The Gait Cycle]] | ||
== Phases of Gait == | == Phases of Gait == | ||
The stance and swing phases of gait can be subdivided into eight sub-phases.<ref name=":4" /><ref name=":3" /> | The stance and swing phases of gait can be subdivided into eight sub-phases.<ref name=":4" /><ref name=":3" /> | ||
# Initial contact ( | # Initial contact (heel strike) | ||
# Foot flat ( | # Foot flat (loading response) | ||
# Midstance ( | # Midstance (single-leg support) | ||
# Heel off ( | # Heel off (terminal stance) | ||
# Toe off ( | # Toe off (preswing) | ||
# Initial sw<span class="reference" id="cite_ref-Shultz_3-1"></span>ing | # Initial sw<span class="reference" id="cite_ref-Shultz_3-1"></span>ing | ||
# Mid swing | # Mid swing | ||
# Late swing ( | # Late swing (deceleration) | ||
See below for a diagram of the gait cycle:[[File:Adapted Gait Cycle.jpg|thumb|alt=|center|800x800px]] | See below for a diagram of the gait cycle:[[File:Adapted Gait Cycle.jpg|thumb|alt=|center|800x800px]] | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
The video below shares a 90-second description of the basics of the gait cycle:{{#ev:youtube|DP5-um6SvQI|400}}<ref>Nicole Comninellis. The Gait Cycle Animation. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=35&v=DP5-um6SvQI [last accessed 19.7.2022]</ref> | The video below shares a 90-second description of the basics of the gait cycle:{{#ev:youtube|DP5-um6SvQI|400}}<ref>Nicole Comninellis. The Gait Cycle Animation. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=35&v=DP5-um6SvQI [last accessed 19.7.2022]</ref> | ||
== Range of Motion Involved in Gait Phases == | == Range of Motion Involved in Gait Phases == | ||
'''Initial contact ( | '''Initial contact (heel strike)''' | ||
* 0% of gait cycle | * Occurs at 0% of the gait cycle | ||
* | * Previously referred to as "heel strike", but in some pathological gaits, the heel strike may not be the initial contact <ref name=":4" /> | ||
*Function: | *Function: | ||
**To establish contact with surface and initiate weight acceptance<ref>Webster JB, Darter BJ. Principles of normal and pathologic gait. InAtlas of Orthoses and Assistive Devices 2019 Jan 1 (pp. 49-62). Elsevier.</ref> | **To establish contact with the surface and initiate weight acceptance<ref>Webster JB, Darter BJ. Principles of normal and pathologic gait. InAtlas of Orthoses and Assistive Devices 2019 Jan 1 (pp. 49-62). Elsevier.</ref> | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
|average 20° of flexion | |average 20° of flexion | ||
|} | |} | ||
'''Foot flat''' | '''Foot flat (loading response)''' | ||
* 8-10% of gait cycle | * Occurs at 8-10% of the gait cycle | ||
*Function: | *Function: | ||
** | **Weight acceptance and shock absorption | ||
* | * | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
Range of Motion (ROM) Requirements | Range of Motion (ROM) Requirements During Foot Flat | ||
!Body part | !Body part | ||
!ROM requirements | !ROM requirements | ||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
|} | |} | ||
'''Midstance''' | '''Midstance (single-leg support)''' | ||
* The greater trochanter is vertically above the mid-point of the foot | * The greater trochanter is vertically above the mid-point of the foot | ||
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
Range of Motion (ROM) Requirements | Range of Motion (ROM) Requirements During Midstance | ||
!Body part | !Body part | ||
!ROM requirements | !ROM requirements | ||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
|} | |} | ||
'''Heel off''' | '''Heel off (terminal stance)''' | ||
* 30-40% of gait cycle | * Occurs at around 30-40% of the gait cycle | ||
* Function | * Function | ||
| Line 110: | Line 110: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
Range of Motion (ROM) Requirements | Range of Motion (ROM) Requirements During Heel Off | ||
!Body part | !Body part | ||
!ROM requirements | !ROM requirements | ||
| Line 124: | Line 124: | ||
|} | |} | ||
'''Toe off''' | '''Toe off (preswing)''' | ||
* 60% of gait cycle (final phase of stance) | * Occurs at 60% of the gait cycle (final phase of stance) | ||
*Function | *Function | ||
| Line 133: | Line 133: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
Range of Motion Requirements During Toe Off | Range of Motion (ROM) Requirements During Toe Off | ||
!Body part | !Body part | ||
!ROM requirements | !ROM requirements | ||
| Line 149: | Line 149: | ||
'''Early swing''' | '''Early swing''' | ||
* 60-75% of gait cycle (beginning of swing phase) | * Occurs at 60-75% of the gait cycle (beginning of swing phase) | ||
* Toe off until the swinging limb is even with the stance limb | * Toe off until the swinging limb is even with the stance limb | ||
*Function | *Function | ||
**To propel the lower extremity forward and shorten the | **To propel the lower extremity forward and shorten the limb for foot clearance | ||
* | * | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
Range of Motion Requirements | Range of Motion Requirements During Early Swing | ||
!Body part | !Body part | ||
!ROM requirements | !ROM requirements | ||
| Line 172: | Line 172: | ||
'''Mid swing''' | '''Mid swing''' | ||
* 75-85% of gait cycle | * Occurs at 75-85% of the gait cycle | ||
* Swinging limb is opposite the stance limb | * Swinging limb is opposite the stance limb | ||
*Function | *Function | ||
**To clear lower extremity from the ground in order to advance into initial contact | **To clear the lower extremity from the ground in order to advance into initial contact | ||
* | * | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
Range of Motion (ROM) Requirements | Range of Motion (ROM) Requirements During Mid Swing | ||
!Body part | !Body part | ||
!ROM requirements | !ROM requirements | ||
| Line 196: | Line 196: | ||
'''Late swing''' | '''Late swing''' | ||
* 85-100% of gait cycle | * Occurs at 85-100% of the gait cycle | ||
* Tibia vertical to initial contact | * Tibia vertical to initial contact | ||
* Function | * Function | ||
** To decelerate lower extremity to establish contact with the ground | ** To decelerate the lower extremity to establish contact with the ground | ||
*** | *** | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
Range of Motion (ROM) Requirements | Range of Motion (ROM) Requirements During Late Swing | ||
!Body part | !Body part | ||
!ROM requirements | !ROM requirements | ||
| Line 223: | Line 223: | ||
== Maximum Values == | == Maximum Values == | ||
It is important for clinicians to be aware of the range of motion values necessary as the minimum prerequisites for a normal gait pattern.<ref>Kopelovich, A. Joint Range of Motion during Gait. Course. Plus. 2022</ref> It is also important to know during which subphase of the gait cycle these ranges of motion occur as this will aid in gait analysis and enable clinicians to observe for specific gait pathology. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
Maximum Range of Motion at Lower Extremity Joints during Gait Cycle | Maximum Range of Motion (ROM) at Lower Extremity Joints during the Gait Cycle | ||
!Body part | !Body part | ||
!Maximum ROM values | !Maximum ROM values | ||
| Line 241: | Line 241: | ||
== Gait Kinetics == | == Gait Kinetics == | ||
* Ground reaction force (GRF) | === '''Definitions''' === | ||
** | * Ground reaction force (GRF) = forces applied by the ground to the foot, when the foot is in contact with the ground<ref>Elhafez SM, Ashour AA, Elhafez NM, Elhafez GM, Abdelmohsen AM. Percentage contribution of lower limb moments to vertical ground reaction force in normal gait. Journal of Chiropractic Medicine. 2019 Jun 1;18(2):90-6.</ref> | ||
** If GRF anterior to joint axis - causes anterior motion of the proximal segment | ** Creates an external plantarflexion or dorsiflexion torque | ||
** If GRF is posterior to joint axis - causes posterior motion of the proximal segment | ** If GRF is anterior to the joint axis - this causes an anterior motion of the proximal segment | ||
** If GRF is posterior to the joint axis - this causes a posterior motion of the proximal segment | |||
** Read more: [[Gait Deviations Associated with Lower Leg and Foot Pain Syndromes#Ground Reaction Forces|Ground Reaction Forces]] | |||
* Lower extremity gait musculature - creates an internal torque | * Lower extremity gait musculature - creates an internal torque | ||
* Centre of pressure - point of application of pressure to the foot segment | * Centre of pressure - point of application of pressure to the foot segment | ||
* Read more: [[Gait Definitions]] | |||
'''Initial contact''' | === '''Initial contact (heel strike)''' === | ||
* Ankle | * Ankle | ||
** At initial contact - lateral calcaneus strikes the ground first. | ** At initial contact - lateral calcaneus strikes the ground first. | ||
** | ** Ground reaction forces are slightly posterior to the axis of rotation of the foot and ankle joint. This creates a plantarflexion moment at the ankle.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
** | ** Ankle dorsiflexors oppose this plantarflexor torque - internal torque is controlled by tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus and extensor hallucis.<ref name=":4" /> | ||
* Knee | * Knee | ||
| Line 264: | Line 265: | ||
* Hip | * Hip | ||
** GRF is anterior to hip joint - | ** GRF is anterior to the hip joint - this creates an external torque (anterior rotation) at the pelvis.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
** Utilise extensor musculature - gluteal musculature - to oppose/control the progression or external torque. | ** Utilise extensor musculature - gluteal musculature - to oppose/control the progression or external torque. | ||
'''Foot flat''' | === '''Foot flat (loading response)''' === | ||
* Ankle | * Ankle | ||
** Centre of pressure remains at the posterior calcaneus - GRF remains posterior to the ankle.<ref name=":3" /> | ** Centre of pressure remains at the posterior calcaneus - GRF remains posterior to the ankle.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
| Line 279: | Line 279: | ||
* Knee | * Knee | ||
** Range of motion moves from 0-15° | ** Range of motion moves from 0-15°. | ||
** GRF posterior to the axis of rotation of the knee joint - creates a flexion torque.<ref name=":3" /> | ** GRF posterior to the axis of rotation of the knee joint - creates a flexion torque.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
** Utilise extensor musculature to control knee from moving into flexion. | ** Utilise extensor musculature to control the knee from moving into flexion. | ||
=== '''Midstance (single-leg support)''' === | |||
* Ankle | * Ankle | ||
** GRF creates a clockwise torque of the proximal segment (on top of distal segment) - causing a dorsiflexion moment at the talocrural joint.<ref name=":3" /> | ** GRF creates a clockwise torque of the proximal segment (on top of distal segment) - causing a dorsiflexion moment at the talocrural joint.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
| Line 290: | Line 289: | ||
* Knee | * Knee | ||
** GRF creates an anterior (clockwise) torque of proximal segment (on top of distal segment) - wants to move into extension by femur moving anteriorly on tibia.<ref name=":3" /> | ** GRF creates an anterior (clockwise) torque of the proximal segment (on top of distal segment) - wants to move into extension by the femur moving anteriorly on the tibia.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
** Utilise flexors to oppose this torque - activates hamstrings. | ** Utilise flexors to oppose this torque - this activates the hamstrings. | ||
* Hip | * Hip | ||
| Line 297: | Line 296: | ||
** Utilise flexors to oppose extension torque. | ** Utilise flexors to oppose extension torque. | ||
'''Heel off''' | === '''Heel off (terminal stance)''' === | ||
* Ankle | * Ankle | ||
** GRF is anterior to the axis of rotation of ankle joint - wants tibia to flex on talus.<ref name=":3" /> | ** GRF is anterior to the axis of rotation of the ankle joint - wants the tibia to flex on the talus.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
** Creates external dorsiflexion moment at talocrural joint. | ** Creates an external dorsiflexion moment at the talocrural joint. | ||
** Utilise plantarflexors to oppose this moment. | ** Utilise plantarflexors to oppose this moment. | ||
* Knee | * Knee | ||
** GRF is anterior to knee joint - pulls femur into extension, creating an external extensor torque.<ref name=":3" /> | ** GRF is anterior to the knee joint - this pulls the femur into extension, creating an external extensor torque.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
** Counteracted by internal flexor torque. | ** Counteracted by an internal flexor torque. | ||
* Hip | * Hip | ||
** GRF is posterior to hip joint - creates an external extensor moment.<ref name=":3" /> | ** GRF is posterior to the hip joint - this creates an external extensor moment.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
** Counteracted by internal flexor moment. | ** Counteracted by an internal flexor moment. | ||
=== '''Toe off (preswing)''' === | |||
* Ankle | * Ankle | ||
** Centre of pressure/GRF stay anterior to axis of rotation of ankle joint.<ref name=":3" /> | ** Centre of pressure/GRF stay anterior to the axis of rotation of the ankle joint.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
** Creates an external dorsiflexion moment. | ** Creates an external dorsiflexion moment. | ||
** Counteracted by internal plantarflexion moment. | ** Counteracted by an internal plantarflexion moment. | ||
* Knee | * Knee | ||
** GRF is posterior to axis of rotation of knee joint as knee is moving into flexion.<ref name=":3" /> | ** GRF is posterior to the axis of rotation of the knee joint as the knee is moving into flexion.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
** Creates an external flexion moment. | ** Creates an external flexion moment. | ||
** Counteracted by an internal extensor ( | ** Counteracted by an internal extensor (quadriceps musculature) moment. | ||
* Hip | * Hip | ||
** GRF is posterior to axis of rotation of hip joint as hip is moving into extension.<ref name=":3" /> | ** GRF is posterior to the axis of rotation of the hip joint as the hip is moving into extension.<ref name=":3" /> | ||
** Creates a posterior pelvic tilt. | ** Creates a posterior pelvic tilt. | ||
** Utilise flexor musculature (iliopsoas) to counteract this moment. | ** Utilise flexor musculature (iliopsoas) to counteract this moment. | ||
== Internal Torque Peaks == | == Internal Torque Peaks == | ||
The sagittal internal torque peaks at the hip, knee and ankle are<ref>Neumann DA. Neumann Kinesiology of the musculoskeletal system: Foundations for Rehabilitation. St Louis: Mosby: 2010.</ref>: | |||
'''Hip:''' | '''Hip:''' | ||
| Line 337: | Line 336: | ||
'''Knee:''' | '''Knee:''' | ||
* Initial contact - flexor torque ( | * Initial contact - flexor torque (hamstrings musculature active) | ||
* Foot flat - extensor torque (quadriceps musculature active) | * Foot flat - extensor torque (quadriceps musculature active) | ||
* Heel off - flexor torque ( | * Heel off - flexor torque (hamstrings musculature active) | ||
'''Ankle:''' | '''Ankle:''' | ||
* Initial contact/ | * Initial contact/foot flat - dorsiflexion torque | ||
* Heel off - plantarflexion torque (gastrocnemius/soleus active) | * Heel off - plantarflexion torque (gastrocnemius/soleus active) | ||
| Line 350: | Line 349: | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Gait]] | [[Category:Gait]] | ||
[[Category:Movement Analysis]] | [[Category:Movement Analysis]] | ||
[[Category:Rehabilitation]] | [[Category:Rehabilitation]] | ||
[[Category:Course Pages]] | [[Category:Course Pages]] | ||
[[Category:ReLAB-HS Course Page]] | |||
Latest revision as of 08:56, 26 September 2022
Top Contributors - Rachel Celentano, Wanda van Niekerk and Jess Bell
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Merriam-Webster dictionary defines gait as “a manner of walking or moving on foot."[1] It involves the interaction between the nervous, musculoskeletal, and cardiorespiratory systems and is heavily impacted by human age, personality, mood, and sociocultural factors.[2][3] Normal gait function is determined by the optimal operation of the following: “locomotor function (for initiating and sustaining rhythmic gait), balance, postural reflexes, sensory function and sensorimotor integration, motor control, the musculoskeletal apparatus and cardiopulmonary functions."[2][4]
Stance Versus Swing Phase[edit | edit source]
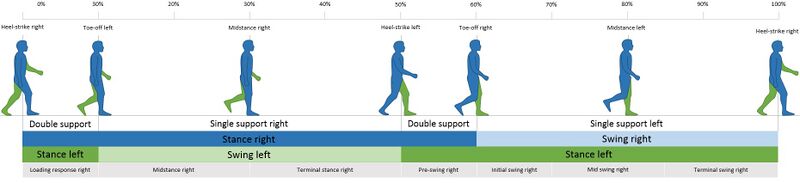
The typical forward stride consists of two phases: stance phase and swing phase.[5]
- The stance phase occupies 0-60% of the gait cycle. During stance phase, one leg and foot bear most or all of the body weight.[6]
- The swing phase occupies 60-100% (total 40%) of the gait cycle. During swing phase, the foot does not touch the walking surface and the body weight is borne by the other leg and foot.[7]
- In a complete two-step cycle, both feet are in contact with the floor at the same time for about 25% of the time. This part of the cycle is called the double-support phase.[6]
- Gait cycle phases: the stance phase and the swing phase involve a combination of open and close chain activities.[8][9]
Read more here: The Gait Cycle
Phases of Gait[edit | edit source]
The stance and swing phases of gait can be subdivided into eight sub-phases.[6][9]
- Initial contact (heel strike)
- Foot flat (loading response)
- Midstance (single-leg support)
- Heel off (terminal stance)
- Toe off (preswing)
- Initial swing
- Mid swing
- Late swing (deceleration)
See below for a diagram of the gait cycle:
The video below shares a 90-second description of the basics of the gait cycle:
Range of Motion Involved in Gait Phases[edit | edit source]
Initial contact (heel strike)
- Occurs at 0% of the gait cycle
- Previously referred to as "heel strike", but in some pathological gaits, the heel strike may not be the initial contact [6]
- Function:
- To establish contact with the surface and initiate weight acceptance[11]
| Body part | ROM requirements |
|---|---|
| Ankle | 0° (neutral position) |
| Knee | 0° (full extension) |
| Hip | average 20° of flexion |
Foot flat (loading response)
- Occurs at 8-10% of the gait cycle
- Function:
- Weight acceptance and shock absorption
| Body part | ROM requirements |
|---|---|
| Ankle | 0-5° plantarflexion |
| Knee | 15° of flexion |
| Hip | 15° of flexion (hip is moving into extension) |
Midstance (single-leg support)
- The greater trochanter is vertically above the mid-point of the foot
- Function:
- Single limb support and stability
| Body part | ROM requirements |
|---|---|
| Ankle | 5° of dorsiflexion |
| Knee | 5° of flexion |
| Hip | 0° of flexion (neutral position) |
Heel off (terminal stance)
- Occurs at around 30-40% of the gait cycle
- Function
- Single limb support, stability, and propulsion
| Body part | ROM requirements |
|---|---|
| Ankle | 0° (neutral position) |
| Knee | 0° of flexion (complete extension) |
| Hip | 10-20° of hyperextension |
Toe off (preswing)
- Occurs at 60% of the gait cycle (final phase of stance)
- Function
- Final burst of propulsion to propel the body forward
| Body part | ROM requirements |
|---|---|
| Ankle | 20° of plantarflexion |
| Knee | 30° of flexion |
| Hip | 10-20° of hyperextension |
Early swing
- Occurs at 60-75% of the gait cycle (beginning of swing phase)
- Toe off until the swinging limb is even with the stance limb
- Function
- To propel the lower extremity forward and shorten the limb for foot clearance
| Body part | ROM requirements |
|---|---|
| Ankle | 10° of plantarflexion |
| Knee | 60° of flexion |
| Hip | moves into 20° of flexion |
Mid swing
- Occurs at 75-85% of the gait cycle
- Swinging limb is opposite the stance limb
- Function
- To clear the lower extremity from the ground in order to advance into initial contact
| Body part | ROM requirements |
|---|---|
| Ankle | 0° (neutral position) |
| Knee | moves into 30° of flexion |
| Hip | 30° of flexion (hip is moving into extension) |
Late swing
- Occurs at 85-100% of the gait cycle
- Tibia vertical to initial contact
- Function
- To decelerate the lower extremity to establish contact with the ground
- To decelerate the lower extremity to establish contact with the ground
| Body part | ROM requirements |
|---|---|
| Ankle | 0° (neutral position) |
| Knee | 0° (complete extension) |
| Hip | 30° of flexion |
The following video describes the range of motion requirements involved in the different gait phases:
Range of Motion during Gait [12]
Maximum Values[edit | edit source]
It is important for clinicians to be aware of the range of motion values necessary as the minimum prerequisites for a normal gait pattern.[13] It is also important to know during which subphase of the gait cycle these ranges of motion occur as this will aid in gait analysis and enable clinicians to observe for specific gait pathology.
| Body part | Maximum ROM values |
|---|---|
| Hip | 20° of extension; 20° of flexion |
| Knee | 0° (complete extension); 60° of flexion |
| Ankle | 5° of dorsiflexion; 20° of plantarflexion |
Gait Kinetics[edit | edit source]
Definitions[edit | edit source]
- Ground reaction force (GRF) = forces applied by the ground to the foot, when the foot is in contact with the ground[14]
- Creates an external plantarflexion or dorsiflexion torque
- If GRF is anterior to the joint axis - this causes an anterior motion of the proximal segment
- If GRF is posterior to the joint axis - this causes a posterior motion of the proximal segment
- Read more: Ground Reaction Forces
- Lower extremity gait musculature - creates an internal torque
- Centre of pressure - point of application of pressure to the foot segment
- Read more: Gait Definitions
Initial contact (heel strike)[edit | edit source]
- Ankle
- At initial contact - lateral calcaneus strikes the ground first.
- Ground reaction forces are slightly posterior to the axis of rotation of the foot and ankle joint. This creates a plantarflexion moment at the ankle.[9]
- Ankle dorsiflexors oppose this plantarflexor torque - internal torque is controlled by tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus and extensor hallucis.[6]
- Knee
- At initial contact - GRF is anterior to the knee joint creating anterior rotation of the femur.[9]
- GRF wants to move into extension.
- Utilise flexor musculature - hamstrings - in order to control progression.
- Hip
- GRF is anterior to the hip joint - this creates an external torque (anterior rotation) at the pelvis.[9]
- Utilise extensor musculature - gluteal musculature - to oppose/control the progression or external torque.
Foot flat (loading response)[edit | edit source]
- Ankle
- Centre of pressure remains at the posterior calcaneus - GRF remains posterior to the ankle.[9]
- Utilise dorsiflexors to prevent plantarflexion from occurring at the ankle.
- Hip
- Centre of pressure and GRF remains the same - anterior to the axis of rotation.[9]
- Anterior pelvic tilt creates a flexion torque.
- Utilise extensor musculature to control this torque.
- Knee
- Range of motion moves from 0-15°.
- GRF posterior to the axis of rotation of the knee joint - creates a flexion torque.[9]
- Utilise extensor musculature to control the knee from moving into flexion.
Midstance (single-leg support)[edit | edit source]
- Ankle
- GRF creates a clockwise torque of the proximal segment (on top of distal segment) - causing a dorsiflexion moment at the talocrural joint.[9]
- Utilise plantarflexors to oppose the external torque.
- Knee
- GRF creates an anterior (clockwise) torque of the proximal segment (on top of distal segment) - wants to move into extension by the femur moving anteriorly on the tibia.[9]
- Utilise flexors to oppose this torque - this activates the hamstrings.
- Hip
- GRF is posterior to the axis of rotation - wants pelvis to move into a posterior pelvic tilt (extension).[9]
- Utilise flexors to oppose extension torque.
Heel off (terminal stance)[edit | edit source]
- Ankle
- GRF is anterior to the axis of rotation of the ankle joint - wants the tibia to flex on the talus.[9]
- Creates an external dorsiflexion moment at the talocrural joint.
- Utilise plantarflexors to oppose this moment.
- Knee
- GRF is anterior to the knee joint - this pulls the femur into extension, creating an external extensor torque.[9]
- Counteracted by an internal flexor torque.
- Hip
- GRF is posterior to the hip joint - this creates an external extensor moment.[9]
- Counteracted by an internal flexor moment.
Toe off (preswing)[edit | edit source]
- Ankle
- Centre of pressure/GRF stay anterior to the axis of rotation of the ankle joint.[9]
- Creates an external dorsiflexion moment.
- Counteracted by an internal plantarflexion moment.
- Knee
- GRF is posterior to the axis of rotation of the knee joint as the knee is moving into flexion.[9]
- Creates an external flexion moment.
- Counteracted by an internal extensor (quadriceps musculature) moment.
- Hip
- GRF is posterior to the axis of rotation of the hip joint as the hip is moving into extension.[9]
- Creates a posterior pelvic tilt.
- Utilise flexor musculature (iliopsoas) to counteract this moment.
Internal Torque Peaks[edit | edit source]
The sagittal internal torque peaks at the hip, knee and ankle are[15]:
Hip:
- Foot flat - extensor torque
- Heel off - flexor torque
Knee:
- Initial contact - flexor torque (hamstrings musculature active)
- Foot flat - extensor torque (quadriceps musculature active)
- Heel off - flexor torque (hamstrings musculature active)
Ankle:
- Initial contact/foot flat - dorsiflexion torque
- Heel off - plantarflexion torque (gastrocnemius/soleus active)
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Merriam-Webster. Gait. Available from: https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/gait [last accessed 23.6.2022]
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Pirker W, Katzenschlager R. Gait disorders in adults and the elderly. Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift. 2017 Feb 1;129(3-4):81-95. Available from:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5318488/ [last accessed 25.6.2022]
- ↑ Das R, Paul S, Mourya GK, Kumar N, Hussain M. Recent Trends and Practices Toward Assessment and Rehabilitation of Neurodegenerative Disorders: Insights From Human Gait. Frontiers in Neuroscience. 2022;16.
- ↑ Mirelman A, Shema S, Maidan I, Hausdorff JM. Gait. Handbook of clinical neurology. 2018 Jan 1;159:119-34.
- ↑ Cicirelli G, Impedovo D, Dentamaro V, Marani R, Pirlo G, D’Orazio TR. Human gait analysis in neurodegenerative diseases: a review. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics. 2021 Jun 28;26(1):229-42.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Magee DJ, Manske RC. Orthopedic physical assessment-E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2020 Dec 11.
- ↑ Loudon J, et al. The clinical orthopedic assessment guide. 2nd ed. Kansas: Human Kinetics, 2008. p.395-408.
- ↑ Shultz SJ et al. Examination of musculoskeletal injuries. 2nd ed, North Carolina: Human Kinetics, 2005. p55-60.
- ↑ 9.00 9.01 9.02 9.03 9.04 9.05 9.06 9.07 9.08 9.09 9.10 9.11 9.12 9.13 9.14 9.15 9.16 Hazari A, Maiya AG, Nagda TV. Kinematics and Kinetics of Gait. InConceptual Biomechanics and Kinesiology 2021 (pp. 181-196). Springer, Singapore.
- ↑ Nicole Comninellis. The Gait Cycle Animation. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=35&v=DP5-um6SvQI [last accessed 19.7.2022]
- ↑ Webster JB, Darter BJ. Principles of normal and pathologic gait. InAtlas of Orthoses and Assistive Devices 2019 Jan 1 (pp. 49-62). Elsevier.
- ↑ Alexandra Kopelovich. Gait Range of Motion. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5Z6shSu96CM [last accessed 19.7.2022]
- ↑ Kopelovich, A. Joint Range of Motion during Gait. Course. Plus. 2022
- ↑ Elhafez SM, Ashour AA, Elhafez NM, Elhafez GM, Abdelmohsen AM. Percentage contribution of lower limb moments to vertical ground reaction force in normal gait. Journal of Chiropractic Medicine. 2019 Jun 1;18(2):90-6.
- ↑ Neumann DA. Neumann Kinesiology of the musculoskeletal system: Foundations for Rehabilitation. St Louis: Mosby: 2010.