Hip Abductors: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
[[File:Trendelenburg Gait.gif|thumb|Trendelenburg Gait]] | |||
The hip abductor muscles contribute to various actions, including pelvic stabilization during walking and running; abduction and rotation at the hip joint<ref>Ganderton C, Pizzari T, Harle T, Cook J, Semciw A. [https://www.researchgate.net/publication/51823221_A_review_of_the_anatomy_of_the_hip_abductor_muscles_gluteus_medius_gluteus_minimus_and_tensor_fascia_lata Gluteus medius, gluteus minimus and tensor fascia latae are overactive during gait in post-menopausal women with greater trochanteric pain syndrome]. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport. 2017 Jan 1;20:e72.Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/51823221_A_review_of_the_anatomy_of_the_hip_abductor_muscles_gluteus_medius_gluteus_minimus_and_tensor_fascia_lata<nowiki/>(accessed 22.1.2022)</ref>. | The hip abductor muscles contribute to various actions, including pelvic stabilization during walking and running; abduction and rotation at the hip joint<ref>Ganderton C, Pizzari T, Harle T, Cook J, Semciw A. [https://www.researchgate.net/publication/51823221_A_review_of_the_anatomy_of_the_hip_abductor_muscles_gluteus_medius_gluteus_minimus_and_tensor_fascia_lata Gluteus medius, gluteus minimus and tensor fascia latae are overactive during gait in post-menopausal women with greater trochanteric pain syndrome]. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport. 2017 Jan 1;20:e72.Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/51823221_A_review_of_the_anatomy_of_the_hip_abductor_muscles_gluteus_medius_gluteus_minimus_and_tensor_fascia_lata<nowiki/>(accessed 22.1.2022)</ref>. | ||
The hip abductor muscles stabilize the hip within the frontal plane during the single-limb support phase of walking. High demand is placed on the hip abductors occurs with walking. eg The right abductor muscles must work when the right leg is in the single-limb support phase of gait, as the left limb is swinging forward. The right hip abductors must supply an adequate contraction force to keep the pelvis from dropping down to the L. Weakness of these muscles results in an unstable pelvis while walking or while attempting to stand on one leg<ref name=":0" />. | The hip abductor muscles stabilize the hip within the frontal plane during the single-limb support phase of walking. High demand is placed on the hip abductors occurs with walking. eg The right abductor muscles must work when the right leg is in the single-limb support phase of gait, as the left limb is swinging forward. The right hip abductors must supply an adequate contraction force to keep the pelvis from dropping down to the L. Weakness of these muscles results in an unstable pelvis while walking or while attempting to stand on one leg<ref name=":0" />. | ||
The trendelenburg gait is caused by a unilateral weakness of the hip abductors, mostly the gluteal musculature. | |||
== Muscles == | == Muscles == | ||
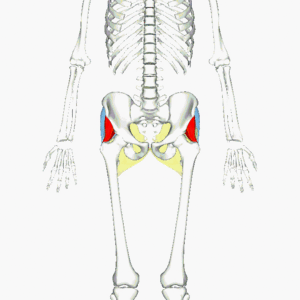
# Gluteus medius is the prime mover of abduction at hip joint. It is located on the lateral aspect of the upper buttock, below the iliac crest. The superior muscle is broad with the muscle narrowing towards its insertional tendon giving it a fan-shape. The anterior portion of Gluteus medius abducts and assists in flexion and medial rotation of hip. The posterior portion of Gluteus medius abducts and assists in extension and lateral rotation of hip.<ref>Physiopedia Gluteus Medius Available:[[Gluteus Medius]] (accessed 22.1.2022)</ref> | # [[File:Gluteus all.gif|thumb|Gluteal Muscles. The Maximus (yellow), medius (blue) and minimus (red).]]Gluteus medius is the prime mover of abduction at hip joint. It is located on the lateral aspect of the upper buttock, below the iliac crest. The superior muscle is broad with the muscle narrowing towards its insertional tendon giving it a fan-shape. The anterior portion of Gluteus medius abducts and assists in flexion and medial rotation of hip. The posterior portion of Gluteus medius abducts and assists in extension and lateral rotation of hip.<ref>Physiopedia Gluteus Medius Available:[[Gluteus Medius]] (accessed 22.1.2022)</ref> | ||
# Gluteus minimus muscle is the smallest one of the three gluteal muscles, it lies deep to the gluteus medius muscle. The gluteus minimus is similiar to the gluteus medius in function, structure, nerve and blood supply. The gluteus minimus acts in synergy with the gluteus medius to abduct and internally rotate the thigh, and contributes to the stabilization of the hip and pelvis<ref>Physiopedia Gluteus Minimus Available: [[Gluteus Minimus]](accessed 22.1.2022)</ref>. | # Gluteus minimus muscle is the smallest one of the three gluteal muscles, it lies deep to the gluteus medius muscle. The gluteus minimus is similiar to the gluteus medius in function, structure, nerve and blood supply. The gluteus minimus acts in synergy with the gluteus medius to abduct and internally rotate the thigh, and contributes to the stabilization of the hip and pelvis<ref>Physiopedia Gluteus Minimus Available: [[Gluteus Minimus]](accessed 22.1.2022)</ref>. | ||
# The tensor fasciae latae (TFL) is a muscle of the proximal anterolateral thigh that lies between the superficial and deep fibres of the iliotibial (IT) band. The TFL works in conjunction with the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus in a wide variety of hip movements, including flexion, abduction, and internal rotation.The TFL is most important clinically for assisting in [[pelvis]] stability while standing and walking<ref>Physiopedia Tensor Fascia Latae Available:[[Tensor Fascia Lata]] (accessed 22.1.2022)</ref>. | # The tensor fasciae latae (TFL) is a muscle of the proximal anterolateral thigh that lies between the superficial and deep fibres of the iliotibial (IT) band. The TFL works in conjunction with the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus in a wide variety of hip movements, including flexion, abduction, and internal rotation.The TFL is most important clinically for assisting in [[pelvis]] stability while standing and walking<ref>Physiopedia Tensor Fascia Latae Available:[[Tensor Fascia Lata]] (accessed 22.1.2022)</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 02:14, 22 January 2022
Original Editor - Lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Sehriban Ozmen and Kim Jackson
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Hip abduction is the movement of the leg away from the midline of the body. This action is used daily eg when we step to the side, get out of bed; get out of the car. We also use it in walking to stop unsupported leg in walking falling "into space".
The Hip abductor muscle group are located laterally on the thigh are the hip abductors.
- The primary hip abductor muscles include the gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and tensor fasciae latae.
- The secondary hip abductors include the piriformis, sartorius, and superior fibers of the gluteus maximus.[1]
Many hip and knee problems arise due to weal hip abductors. Hip abduction strengthening exercises help to prevent and treat pain in the hips and knees[2].
Function[edit | edit source]
The hip abductor muscles contribute to various actions, including pelvic stabilization during walking and running; abduction and rotation at the hip joint[3].
The hip abductor muscles stabilize the hip within the frontal plane during the single-limb support phase of walking. High demand is placed on the hip abductors occurs with walking. eg The right abductor muscles must work when the right leg is in the single-limb support phase of gait, as the left limb is swinging forward. The right hip abductors must supply an adequate contraction force to keep the pelvis from dropping down to the L. Weakness of these muscles results in an unstable pelvis while walking or while attempting to stand on one leg[1].
The trendelenburg gait is caused by a unilateral weakness of the hip abductors, mostly the gluteal musculature.
Muscles[edit | edit source]
- Gluteus medius is the prime mover of abduction at hip joint. It is located on the lateral aspect of the upper buttock, below the iliac crest. The superior muscle is broad with the muscle narrowing towards its insertional tendon giving it a fan-shape. The anterior portion of Gluteus medius abducts and assists in flexion and medial rotation of hip. The posterior portion of Gluteus medius abducts and assists in extension and lateral rotation of hip.[4]
- Gluteus minimus muscle is the smallest one of the three gluteal muscles, it lies deep to the gluteus medius muscle. The gluteus minimus is similiar to the gluteus medius in function, structure, nerve and blood supply. The gluteus minimus acts in synergy with the gluteus medius to abduct and internally rotate the thigh, and contributes to the stabilization of the hip and pelvis[5].
- The tensor fasciae latae (TFL) is a muscle of the proximal anterolateral thigh that lies between the superficial and deep fibres of the iliotibial (IT) band. The TFL works in conjunction with the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus in a wide variety of hip movements, including flexion, abduction, and internal rotation.The TFL is most important clinically for assisting in pelvis stability while standing and walking[6].
The secondary hip abductors include the
- Piriformis is a flat muscle and the most superficial muscle of the deep gluteal muscles. It is part of the lateral rotators of the hip (obturator internus, superior and inferior gemelli, quadratus femoris, obturator externus, and gluteus maximus). It assists in hip abduction when hip is flexed.[7]
- The Sartorius muscle is a thin, long, superficial muscle in the anterior compartment of the thigh. It runs down the length of the thigh, runs over 2 joints—hip and knee joints and is the longest muscle in the human body. At the hip it flexes, weakly abducts, and rotates the thigh laterally[8].
- Superior fibers of the Gluteus Maximus, the largest and heaviest muscle in the body. It is the most superficial of all gluteal muscles that are located at the posterior aspect of the hip joint.
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Mansfield PJ, Neumann DA. Essentials of kinesiology for the physical therapist assistant e-book. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2018 Oct 23.Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/book/9780323544986/essentials-of-kinesiology-for-the-physical-therapist-assistant(accessed 21.1.2022)
- ↑ Healthline The Benefits and Effectiveness of Hip Abduction Exercises Available:https://www.healthline.com/health/fitness-exercise/hip-abduction#TOC_TITLE_HDR_1 (accessed 22.1.2022)
- ↑ Ganderton C, Pizzari T, Harle T, Cook J, Semciw A. Gluteus medius, gluteus minimus and tensor fascia latae are overactive during gait in post-menopausal women with greater trochanteric pain syndrome. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport. 2017 Jan 1;20:e72.Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/51823221_A_review_of_the_anatomy_of_the_hip_abductor_muscles_gluteus_medius_gluteus_minimus_and_tensor_fascia_lata(accessed 22.1.2022)
- ↑ Physiopedia Gluteus Medius Available:Gluteus Medius (accessed 22.1.2022)
- ↑ Physiopedia Gluteus Minimus Available: Gluteus Minimus(accessed 22.1.2022)
- ↑ Physiopedia Tensor Fascia Latae Available:Tensor Fascia Lata (accessed 22.1.2022)
- ↑ Physiopedia piriformis Available:Piriformis (accessed 22.1.2022)
- ↑ Physiopedia Sartorius Available:Sartorius (accessed 22.1.2022)