Dynamic Stabilisers of the Shoulder Complex: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
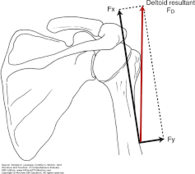
[[File:Line of action of three parts of deltoid .png|thumb|figure 1 | [[File:Line of action of three parts of deltoid .png|thumb|figure 1 | ||
line of action of three parts of deltoid follows line of pull of middle deltoid | line of action of three parts of deltoid follows line of pull of middle deltoid | ||
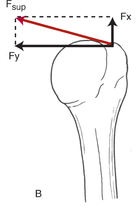
the resultant (Fd) resolved into a very large translatory component (Fx) and a small rotatory component (Fy).<ref name=":0">Levangie PK, Norkin CC. Joint Structure and Function; A Comprehensive Analysis. 5th. Philadelphia: Fadavis Company. 2012.</ref> | the resultant (Fd) resolved into a very large translatory component (Fx) and a small rotatory component (Fy).<ref name=":0">Levangie PK, Norkin CC. Joint Structure and Function; A Comprehensive Analysis. 5th. Philadelphia: Fadavis Company. 2012.</ref> | ||
]] | |195x195px]] | ||
Deltoid has a significant role as a stabilizer and generally accepted as a prime mover for glenohumeral abduction along with supraspinatus. | Deltoid has a significant role as a stabilizer and generally accepted as a prime mover for glenohumeral abduction along with supraspinatus. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 19: | ||
Rotator cuff not only abduct the shoulder it play a role as a stabilizer muscles<ref>Escamilla RF, Yamashiro K, Paulos L, Andrews JR. [[Shoulder muscle activity and function in common shoulder rehabilitation exercises. Sports medicine.]] 2009 Aug 1;39(8):663-85.</ref> | Rotator cuff not only abduct the shoulder it play a role as a stabilizer muscles<ref>Escamilla RF, Yamashiro K, Paulos L, Andrews JR. [[Shoulder muscle activity and function in common shoulder rehabilitation exercises. Sports medicine.]] 2009 Aug 1;39(8):663-85.</ref> | ||
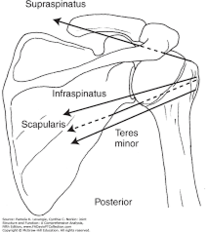
From figure 2 we can see all three muscles (teres minor,subscapularis,infraspinatus) have similar inferior line of pull<ref name=":0" /> and with the summation of three forces of rotator cuff they nearly offset superior translation of humeral head created by deltoid. The wide range of motion of the shoulder is allowed by the variety of rotational moments of the cuff muscles<ref>Longo UG, Berton A, Papapietro N, Maffulli N, Denaro V. Biomechanics of the rotator cuff: European perspective. InRotator Cuff Tear 2012 (Vol. 57, pp. 10-17). Karger Publishers.</ref>. Teres minor ,Infraspinatus as they are external rotators they contribute in abduction of arm by external rotation that participate clearing greater tubercle underneath the acromion. | From figure 2 we can see all three muscles (teres minor,subscapularis,infraspinatus) have similar inferior line of pull<ref name=":0" /> and with the summation of three forces of rotator cuff they nearly offset superior translation of humeral head created by deltoid. The wide range of motion of the shoulder is allowed by the variety of rotational moments of the cuff muscles<ref>Longo UG, Berton A, Papapietro N, Maffulli N, Denaro V. Biomechanics of the rotator cuff: European perspective. InRotator Cuff Tear 2012 (Vol. 57, pp. 10-17). Karger Publishers.</ref>. Teres minor ,Infraspinatus as they are external rotators they contribute in abduction of arm by external rotation that participate clearing greater tubercle underneath the acromion. [[File:Rotator cuff line of action.png|thumb|figure 2 | ||
line of action of all four rotator cuff | |||
|center|232x232px]] | |||
=== '''Supraspinatus and glenohumeral stabilization''' === | === '''Supraspinatus and glenohumeral stabilization''' === | ||
regarding to supraspinatus location it has a line of pull superior that can't offset deltoid force. | regarding to supraspinatus location it has a line of pull superior that can't offset deltoid force. | ||
| Line 37: | Line 34: | ||
== Related articles == | == Related articles == | ||
[[Rotator Cuff|rotator cuff | * [[Rotator Cuff|rotator cuff -physiopedia]] | ||
* [[Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy|rotator cuff tendonopathy -physiopedia]] | |||
discuss epidemiology,risk factors,examination ,physical and medical intervention | discuss epidemiology,risk factors,examination ,physical and medical intervention | ||
s[https://www.physiospot.com/sponsors/selecting-exercises-for-rotator-cuff-related-shoulder-pain-interview electing-exercises-for-rotator-cuff-related-shoulder-pain-interview-with-hilkka-virtapohja] | * s[https://www.physiospot.com/sponsors/selecting-exercises-for-rotator-cuff-related-shoulder-pain-interview electing-exercises-for-rotator-cuff-related-shoulder-pain-interview-with-hilkka-virtapohja] | ||
What kind of exercises can be used /select exercises for rotator cuff strengthening | What kind of exercises can be used /select exercises for rotator cuff strengthening | ||
Stability and instability of the glenohumeral joint: the role of shoulder muscles<ref>Labriola JE, Lee TQ, Debski RE, McMahon PJ. Stability and instability of the glenohumeral joint: the role of shoulder muscles. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery. 2005 Jan 1;14(1):S32-8.</ref> | * Stability and instability of the glenohumeral joint: the role of shoulder muscles<ref>Labriola JE, Lee TQ, Debski RE, McMahon PJ. Stability and instability of the glenohumeral joint: the role of shoulder muscles. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery. 2005 Jan 1;14(1):S32-8.</ref> | ||
=== References === | === References === | ||
Revision as of 03:06, 13 February 2020
Original Editor - Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page.
Top Contributors - Khloud Shreif, Amanda Ager, Kim Jackson and Rishika Babburu
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Glenohumeral joint relies on static and dynamic contributions to maintain joint stability,static stability include joint labrum and associated capsuloligamentous components .Dynamic stabilizers refer to rotator cuff (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis ,teres minor) and periscapular muscles[1].Dynamic stabilizers are important to work synergistically for proper movement and to avoid impingement of shoulder.
Deltoid and glenohumeral stabilization[edit | edit source]
Deltoid has a significant role as a stabilizer and generally accepted as a prime mover for glenohumeral abduction along with supraspinatus.
From the figure that show the line of action of deltoid with arm at side , the parallel force component (fx)directed superior is larger of three other component so that , the majority of deltoid contraction causes humeral head translate superior and a small applied perpendicular force is directed to rotate humerus . That we need an inferior pull force to offset the (fx) component of middle deltoid for active arm elevation as gravity force can't balance this force.[3]
Rotator cuff and glenohumeral stabilization[edit | edit source]
Rotator cuff not only abduct the shoulder it play a role as a stabilizer muscles[4]
From figure 2 we can see all three muscles (teres minor,subscapularis,infraspinatus) have similar inferior line of pull[2] and with the summation of three forces of rotator cuff they nearly offset superior translation of humeral head created by deltoid. The wide range of motion of the shoulder is allowed by the variety of rotational moments of the cuff muscles[5]. Teres minor ,Infraspinatus as they are external rotators they contribute in abduction of arm by external rotation that participate clearing greater tubercle underneath the acromion.
Supraspinatus and glenohumeral stabilization[edit | edit source]
regarding to supraspinatus location it has a line of pull superior that can't offset deltoid force.
even though it still an effective stabilizer due to it's larger moment arm (f sup) as seen in figure
it's capable to elevate glenohumeral joint near normal.[2]
from illustrated above we can consider deltoid and rotator cuff as one of a force couple of glenohumeral joint.
Imbalance of one or more of these muscle consider a contribution cause to shoulder problems (impingement , bursitis , instability )
Related articles[edit | edit source]
discuss epidemiology,risk factors,examination ,physical and medical intervention
What kind of exercises can be used /select exercises for rotator cuff strengthening
- Stability and instability of the glenohumeral joint: the role of shoulder muscles[6]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Curl LA, Warren RF. Glenohumeral joint stability: selective cutting studies on the static capsular restraints. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research®. 1996 Sep 1;330:54-65.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Levangie PK, Norkin CC. Joint Structure and Function; A Comprehensive Analysis. 5th. Philadelphia: Fadavis Company. 2012.
- ↑ Levangie PK, Norkin CC. Joint Structure and Function; A Comprehensive Analysis. 5th. Philadelphia: Fadavis Company. 2012.
- ↑ Escamilla RF, Yamashiro K, Paulos L, Andrews JR. Shoulder muscle activity and function in common shoulder rehabilitation exercises. Sports medicine. 2009 Aug 1;39(8):663-85.
- ↑ Longo UG, Berton A, Papapietro N, Maffulli N, Denaro V. Biomechanics of the rotator cuff: European perspective. InRotator Cuff Tear 2012 (Vol. 57, pp. 10-17). Karger Publishers.
- ↑ Labriola JE, Lee TQ, Debski RE, McMahon PJ. Stability and instability of the glenohumeral joint: the role of shoulder muscles. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery. 2005 Jan 1;14(1):S32-8.