Teres Minor: Difference between revisions
Wendy Walker (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{subst:Muscles}} ") |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "[[Brachial plexus|" to "[[Brachial Plexus|") |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | <div class="editorbox"> | ||
'''Original Editor '''- | '''Original Editor '''- [http://www.physio-pedia.com/User:Wendy_Walker Wendy Walker] | ||
'''Lead Editors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Lead Editors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
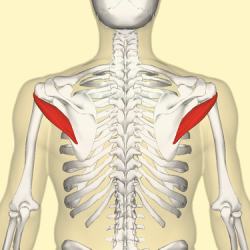
Teres Minor is a narrow muscle which liesbelow [[Infraspinatus|infraspinatus]], above teres major and triceps brachii, and deep to [[Deltoid|deltoid]]. It is one of the four muscles which comprise the [[Rotator Cuff|Rotator Cuff]]. [[Image:Teres minor muscle.png|border|right|250px]] | |||
== | ==Origin== | ||
= | The upper two-thirds of the lateral border of the posterior surface of the [[scapula]].<ref name="grays">Gray, Henry. [http://www.bartleby.com/107/123.html Anatomy of the Human Body. Philadelphia]: Lea & Febiger, 1918; Bartleby.com, 2000. </ref> | ||
== | ==Insertion== | ||
= | The upper fibres end in a tendon which inserts into the inferior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus. The lower fibres insert into the [[humerus]] directly below the inferior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus.<ref name="grays" /> | ||
== | ==Nerve Supply== | ||
= | The axillary nerve (roots C5, C6) from the posterior cord of the [[Brachial Plexus|brachial plexus]].<ref name="aex">Juneja P, Hubbard JB. Anatomy, shoulder and upper limb, arm Teres minor muscle. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. </ref> | ||
== | ==Blood Supply== | ||
< | |||
The subscapular artery ,the circumflex scapular artery and the posterior circumflex humeral artery.<ref name="aex" /> | |||
== References | The subscapular artery and the posterior circumflex humeral artery arise from the third, most distal portion of the axillary artery. <ref name="aex" /> | ||
==Action== | |||
*Teres Minor, along with [[Infraspinatus]], primarily produces external rotation of the shoulder joint.<ref name="aex" /> | |||
*It assists in adduction and extension of the shoulder.<ref name="wheeles">Editor DT. Teres Minor : [https://www.wheelessonline.com/joints/teres-minor/ Wheeless’ Textbook of Orthopaedics] [Internet]. Wheeless’ Textbook of Orthopaedics. 2020 </ref> | |||
*When the humerus is stabilized, abducts the inferior angle of the scapula.<ref name="wheeles" /> | |||
==Function== | |||
In concert with the other rotator cuff muscles, Teres Minor is instrumental in providing stability to the shoulder joint, and helps to hold the humeral head in the glenoid cavity of the scapula.<ref name="aex" /> | |||
=='''Assessment: Hornblower’s sign'''== | |||
Hornblower's sign can be used to evaluate the teres minor for injuries, particularly tears. The patient's arm should be 90 degrees in the scapular plane, with the elbow flexed. The patient will then externally rotate against resistance, attempting to form a "field goal" sign. The test is positive if the patient is unable to rotate their shoulder externally, indicating minor pathology.<ref>D’Ambrosi R, Ragone V, Comaschi G, Usuelli FG, Ursino N. [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30673902/ Retears and complication rates after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair with scaffolds: a systematic review.] Cell Tissue Bank [Internet]. 2019;20(1):1–10. <nowiki>https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30673902/</nowiki></ref> | |||
{{#ev:youtube|w6bfFQ0Q6WA}} <ref>CRTechnologies. Hornblower’s Sign Test (CR) [Internet]. Youtube; 2011. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w6bfFQ0Q6WA</ref> | |||
==Resources== | |||
{{#ev:youtube|W8-qNHh6tfc}}<ref>Kenhub-Learn Human Anatomy. [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W8-qNHh6tfc Teres Minor Muscle - Origins & Action - Human Anatomy] | Kenhub [Internet]. Youtube; 2014.</ref> | |||
{| width="100%" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" | |||
|- | |||
|{{#ev:youtube|UlADwGId8UI|412}}<ref>AnatomyZone. [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UlADwGId8UI Teres Minor | Muscle Anatomy] [Internet]. Youtube; 2018 </ref> | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
==References== | |||
<references /> | |||
[[Category:Shoulder]] | |||
[[Category:Anatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Shoulder - Anatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Shoulder - Anatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Muscles]] | |||
[[Category:Shoulder - Muscles]] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:59, 8 March 2024
Original Editor - Wendy Walker
Lead Editors - Kim Jackson, Wendy Walker, WikiSysop, George Prudden, Joao Costa, Aya Alhindi, 127.0.0.1, Oyemi Sillo and Naomi O'Reilly
Description[edit | edit source]
Teres Minor is a narrow muscle which liesbelow infraspinatus, above teres major and triceps brachii, and deep to deltoid. It is one of the four muscles which comprise the Rotator Cuff.
Origin[edit | edit source]
The upper two-thirds of the lateral border of the posterior surface of the scapula.[1]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
The upper fibres end in a tendon which inserts into the inferior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus. The lower fibres insert into the humerus directly below the inferior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus.[1]
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
The axillary nerve (roots C5, C6) from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus.[2]
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
The subscapular artery ,the circumflex scapular artery and the posterior circumflex humeral artery.[2]
The subscapular artery and the posterior circumflex humeral artery arise from the third, most distal portion of the axillary artery. [2]
Action[edit | edit source]
- Teres Minor, along with Infraspinatus, primarily produces external rotation of the shoulder joint.[2]
- It assists in adduction and extension of the shoulder.[3]
- When the humerus is stabilized, abducts the inferior angle of the scapula.[3]
Function[edit | edit source]
In concert with the other rotator cuff muscles, Teres Minor is instrumental in providing stability to the shoulder joint, and helps to hold the humeral head in the glenoid cavity of the scapula.[2]
Assessment: Hornblower’s sign[edit | edit source]
Hornblower's sign can be used to evaluate the teres minor for injuries, particularly tears. The patient's arm should be 90 degrees in the scapular plane, with the elbow flexed. The patient will then externally rotate against resistance, attempting to form a "field goal" sign. The test is positive if the patient is unable to rotate their shoulder externally, indicating minor pathology.[4]
Resources[edit | edit source]
| [7] |
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Gray, Henry. Anatomy of the Human Body. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger, 1918; Bartleby.com, 2000.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Juneja P, Hubbard JB. Anatomy, shoulder and upper limb, arm Teres minor muscle. StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Editor DT. Teres Minor : Wheeless’ Textbook of Orthopaedics [Internet]. Wheeless’ Textbook of Orthopaedics. 2020
- ↑ D’Ambrosi R, Ragone V, Comaschi G, Usuelli FG, Ursino N. Retears and complication rates after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair with scaffolds: a systematic review. Cell Tissue Bank [Internet]. 2019;20(1):1–10. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30673902/
- ↑ CRTechnologies. Hornblower’s Sign Test (CR) [Internet]. Youtube; 2011. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w6bfFQ0Q6WA
- ↑ Kenhub-Learn Human Anatomy. Teres Minor Muscle - Origins & Action - Human Anatomy | Kenhub [Internet]. Youtube; 2014.
- ↑ AnatomyZone. Teres Minor | Muscle Anatomy [Internet]. Youtube; 2018