Template:Nerves: Difference between revisions
(Undo revision 151158 by Tarina van der Stockt (talk)) |
(Add a table) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Description<br> == | == Description<br> == | ||
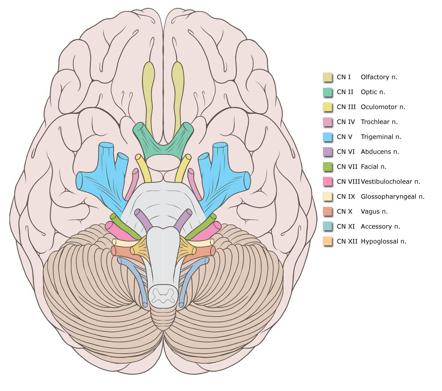
There are 12 pairs cranial nerves and they are numbered according to their position of where they originate on the inferior surface of the brain.< | There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves and they are numbered according to their position of where they originate on the inferior surface of the brain. The names of the cranial nerves (CN) are: CN I - olfactory, CN II - optic, CN III - oculomotor, CN IV - trochlear, CN V - trigeminal, CN VI - abducens, CN VII - fascial, CN VIII - vestibulocochlear, CN IX - glossopharyngeal, CN X - vagus, CN XI - accessory, and CN XII - hypoglossal. <ref name="Ana">McKinley M, O'Loughlin VD. Human Anatomy. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2008fckLRfckLRHill C. Practical guidelines for cystic fibrosis care. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 1998.</ref> | ||
[[Image:CNs Brain.jpg|Cranial Nerves]]<br> | [[Image:CNs Brain.jpg|Cranial Nerves]]<br> | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
The | The names of the cranial nerves sometimes correspond with their individual function. The cranial nerves are comprised of axons that are either sensory, motor or both. <ref name="Ana" /> <br> | ||
{| width="200" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" border="1" | |||
|+ Cranial nerves and their primary functions | |||
|- | |||
! scope="col" | Cranial Nerve | |||
! scope="col" | Sensory Function | |||
! scope="col" | Somatic Motor Function | |||
! scope="col" | Autonomic (parasympathetic motor) Function | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
<br> | |||
=== Motor === | === Motor === | ||
Revision as of 00:56, 5 October 2016
Original Editor - Tarina van der Stockt
Top Contributors - Tarina van der Stockt, George Prudden and Evan Thomas
Description
[edit source]
There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves and they are numbered according to their position of where they originate on the inferior surface of the brain. The names of the cranial nerves (CN) are: CN I - olfactory, CN II - optic, CN III - oculomotor, CN IV - trochlear, CN V - trigeminal, CN VI - abducens, CN VII - fascial, CN VIII - vestibulocochlear, CN IX - glossopharyngeal, CN X - vagus, CN XI - accessory, and CN XII - hypoglossal. [1]
Function[edit source]
The names of the cranial nerves sometimes correspond with their individual function. The cranial nerves are comprised of axons that are either sensory, motor or both. [1]
| Cranial Nerve | Sensory Function | Somatic Motor Function | Autonomic (parasympathetic motor) Function |
|---|---|---|---|