Subscapularis: Difference between revisions
Wendy Walker (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{subst:Muscles}} ") |
Wendy Walker (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | <div class="editorbox"> | ||
'''Original Editor '''- | '''Original Editor '''- [http://www.physio-pedia.com/User:Wendy_Walker Wendy Walker] | ||
'''Lead Editors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Lead Editors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
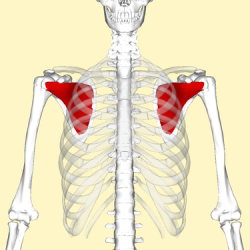
== Description == | == Description == | ||
== Origin == | A large triangular-shaped muscle which fills the costal surface of the scapula. [[Image:Subscapularis_muscle.png|border|right|250px]] | ||
== Origin == | |||
Subscapular fossa on the costal/anterior surface of the scapula. | |||
== Insertion == | == Insertion == | ||
The fibres form a tendon which inserts into the lesser tuberosity of the humerus and the front of the shoulder joint capsule. | |||
== Nerve Supply == | == Nerve Supply == | ||
Suprascapular Nerve, C5 & C6. | |||
Subscapularis is innervated by both the upper and lower subscapular nerves which come from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus.The upper subscapular nerve supplies the upper part of subscapularis, while the lower subscapular nerve branches into two, with one branch supplying the lower part of subscapularis. | |||
== Blood Supply == | == Blood Supply == | ||
Subscapular Artery. | |||
== Action == | == Action == | ||
Contraction of the subscapulaisr can cause medial rotation and depression of the humerus at the glenuhumeral joint. | |||
In certain positions, it also helps produce extension and adduction of the shoulder joint. | |||
Arm position has a marked effect on the actions caused by this muscle: when the arm is raised, subscapularis pulls the humerus forward and downward; when the humerus is in a fixed position, subscapularis’ insertion can act as an origin and it producees abduction of the inferior border of the scapula. | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
As part of the Rotator Cuff, Subscapularis plays an important role in stabilisation of the shoulder, and prevention of dislocation.<br> | |||
It commonly helps produce medial/internal rotation of the shoulder joint. | |||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
| Line 28: | Line 50: | ||
References will automatically be added here, see [[Adding References|adding references tutorial]]. | References will automatically be added here, see [[Adding References|adding references tutorial]]. | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
| |||
Revision as of 01:11, 8 December 2014
Original Editor - Wendy Walker
Lead Editors - Andeela Hafeez, Kim Jackson, Lilian Ashraf, Wendy Walker, Aya Alhindi, 127.0.0.1, Tony Lowe, Naomi O'Reilly, George Prudden, Kai A. Sigel, WikiSysop, Joao Costa and Daphne Xuan
Description[edit | edit source]
A large triangular-shaped muscle which fills the costal surface of the scapula.
Origin[edit | edit source]
Subscapular fossa on the costal/anterior surface of the scapula.
Insertion[edit | edit source]
The fibres form a tendon which inserts into the lesser tuberosity of the humerus and the front of the shoulder joint capsule.
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Suprascapular Nerve, C5 & C6.
Subscapularis is innervated by both the upper and lower subscapular nerves which come from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus.The upper subscapular nerve supplies the upper part of subscapularis, while the lower subscapular nerve branches into two, with one branch supplying the lower part of subscapularis.
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
Subscapular Artery.
Action[edit | edit source]
Contraction of the subscapulaisr can cause medial rotation and depression of the humerus at the glenuhumeral joint.
In certain positions, it also helps produce extension and adduction of the shoulder joint.
Arm position has a marked effect on the actions caused by this muscle: when the arm is raised, subscapularis pulls the humerus forward and downward; when the humerus is in a fixed position, subscapularis’ insertion can act as an origin and it producees abduction of the inferior border of the scapula.
Function[edit | edit source]
As part of the Rotator Cuff, Subscapularis plays an important role in stabilisation of the shoulder, and prevention of dislocation.
It commonly helps produce medial/internal rotation of the shoulder joint.
Resources[edit | edit source]
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Extension:RSS -- Error: Not a valid URL: Feed goes here!!|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.