Pediatric Patient Resources: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) m (Formatting and updating links) |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | <div class="editorbox"> | ||
''' | '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Alicia Dupilka|Alicia Dupilka]] | ||
''' | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
== Introduction == | |||
= | |||
| This page contains resources for physiotherapists and families relating to rare conditions diagnosed within the pediatric population. | ||
== Autism Spectrum Disorder and Autism [[Image:Autism ribbon.png|120x132px]] == | |||
< | ===Definition=== | ||
Group of complex disorders of the brain. Varying degrees of characteristics including: difficulties in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication and repetitive behaviors<ref name="Autism Speaks">Autism Speaks. It's Time to Listen. Available from:http://www.autismspeaks.org/ (accessed 27/06/2013).</ref>. | |||
* Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): can display with intellectual disabilities, difficulties in coordination and attention and physical health issues. | |||
* Autism: most obvious signs and symptoms tend to emerge between 2 and 3 years old | |||
===How Common Are Autism And ASD? === | |||
* ASD: Affects over 2 million individuals in the United States | |||
* Autism: | |||
** Effects ~1:88 children | |||
** ~4-5 more times likely in boys than girls | |||
** An estimated 1 out of 54 boys and 1 in 252 girls are diagnosed in the United States | |||
===Causes=== | |||
* No one cause | |||
* Rare gene changes Most cases are a combination of gene changes and environmental factor | |||
* Risk factors (do not cause autism by themselves, but could have an influence when combined with genetic risk factors): | |||
** Clearest evidence involve events before and during birth | |||
** Advance age at conception | |||
** Maternal illness during pregnancy | |||
** Difficulties during birth (i.e. Oxygen deprivation) | |||
* Genetic risk factors (Autism tends to happen more frequently in the following conditions)<ref name="Autism Society">Autism Society. Improving the Lives of All Affected by Autism. Available from: http://www.autism-society.org/ (Accessed 27/06/2013).</ref> | |||
** Fragile X Syndrome | |||
** Tuberous sclerosis | |||
** Congenital rubella syndrome | |||
** Untreated phenylketonuria (PKU) | |||
===How is ASD/Autism Diagnosed?=== | |||
* No specific medical test | |||
* Administer autism-specific behavioural evaluations | |||
* Parents usually notice: | |||
** Failure to make eye contact | |||
** Not responding to their name | |||
** Playing with toys in unusual or repetitive ways | |||
** [http://www.autismspeaks.org/what-autism/learn-signs Other signs] | |||
* The Modified Checklist of Autism in Toddlers: | |||
** List of informative questions about child | |||
** Answers can indicate whether further evaluation by a specialist is needed | |||
[[Image:Eac-block.jpg]] | |||
** [https://www.autismspeaks.org/screen-your-child Screening tool] | |||
* Typical diagnosis involves a multidisciplinary team | |||
* Genetic testing may be recommended | |||
===Resources for Autism=== | |||
'''Kentucky Autism Training Center''' | |||
* [http://katcproviders.louisville.edu/ Find specific services by region or county] | |||
* Examples of services include: hippo therapy, social skills group, community living supports and day care | |||
'''Autism Society of Kentuckiana''' | |||
* Become a member | |||
* [http://www.ask-lou.org/ Find resources, learn about news and events] | |||
* Offers an autism dad’s group | |||
'''[https://www.autismspeaks.org/ Autism Speaks]''' | |||
* Has information on current news and research, family services and events around the United States | |||
* There is also a blog available; as well as ideas for autism apps<br> | |||
'''National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke''' | |||
* [http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/autism/detail_autism.htm Fact sheet] on ASD and Autism | |||
'''Autism Research Institute''' | |||
* Find out about current research | |||
* http://www.autism.com/ | |||
'''[http://www.autism-society.org/ Autism Society]''' | |||
* Has news, research and ways to get involved | |||
* Section about living with Autism | |||
== Cerebral Palsy (CP) [[Image:Cerebral-palsy-awareness-ribbon.jpg.png|120x132px]] == | == Cerebral Palsy (CP) [[Image:Cerebral-palsy-awareness-ribbon.jpg.png|120x132px]] == | ||
===Definition=== | |||
[[Cerebral Palsy Introduction|Cerebral Palsy]] describes a disorder of movement, muscle tone or posture that is caused by injury or abnormal development in the immature brain.<ref name="Mayo">Mayo Clinic. Cerebral Palsy. Available from:http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/cerebral-palsy/DS00302/DSECTION=complications (accessed 30/06/2013).</ref> | |||
===How Common is CP? <ref name="American Prego">American Pregnancy Association: Promoting Pregnancy Wellness. Cerebral Palsy. United Cerebral Palsy. Available from:http://americanpregnancy.org/birthdefects/cerebralpalsy.htm (accessed 30/06/2013).</ref>=== | |||
* Usually not diagnosed until the age of 2 or 3 | |||
* ~2-3:1,000 children over the age of three have the condition | |||
* ~500,000 children and adults have CP in the United States | |||
< | ===Types<ref name="American Prego" /> === | ||
* [[Spasticity|Spastic]]: | |||
** ~70-80% of cases | |||
** Associated with stiff muscles, making movement difficult | |||
** Spastic diplegia: | |||
*** Both legs are affected | |||
*** Causes tight muscles in the hips and legs | |||
*** Inward turned legs leading to crossed knees (scissoring) | |||
[[Image:Diplegic cp.png]] | |||
** Spastic hemiplegia: | |||
*** One side of the body affected | |||
*** Arm often more affected than the leg | |||
[[Image:Hemiplegic CP.png]] | |||
** Spastic quadriplegia: | |||
*** Most severe | |||
*** All four limbs and the trunk are affected | |||
*** Often also affect muscle of tongue and mouth<br> | |||
[[Image:Quad cp.png]] | |||
* Athetoid or Dyskinetic: | |||
** 10-20% of cases | |||
** Affects entire body | |||
** Fluctuations in muscle tone | |||
** Uncontrolled movements | |||
** Difficulty with: | |||
*** Learning to control body | |||
*** Sucking | |||
*** Swallowing | |||
*** Speech | |||
* Ataxic | |||
** 5-10% of cases | |||
** Affects [[balance]] and coordination: | |||
*** Unsteady [[gait]] | |||
*** Difficulty with motions that require precise coordination | |||
< | ===Causes<ref name="Mayo" />=== | ||
* Abnormality or disruption in brain development | |||
* Random mutations in genes | |||
* Infections of the mother that would affect the developing baby | |||
* Disruption of blood supply to the developing brain | |||
* Lack of oxygen to the baby’s brain | |||
* Infant infections leading to inflammation around the brain | |||
* [[Traumatic Brain Injury|Traumatic head injury]] | |||
===Risk Factors<ref name="Mayo" />=== | |||
* Mother’s health: | |||
** Certain infections or health problems significantly increase the chance to giving birth to a baby with CP: | |||
*** Rubella | |||
*** Syphilis | |||
*** Chickenpox | |||
*** [http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/cerebral-palsy/DS00302/DSECTION=risk-factors Other conditions] | |||
* Infant’s health: | |||
** Certain illnesses in a newborn significantly increase the chance of the baby developing CP: | |||
*** Bacterial meningitis | |||
*** Severe or untreated jaundice (yellowing of the skin) | |||
*** Viral encephalitis | |||
* Other factors: | |||
** Premature birth | |||
** Low birth weight | |||
** Breech births | |||
** Multiple babies | |||
== | ===How is CP Diagnosed?<ref name="Mayo" />=== | ||
* Signs and symptoms usually appear during infancy or preschool years: | |||
** Impaired movement associated with: | |||
*** Exaggerated [[reflexes]] or rigidity of the limbs and trunk | |||
*** Abnormal [[posture]] | |||
*** Involuntary movements | |||
*** Unsteadiness of walking | |||
*** Combination of these | |||
*** [http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/cerebral-palsy/DS00302/DSECTION=symptoms Other signs and symptoms] | |||
* Brain scans: | |||
** [[MRI Scans|MRI]]: usually the preferred test to use, will usually be given a mild sedative to remain still | |||
** Cranial [[Ultrasound Scans|ultrasound]]: can provide a preliminary assessment, placed over the soft spot (fontanel) of the baby’s head | |||
** [[CT Scans|CT scan]]: will likely be given a mild sedative to remain still | |||
* Electroencephalogram (EEG): | |||
** Done if the child has a history of seizures | |||
** Records the electrical activity of the brain | |||
** Used to determine if child has epilepsy | |||
* Lab tests: | |||
** Blood is checked to rule out other conditions | |||
** May also screen for metabolic or genetic problems | |||
<br> | * Additional tests: | ||
** If diagnosed with CP, may go through these other tests to screen for other associated conditions: | |||
*** Vision impairment | |||
*** Hearing impairment | |||
*** Speech delays or impairments | |||
*** Intellectual disabilities or mental retardation | |||
*** Other developmental delays<br> | |||
===Resources for Cerebral Palsy=== | |||
'''[http://cerebralpalsy.org/ MyChild™]:''' | |||
* Their mission: “to provide you with the most comprehensive resource and compassionate voice for all things related to caring for a child with cerebral palsy, and other neurological conditions. We strive, everyday, to be your ULTIMATE Resource for EVERYTHING Cerebral Palsy.” | |||
'''[http://cerebralpalsyresources.com/kentucky Cerebral Palsy Resources]''' | |||
| '''[http://www.mattinglycenter.org/aboutus.html Mattingly Center, Inc.]''' | ||
* Cerebral Palsy School of Louisville, Inc. | |||
* Their mission “To provide the highest quality of structured day services for adults with severe developmental disabilities.” | |||
== Down Syndrome [[Image:Down.syndrome.ribbon.magnet.jpg|120x132px]] == | |||
===Definition=== | |||
[[Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)|Down's Syndrome]] is a genetic disorder occurring when the individual has full or a partial copy of chromosome 21. This extra genetic material causes an alteration in the development of the child.<ref name="NDSS">National Down Syndrome Society. Down Syndrome. National Down Syndrome Society. http://www.ndss.org/Down-Syndrome/What-Is-Down-Syndrome/. Published 2012. Accessed June 24, 2013.</ref> | |||
===How Common is Down's Syndrome?=== | |||
* Most common genetic disorder | |||
* ~1:691 babies are born each year with Down’s Syndrome | |||
* ~6,000 babies are born each year with Down’s Syndrome | |||
===Types=== | |||
* Trisomy 21 (Nondisjunction): | |||
** The pair of the 21st chromosome fails to separate | |||
** Extra chromosome is replicated in every cell in the body | |||
** Accounts for ~95% of cases | |||
[[Image:Nondisjunction Cell Division.jpg]] | |||
** Mosaicism: | |||
*** Nondisjunction takes place in chromosome 21 in one cell but not all cells | |||
*** Accounts for ~1% of cases | |||
*** May have fewer characteristics than other types of Down’s Syndrome | |||
[[Image:Mosaicism.jpg]]<br> | |||
** Translocation: | |||
*** Part of chromosome 21 breaks off during cell division and attaches to another chromosome, typically chromosome 14 | |||
*** Accounts for ~4% of cases | |||
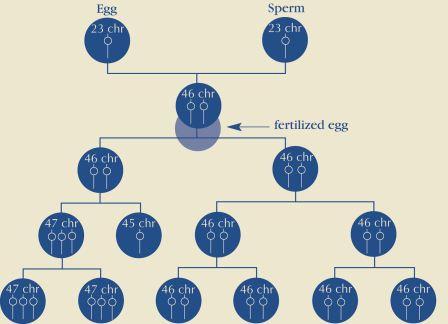
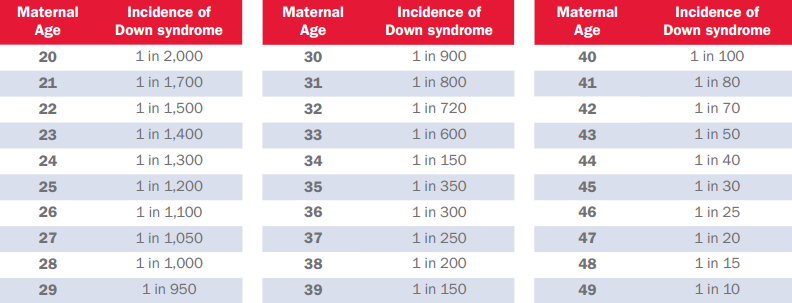
===Causes=== | |||
* Cause of non-disjunction is currently unknown: | |||
** Research suggests the likelihood increases as women age | |||
** No definitive research suggesting environmental factors of the parents before or during pregnancy | |||
[[Image:Maternal Age Chart2.png]] | [[Image:Maternal Age Chart2.png]] | ||
*Note: Age 34 is not accurate. NDSS has noted the error but has yet to find out the correct information. | **Note: Age 34 is not accurate. NDSS has noted the error but has yet to find out the correct information. | ||
===How is Down’s Syndrome Diagnosed? === | |||
<u>Prenatally</u> | |||
* Screening tests: | |||
** Most only provide a probability | |||
** Blood test: measures quantities of various substances in the mother’s blood | |||
** [[Ultrasound Scans|Ultrasound]]: checks for “markers” | |||
** Diagnostic tests: | |||
*** Can provide a definite diagnosis with almost 100% accuracy | |||
*** Carry up to a 1% risk of causing a spontaneous termination | |||
*** Chorionic villus sampling (CVS): usually performed in first trimester between 9 and 11 weeks | |||
*** Amniocentesis: usually performed in the second trimester after 15 weeks | |||
<u>At birth</u> | |||
* Usually identified by certain physical traits: | |||
** Low muscle tone | |||
** Single deep crease across the palm of the hand | |||
** Slightly flattened facial profile | |||
** Upward slant to the eyes | |||
* Chromosomal analysis may also need to be done to confirm the diagnosis: | |||
** This is done by drawing a sample of the baby’s blood | |||
===Resources for Down Syndrome=== | |||
'''[http://www.downsyndromeoflouisville.org/ Down Syndrome of Louisville]''' | |||
* Lifelong learning center for individuals with Down Syndrome | |||
<br> | * National Down Syndrome Society | ||
** Information about Down Syndrome | |||
** Lists [http://www.ndss.org/Resources/ resources] including: | |||
*** Publications | |||
*** Managing behavior | |||
*** Research | |||
*** And more!<br> | |||
'''National Association for Down Syndrome''' | |||
* Programs | |||
* [http://www.nads.org/pages_new/resources.html Resources] and information<br> | |||
'''Real Life Down Syndrome''' | |||
* Blog spot | |||
* Gives insight on how to raise a child with DS | |||
* [http://reallifedownsyndrome-resources.blogspot.com/ Search resources by state]<br> | |||
'''[http://dbhdid.ky.gov/dbh/files/oflsecb.pdf Kentucky Parent Support Groups]''' | |||
* Lists support groups by county | |||
== Activities and Equipment Sites for the Pediatric Population == | |||
<div class="researchbox">Below are websites for you to look around for fun activities to enjoy outside of therapy sessions: | |||
*'''[http://pinterest.com/pediastaff/ PediaStaff]''' | |||
*[http://pinterest.com/ytherapysource/ '''Your Therapy Source'''] | |||
*[http://pinterest.com/motorsmartkids/ '''Starfish Therapies'''] | |||
<br> Below is a list of equipment sites for you to look around: | |||
*'''[http://equipmentshop.com/ Equipment Shop]''' | |||
*'''[http://cascadeshop.com/ Cascade]''' | |||
*[http://www.therapyshoppe.com/ '''Therapy Shoppe'''] | |||
*[http://www.flaghouse.com/ '''Flaghouse'''] | |||
*[http://www.rifton.com/ '''Rifton'''] | |||
*[http://www.adaptivemall.com/ '''Adaptive Mall'''] | |||
*'''[https://store.schoolspecialty.com/OA_HTML/ibeCCtpSctDspRte.jsp?sname=Special+Needs&rootSection=95750§ion=95750&minisite=10206 Abilitations]''' | |||
*'''[http://funandfunction.com/ Fun and Function]''' | |||
*'''[http://yellowbrickroadshop.com/ Yellow Brick Road Shop]''' | |||
*'''[http://www.especialneeds.com/home.php eSpecial Needs]''' | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
== | == Resources == | ||
[[Image:Kosair.jpg|120x132px]] | |||
'''Kosair Childrens Hospital''' | |||
* Look into conditions and services | |||
* Find a doctor | |||
* See current news | |||
* Visit their [http://www.kosairchildrens.com/ health library] | |||
<br> '''Pediatric Leukemias''' | |||
* The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia | |||
* In depth [http://www.chop.edu/service/oncology/cancers-explained/leukemia-diagnosis-and-treatment.html resource of pediatric leukemias]<br> [[Image:Logo.gif]] | |||
'''Pediatric Rheumatology''' | |||
* [http://www.ped-rheum.com/content/6/1/16 Review of childhood sarcoidosis] <br> [[Image:Msf.jpg|120x132px]] | |||
'''Multiple Sclerosis Foundation''' | |||
* Insight on pediatric MS | |||
* [http://www.msfocus.org/article-details.aspx?articleID=374 Coping with MS] | |||
<br> '''Failure to Thrive''' | |||
* Clinical key by Elsevier | |||
* [https://www.clinicalkey.com/topics/pediatrics/failure-to-thrive.html In depth overview of diagnosis]<br> | |||
'''National Organization for Rare Diseases''' | |||
* Search the [http://www.rarediseases.org/rare-disease-information/rare-diseases rare disease database] and download the free report | |||
<br> '''The Global Genes Project''' | |||
* [http://globalgenes.org/ Learn what they are about] | |||
* Get involved | |||
* Resources available: | |||
** Search their [http://globalgenes.org/rarelist/ RARE list] | |||
** Search their [http://globalgenes.org/rarefacts/ RARE facts] | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 225: | Line 318: | ||
[[Category:Bellarmine_Student_Project]] | [[Category:Bellarmine_Student_Project]] | ||
[[Category:Cerebral_Palsy]] | |||
[[Category:Paediatrics]] | |||
[[Category:Resources - Paediatrics]] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:21, 1 April 2020
Original Editor - Alicia Dupilka
Top Contributors - Alicia Dupilka, Elaine Lonnemann, Kim Jackson, Leana Louw, WikiSysop, Admin and Scott Buxton
Introduction[edit | edit source]
This page contains resources for physiotherapists and families relating to rare conditions diagnosed within the pediatric population.
Autism Spectrum Disorder and Autism  [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
Definition[edit | edit source]
Group of complex disorders of the brain. Varying degrees of characteristics including: difficulties in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication and repetitive behaviors[1].
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): can display with intellectual disabilities, difficulties in coordination and attention and physical health issues.
- Autism: most obvious signs and symptoms tend to emerge between 2 and 3 years old
How Common Are Autism And ASD? [edit | edit source]
- ASD: Affects over 2 million individuals in the United States
- Autism:
- Effects ~1:88 children
- ~4-5 more times likely in boys than girls
- An estimated 1 out of 54 boys and 1 in 252 girls are diagnosed in the United States
Causes[edit | edit source]
- No one cause
- Rare gene changes Most cases are a combination of gene changes and environmental factor
- Risk factors (do not cause autism by themselves, but could have an influence when combined with genetic risk factors):
- Clearest evidence involve events before and during birth
- Advance age at conception
- Maternal illness during pregnancy
- Difficulties during birth (i.e. Oxygen deprivation)
- Genetic risk factors (Autism tends to happen more frequently in the following conditions)[2]
- Fragile X Syndrome
- Tuberous sclerosis
- Congenital rubella syndrome
- Untreated phenylketonuria (PKU)
How is ASD/Autism Diagnosed?[edit | edit source]
- No specific medical test
- Administer autism-specific behavioural evaluations
- Parents usually notice:
- Failure to make eye contact
- Not responding to their name
- Playing with toys in unusual or repetitive ways
- Other signs
- The Modified Checklist of Autism in Toddlers:
- List of informative questions about child
- Answers can indicate whether further evaluation by a specialist is needed
- Typical diagnosis involves a multidisciplinary team
- Genetic testing may be recommended
Resources for Autism[edit | edit source]
Kentucky Autism Training Center
- Find specific services by region or county
- Examples of services include: hippo therapy, social skills group, community living supports and day care
Autism Society of Kentuckiana
- Become a member
- Find resources, learn about news and events
- Offers an autism dad’s group
- Has information on current news and research, family services and events around the United States
- There is also a blog available; as well as ideas for autism apps
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
- Fact sheet on ASD and Autism
Autism Research Institute
- Find out about current research
- http://www.autism.com/
- Has news, research and ways to get involved
- Section about living with Autism
Cerebral Palsy (CP)  [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
Definition[edit | edit source]
Cerebral Palsy describes a disorder of movement, muscle tone or posture that is caused by injury or abnormal development in the immature brain.[3]
How Common is CP? [4][edit | edit source]
- Usually not diagnosed until the age of 2 or 3
- ~2-3:1,000 children over the age of three have the condition
- ~500,000 children and adults have CP in the United States
Types[4][edit | edit source]
- Spastic:
- ~70-80% of cases
- Associated with stiff muscles, making movement difficult
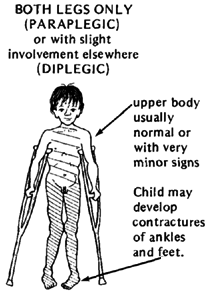
- Spastic diplegia:
- Both legs are affected
- Causes tight muscles in the hips and legs
- Inward turned legs leading to crossed knees (scissoring)
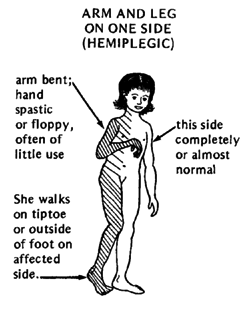
- Spastic hemiplegia:
- One side of the body affected
- Arm often more affected than the leg
- Spastic hemiplegia:
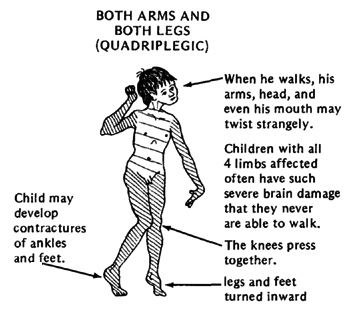
- Spastic quadriplegia:
- Most severe
- All four limbs and the trunk are affected
- Often also affect muscle of tongue and mouth
- Spastic quadriplegia:
- Athetoid or Dyskinetic:
- 10-20% of cases
- Affects entire body
- Fluctuations in muscle tone
- Uncontrolled movements
- Difficulty with:
- Learning to control body
- Sucking
- Swallowing
- Speech
- Ataxic
Causes[3][edit | edit source]
- Abnormality or disruption in brain development
- Random mutations in genes
- Infections of the mother that would affect the developing baby
- Disruption of blood supply to the developing brain
- Lack of oxygen to the baby’s brain
- Infant infections leading to inflammation around the brain
- Traumatic head injury
Risk Factors[3][edit | edit source]
- Mother’s health:
- Certain infections or health problems significantly increase the chance to giving birth to a baby with CP:
- Rubella
- Syphilis
- Chickenpox
- Other conditions
- Certain infections or health problems significantly increase the chance to giving birth to a baby with CP:
- Infant’s health:
- Certain illnesses in a newborn significantly increase the chance of the baby developing CP:
- Bacterial meningitis
- Severe or untreated jaundice (yellowing of the skin)
- Viral encephalitis
- Certain illnesses in a newborn significantly increase the chance of the baby developing CP:
- Other factors:
- Premature birth
- Low birth weight
- Breech births
- Multiple babies
How is CP Diagnosed?[3][edit | edit source]
- Signs and symptoms usually appear during infancy or preschool years:
- Impaired movement associated with:
- Exaggerated reflexes or rigidity of the limbs and trunk
- Abnormal posture
- Involuntary movements
- Unsteadiness of walking
- Combination of these
- Other signs and symptoms
- Impaired movement associated with:
- Brain scans:
- MRI: usually the preferred test to use, will usually be given a mild sedative to remain still
- Cranial ultrasound: can provide a preliminary assessment, placed over the soft spot (fontanel) of the baby’s head
- CT scan: will likely be given a mild sedative to remain still
- Electroencephalogram (EEG):
- Done if the child has a history of seizures
- Records the electrical activity of the brain
- Used to determine if child has epilepsy
- Lab tests:
- Blood is checked to rule out other conditions
- May also screen for metabolic or genetic problems
- Additional tests:
- If diagnosed with CP, may go through these other tests to screen for other associated conditions:
- Vision impairment
- Hearing impairment
- Speech delays or impairments
- Intellectual disabilities or mental retardation
- Other developmental delays
- If diagnosed with CP, may go through these other tests to screen for other associated conditions:
Resources for Cerebral Palsy[edit | edit source]
- Their mission: “to provide you with the most comprehensive resource and compassionate voice for all things related to caring for a child with cerebral palsy, and other neurological conditions. We strive, everyday, to be your ULTIMATE Resource for EVERYTHING Cerebral Palsy.”
- Cerebral Palsy School of Louisville, Inc.
- Their mission “To provide the highest quality of structured day services for adults with severe developmental disabilities.”
Down Syndrome  [edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
Definition[edit | edit source]
Down's Syndrome is a genetic disorder occurring when the individual has full or a partial copy of chromosome 21. This extra genetic material causes an alteration in the development of the child.[5]
How Common is Down's Syndrome?[edit | edit source]
- Most common genetic disorder
- ~1:691 babies are born each year with Down’s Syndrome
- ~6,000 babies are born each year with Down’s Syndrome
Types[edit | edit source]
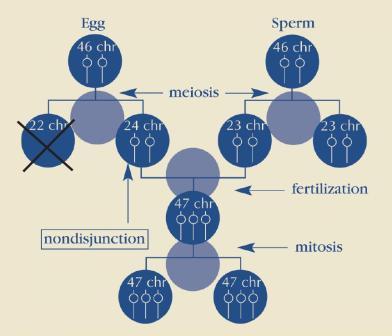
- Trisomy 21 (Nondisjunction):
- The pair of the 21st chromosome fails to separate
- Extra chromosome is replicated in every cell in the body
- Accounts for ~95% of cases
- Mosaicism:
- Nondisjunction takes place in chromosome 21 in one cell but not all cells
- Accounts for ~1% of cases
- May have fewer characteristics than other types of Down’s Syndrome
- Mosaicism:
- Translocation:
- Part of chromosome 21 breaks off during cell division and attaches to another chromosome, typically chromosome 14
- Accounts for ~4% of cases
- Translocation:
Causes[edit | edit source]
- Cause of non-disjunction is currently unknown:
- Research suggests the likelihood increases as women age
- No definitive research suggesting environmental factors of the parents before or during pregnancy
- Note: Age 34 is not accurate. NDSS has noted the error but has yet to find out the correct information.
How is Down’s Syndrome Diagnosed?[edit | edit source]
Prenatally
- Screening tests:
- Most only provide a probability
- Blood test: measures quantities of various substances in the mother’s blood
- Ultrasound: checks for “markers”
- Diagnostic tests:
- Can provide a definite diagnosis with almost 100% accuracy
- Carry up to a 1% risk of causing a spontaneous termination
- Chorionic villus sampling (CVS): usually performed in first trimester between 9 and 11 weeks
- Amniocentesis: usually performed in the second trimester after 15 weeks
- Diagnostic tests:
At birth
- Usually identified by certain physical traits:
- Low muscle tone
- Single deep crease across the palm of the hand
- Slightly flattened facial profile
- Upward slant to the eyes
- Chromosomal analysis may also need to be done to confirm the diagnosis:
- This is done by drawing a sample of the baby’s blood
Resources for Down Syndrome[edit | edit source]
- Lifelong learning center for individuals with Down Syndrome
- National Down Syndrome Society
- Information about Down Syndrome
- Lists resources including:
- Publications
- Managing behavior
- Research
- And more!
National Association for Down Syndrome
- Programs
- Resources and information
Real Life Down Syndrome
- Blog spot
- Gives insight on how to raise a child with DS
- Search resources by state
Kentucky Parent Support Groups
- Lists support groups by county
Activities and Equipment Sites for the Pediatric Population[edit | edit source]
Below is a list of equipment sites for you to look around:
Resources[edit | edit source]
Kosair Childrens Hospital
- Look into conditions and services
- Find a doctor
- See current news
- Visit their health library
Pediatric Leukemias
- The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia
- In depth resource of pediatric leukemias

Pediatric Rheumatology
Multiple Sclerosis Foundation
- Insight on pediatric MS
- Coping with MS
Failure to Thrive
- Clinical key by Elsevier
- In depth overview of diagnosis
National Organization for Rare Diseases
- Search the rare disease database and download the free report
The Global Genes Project
- Learn what they are about
- Get involved
- Resources available:
- Search their RARE list
- Search their RARE facts
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Autism Speaks. It's Time to Listen. Available from:http://www.autismspeaks.org/ (accessed 27/06/2013).
- ↑ Autism Society. Improving the Lives of All Affected by Autism. Available from: http://www.autism-society.org/ (Accessed 27/06/2013).
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Mayo Clinic. Cerebral Palsy. Available from:http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/cerebral-palsy/DS00302/DSECTION=complications (accessed 30/06/2013).
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 American Pregnancy Association: Promoting Pregnancy Wellness. Cerebral Palsy. United Cerebral Palsy. Available from:http://americanpregnancy.org/birthdefects/cerebralpalsy.htm (accessed 30/06/2013).
- ↑ National Down Syndrome Society. Down Syndrome. National Down Syndrome Society. http://www.ndss.org/Down-Syndrome/What-Is-Down-Syndrome/. Published 2012. Accessed June 24, 2013.