Middle Scalene: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(Clinical significance paragraph updated and citations added) |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
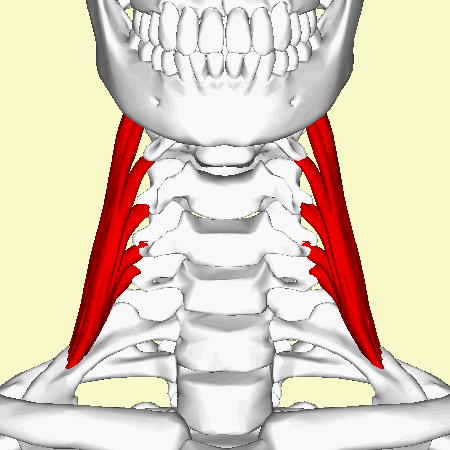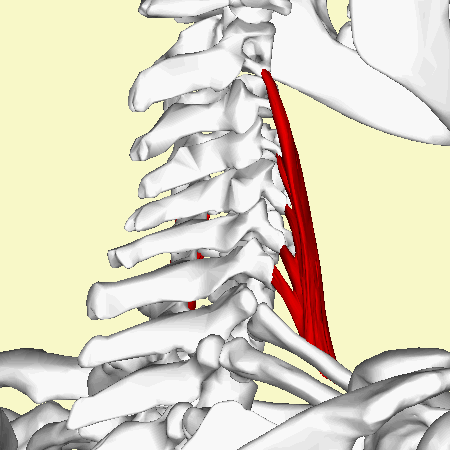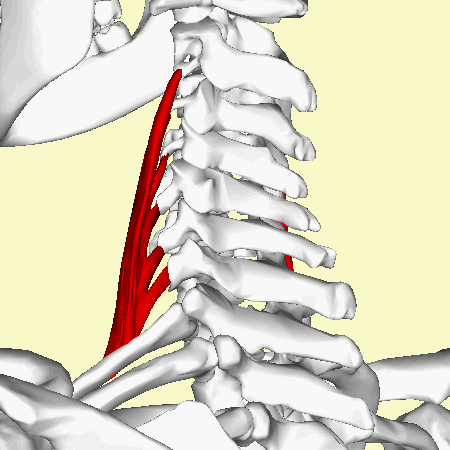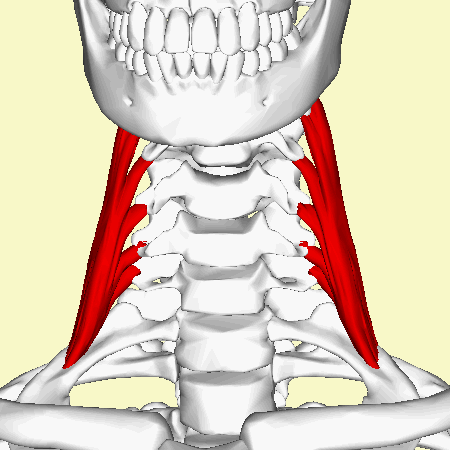
Middle | Middle scalene or scalenus medius (Latin: musculus scalenus medius), is the largest and longest muscle in the scalene group of lateral neck muscles.<ref name=":0">Kenhub 2022, ''Kenhub: scalene muscles, viewed 16/12/22,''https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/scalene-muscles</ref> Often penetrated by the dorsal scapular<ref name=":0" /> and long thoracic nerves<ref name=":1">Bordoni B, Varacallo M. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519058/ Anatomy, head and neck, scalenus muscle]. StatPearls [Internet]. 2022 Apr 16.</ref>, it is deeply placed, lying behind [[sternocleidomastoid]]<ref name=":1" />.<br> | ||
[[Image:Scalenus medius muscle - animation02.gif|center]] | [[Image:Scalenus medius muscle - animation02.gif|center]] | ||
== Origin == | == Origin == | ||
<div>C2 to C7</ | <div>It originates from the transverse process' posterior tubercles of C2 to C7.<ref name=":1" /><ref name=":2">Anatomy.app 2022, ''Anatomy.app: Middle scalene, viewed 16/12/22,''https://anatomy.app/encyclopedia/middle-scalene</ref>. Origin deviations can include the transverse transverse process of the atlas <ref name=":1" /><ref name=":0" /><ref name=":3">Georgakopoulos B, Lasrado S. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544222/ Anatomy, Head and Neck, Inter-scalene Triangle]. InStatPearls [Internet] 2021 Nov 5. StatPearls Publishing.</ref>.</div> | ||
== Insertion == | == Insertion == | ||
The tendon inserts onto the superior border of the 1st rib, anterior to the 1st rib's tubercle and posterior to the subclavian groove.<ref name=":0" /><ref name=":1" /><ref name=":2" />.Insertion variations include insertion onto the 2nd rib<ref name=":3" /><ref name=":1" />. | |||
== Nerve Supply == | == Nerve Supply == | ||
Anterior rami of cervical spinal nerves C3 - C8 <ref name=":0" /><ref name=":1" /><ref name=":2" />. | |||
== Blood Supply == | == Blood Supply == | ||
The ascending cervical artery branch of the inferior thyroid artery supplies the middle scalene<ref name=":1" /><ref name=":2" /><ref name=":0" />. | |||
< | |||
== | == Action and Function == | ||
The middle scalene work with the [[Scalene|anterior scalene]] to elevate the first rib during respiration<ref name=":0" /><ref name=":2" /> and are also strong ipsilateral flexors during unilateral contraction<ref name=":2" /><ref name=":0" />. The middle scalene are also involved with cervical rotation<ref name=":2" /><ref name=":1" />. | |||
== Clinical significance == | |||
The interscalene triangle (scalene triangle) is the anatomical triangle formed between the scalenus anterior muscle (anteriorly), the scalenus medius muscle (posteriorly) and the first rib (inferiorly)<ref name=":0" /><ref name=":3" />. Structures including the subclavian artery and brachial plexus pass through it<ref name=":0" />. Abnormal anatomy or injury to this region can cause compression of the neurovascular structures leading to [[Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS)|thoracic outlet syndrome]] (TOS)<ref name=":1" /><ref name=":3" />. TOS typically leads to paraestheisa, pain and weakness in the ipsilateral upper limb<ref name=":1" />. Please see the page on [[Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS)|TOS]] for more information regarding this syndrome. | |||
== References == | |||
<references /><br> | <references /><br> | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Cervical Spine - Anatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Cervical_Spine]] | |||
[[Category:Muscles]] | |||
[[Category:Musculoskeletal/Orthopaedics]] | |||
[[Category: | [[Category:Cervical Spine - Muscles]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:39, 16 December 2022
Original Editor - Wendy Walker
Lead Editors - Wendy Walker, Kim Jackson, Milijana Delevic, Admin, WikiSysop, Wendy Snyders and Evan Thomas
Description[edit | edit source]
Middle scalene or scalenus medius (Latin: musculus scalenus medius), is the largest and longest muscle in the scalene group of lateral neck muscles.[1] Often penetrated by the dorsal scapular[1] and long thoracic nerves[2], it is deeply placed, lying behind sternocleidomastoid[2].
Origin[edit | edit source]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
The tendon inserts onto the superior border of the 1st rib, anterior to the 1st rib's tubercle and posterior to the subclavian groove.[1][2][3].Insertion variations include insertion onto the 2nd rib[4][2].
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Anterior rami of cervical spinal nerves C3 - C8 [1][2][3].
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
The ascending cervical artery branch of the inferior thyroid artery supplies the middle scalene[2][3][1].
Action and Function[edit | edit source]
The middle scalene work with the anterior scalene to elevate the first rib during respiration[1][3] and are also strong ipsilateral flexors during unilateral contraction[3][1]. The middle scalene are also involved with cervical rotation[3][2].
Clinical significance[edit | edit source]
The interscalene triangle (scalene triangle) is the anatomical triangle formed between the scalenus anterior muscle (anteriorly), the scalenus medius muscle (posteriorly) and the first rib (inferiorly)[1][4]. Structures including the subclavian artery and brachial plexus pass through it[1]. Abnormal anatomy or injury to this region can cause compression of the neurovascular structures leading to thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS)[2][4]. TOS typically leads to paraestheisa, pain and weakness in the ipsilateral upper limb[2]. Please see the page on TOS for more information regarding this syndrome.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 Kenhub 2022, Kenhub: scalene muscles, viewed 16/12/22,https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/scalene-muscles
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 Bordoni B, Varacallo M. Anatomy, head and neck, scalenus muscle. StatPearls [Internet]. 2022 Apr 16.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Anatomy.app 2022, Anatomy.app: Middle scalene, viewed 16/12/22,https://anatomy.app/encyclopedia/middle-scalene
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Georgakopoulos B, Lasrado S. Anatomy, Head and Neck, Inter-scalene Triangle. InStatPearls [Internet] 2021 Nov 5. StatPearls Publishing.