Biceps Femoris: Difference between revisions
Evan Thomas (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Evan Thomas (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
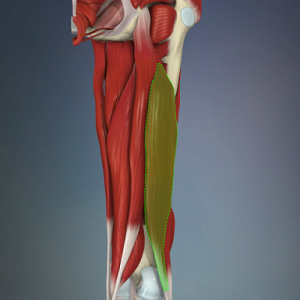
! scope="col" width="400" | [[Image:Biceps fem 2.png|center|300x300px|Biceps_fem_2]]<ref name="anatomytv" /> | ! scope="col" width="400" | [[Image:Biceps fem 2.png|center|300x300px|Biceps_fem_2]]<ref name="anatomytv" /> | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Anatomy == | == Anatomy == | ||
| Line 41: | Line 39: | ||
=== Actions === | === Actions === | ||
*Long head: flexes the knee, extends hip, laterally rotates lower leg when knee slightly flexed, assists in lateral rotation of the thigh when hip extended<ref name=" | *Long head: flexes the knee, extends hip, laterally rotates lower leg when knee slightly flexed, assists in lateral rotation of the thigh when hip extended<ref name="anatomytv" /><ref name="Netter" /> | ||
*Short head: flexes the knee, laterally rotates lower leg when knee slightly flexed<ref name=" | *Short head: flexes the knee, laterally rotates lower leg when knee slightly flexed<ref name="anatomytv" /><ref name="Netter" /> | ||
=== Functional contributions === | === Functional contributions === | ||
Revision as of 01:53, 8 May 2015
This anatomy page requires improvement to meet Physiopedia's quality standards. The reasons have been specified below this alert box. Please help improve this page if you can. #qualityalert #qualityalert_anatomy
Original Editor - Evan Thomas
Top Contributors - Sai Kripa, Evan Thomas, Kim Jackson, Joao Costa, Ahmed M Diab, 127.0.0.1, George Prudden and WikiSysop
Description[edit | edit source]
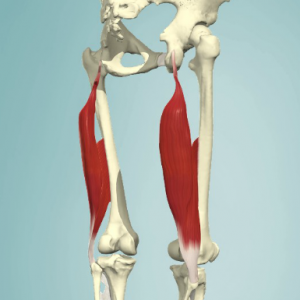
Biceps femoris is a muscle of the posterior compartment of the thigh, and lies in the posterolateral aspect. It arises proximally by two 'heads', termed the 'long head' and the 'short head'. It is part of the hamstrings.[1]
| [2] | [1] |
|---|
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Origin[edit | edit source]
- Long head: ischial tuberosity[3]
- Short head: linea aspera and lateral supracondylar line of the femur[3]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
- Lateral aspect of fibular head[3]
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
- Long head: tibial division of the sciatic nerve (L5-S2)[3]
- Short head: common peroneal division of the sciatic nerve[3]
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
- Perforating branches of profunda femoris, inferior gluteal, and medial circumflex femoral arteries[3]
Function[edit | edit source]
Actions[edit | edit source]
- Long head: flexes the knee, extends hip, laterally rotates lower leg when knee slightly flexed, assists in lateral rotation of the thigh when hip extended[1][3]
- Short head: flexes the knee, laterally rotates lower leg when knee slightly flexed[1][3]
Functional contributions[edit | edit source]
Techniques[edit | edit source]
Palpation[edit | edit source]
Length Tension Testing / Stretching[edit | edit source]
Trigger Point Referral Pattern[edit | edit source]
- Pain referred from TrPs in the lower half of the biceps femoris (long or short head) focuses on the back of the knee and may extend up the posterolateral area of the thigh as far as the crease of the buttock.
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Extension:RSS -- Error: Not a valid URL: Feed goes here!!|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10