Alar ligaments: Difference between revisions
Rachael Lowe (talk | contribs) (Created page with "__FORCETOC__ <div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- Rachael Lowe '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} </di...") |
Rachael Lowe (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[[Image:Upper cervical ligaments.png|thumb|right]] | [[Image:Upper cervical ligaments.png|thumb|right]] | ||
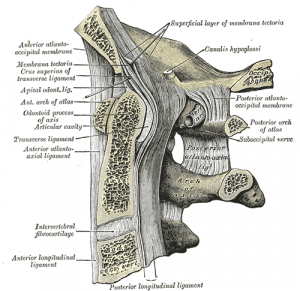
Two strong rounded cords that attach rthe skull to C2 ([[Axis]]). | |||
==Attachments== | |||
Arise from either side of the odontoid process and attach to the medial aspect of the occipital condyles. | |||
==Function== | |||
Taut in flexion, limit rotation and side flexio to the opposite site. | |||
==Pathology== | |||
Injured in rear end shunts when cervical spine is in extremes of rotation. | |||
== Recent Related Research (from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ Pubmed]) == | == Recent Related Research (from [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/ Pubmed]) == | ||
Revision as of 21:04, 18 January 2014
Original Editor - Rachael Lowe
Top Contributors - Rachael Lowe, Kim Jackson, Evan Thomas, WikiSysop, Alistair James, George Prudden and Wendy Snyders
Description[edit | edit source]
Two strong rounded cords that attach rthe skull to C2 (Axis).
Attachments[edit | edit source]
Arise from either side of the odontoid process and attach to the medial aspect of the occipital condyles.
Function[edit | edit source]
Taut in flexion, limit rotation and side flexio to the opposite site.
Pathology[edit | edit source]
Injured in rear end shunts when cervical spine is in extremes of rotation.
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Failed to load RSS feed from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=1ve5_AlTrKT2E32qQKFiSIQiy0LeihushGlwh63xHDv6XJvM2F|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10: Error parsing XML for RSS