Panner's Disease: Difference between revisions
Chloe Waller (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Chloe Waller (talk | contribs) (Updated anatomy, process and presentation) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Definition == | == Definition == | ||
Panner's disease is [[bone]] growth disorder (osteochondrosis) of the humeral | Panner's disease is [[bone]] growth disorder (osteochondrosis) of the humeral capitellum ossification centre, at the lateral aspect of the [[elbow]]<ref>Nordlie H, Rognstad M, Iveland H. [https://tidsskriftet.no/en/2021/06/medisin-i-bilder/panners-disease Panner's disease.] Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2021 Jun 24;141(10). English, Norwegian</ref>. | ||
It is a rare disease, found most commonly in boys under 10 years old, and in a unilateral presentation<ref name=":0">Claessen FM, Louwerens JK, Doornberg JN, van Dijk CN, Eygendaal D, van den Bekerom MP. [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25663360/ Panner's disease: literature review and treatment recommendations.] J Child Orthop. 2015 Feb;9(1):9-17.</ref>. | |||
== Clinically Relevant Anatomy<br> == | == Clinically Relevant Anatomy<br> == | ||
The [[elbow]] joint is a synovial hinge joint. The three bones that make up the articulation of the joint are: the distal end of the [[humerus]] and proximal ends of the [[radius]] and [[ulna]]. The capitellum is the smooth,rounded lateral aspect of the distal articular surface of the humerus, which articulates with the head of the radius.<br> | |||
== | == Pathological Process == | ||
If the blood vessels suppyling the nuleus of the capitellum are disrupted, ischemia can occur<ref name=":0" />. This could be due to: | |||
* Repetitive valgus stress (e.g. throwing and catching). | |||
* Trauma to the elbow.<br> | |||
== Clinical Presentation == | == Clinical Presentation == | ||
* Lateral elbow pain, aggravted by activity and eased with rest<ref name=":1">John Hopkins Medicine. Panner's Disease. Available from: http://www.hopkinsallchildrens.org/Patients-Families/Health-Library/HealthDocNew/Panner-s-Disease (Accessed 14/10/2022)</ref>. | |||
* Elbow stiffness<ref name=":1" />. | |||
* Elbow swelling<ref name=":1" />. | |||
* <br> | |||
== Diagnostic Procedures == | == Diagnostic Procedures == | ||
[[X-Rays|Plain radiographs]] were used for diagnosing Panner's disease. | |||
Initially the capitulum appears irregular with areas of radiolucency (indicating resorption), particularly adjacent to the articular surface, and sclerosis | |||
- in 3-5 months, radiographs show larger radiolucent areas followed by reconstruction of the bony epiphysis; | |||
- in 1 to 2 years, the epiphysis returns to its normal configuration with no flattening, presumably because the elbow is not weight bearing joint | |||
- in about 50% of patients, adjacent radial head shows early maturation compared with the uninvolved elbow | |||
A ''magnetic resonance imaging'' ([[MRI Scans|MRI]]) scan may show more detail. The MRI can give a better view of bone irregularities and can detect effusion.<br> | |||
== Outcome Measures == | |||
[[DASH Outcome Measure|DASH Outcome measure]] | |||
== | == Management / Interventions == | ||
Symptomatic treatment for Panner's disease is sufficient because epiphysis becomes revascularized & develops normal configuration. Reducing elbow activities and avoiding straining activities can help with pain management and healing process. The use of a long arm splint for 3 to 4 weeks may be necessary until pain, swelling, and local tenderness subside. A cast was recommended for an inconsistent period of time ranging from 4 weeks to 11 months.<ref>Claessen FM, Louwerens JK, Doornberg JN, van Dijk CN, Eygendaal D, van den Bekerom MP. Panner’s disease: literature review and treatment recommendations. Journal of children's orthopaedics. 2015 Feb 1;9(1):9-17.</ref>Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be helpful. | |||
It takes one to two years for the growth plate that makes up the capitellum to grow into solid bone. At this point, pain and symptoms usually go away completely. Treatments such as heat, [[cryotherapy]], and [[Ultrasound therapy|ultrasound]] may be used to ease pain and swelling.<br> | |||
== Differential Diagnosis == | |||
[[Osteochondritis Dissecans|Osteochondritis dissecans]] | |||
== Resources == | |||
[https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1007/s11832-015-0635-2 Panner's disease: Literature review and treatment recommendations] | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
* | |||
== Diagnostic Procedures == | |||
== Outcome Measures == | |||
== Outcome Measures == | |||
== Management / Interventions == | == Management / Interventions == | ||
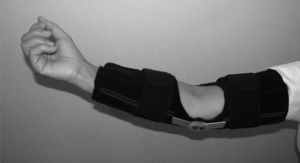
[[File:Elbow brace.jpg|thumb]] | [[File:Elbow brace.jpg|thumb]] | ||
<br> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 11:00, 14 October 2022
Top Contributors - Chloe Waller, Shreya Pavaskar and Vidya Acharya
Definition[edit | edit source]
Panner's disease is bone growth disorder (osteochondrosis) of the humeral capitellum ossification centre, at the lateral aspect of the elbow[1].
It is a rare disease, found most commonly in boys under 10 years old, and in a unilateral presentation[2].
Clinically Relevant Anatomy
[edit | edit source]
The elbow joint is a synovial hinge joint. The three bones that make up the articulation of the joint are: the distal end of the humerus and proximal ends of the radius and ulna. The capitellum is the smooth,rounded lateral aspect of the distal articular surface of the humerus, which articulates with the head of the radius.
Pathological Process[edit | edit source]
If the blood vessels suppyling the nuleus of the capitellum are disrupted, ischemia can occur[2]. This could be due to:
- Repetitive valgus stress (e.g. throwing and catching).
- Trauma to the elbow.
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
- Lateral elbow pain, aggravted by activity and eased with rest[3].
- Elbow stiffness[3].
- Elbow swelling[3].
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
Plain radiographs were used for diagnosing Panner's disease.
Initially the capitulum appears irregular with areas of radiolucency (indicating resorption), particularly adjacent to the articular surface, and sclerosis
- in 3-5 months, radiographs show larger radiolucent areas followed by reconstruction of the bony epiphysis;
- in 1 to 2 years, the epiphysis returns to its normal configuration with no flattening, presumably because the elbow is not weight bearing joint
- in about 50% of patients, adjacent radial head shows early maturation compared with the uninvolved elbow
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan may show more detail. The MRI can give a better view of bone irregularities and can detect effusion.
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
Management / Interventions[edit | edit source]
Symptomatic treatment for Panner's disease is sufficient because epiphysis becomes revascularized & develops normal configuration. Reducing elbow activities and avoiding straining activities can help with pain management and healing process. The use of a long arm splint for 3 to 4 weeks may be necessary until pain, swelling, and local tenderness subside. A cast was recommended for an inconsistent period of time ranging from 4 weeks to 11 months.[4]Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be helpful.
It takes one to two years for the growth plate that makes up the capitellum to grow into solid bone. At this point, pain and symptoms usually go away completely. Treatments such as heat, cryotherapy, and ultrasound may be used to ease pain and swelling.
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
Panner's disease: Literature review and treatment recommendations
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Nordlie H, Rognstad M, Iveland H. Panner's disease. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2021 Jun 24;141(10). English, Norwegian
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Claessen FM, Louwerens JK, Doornberg JN, van Dijk CN, Eygendaal D, van den Bekerom MP. Panner's disease: literature review and treatment recommendations. J Child Orthop. 2015 Feb;9(1):9-17.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 John Hopkins Medicine. Panner's Disease. Available from: http://www.hopkinsallchildrens.org/Patients-Families/Health-Library/HealthDocNew/Panner-s-Disease (Accessed 14/10/2022)
- ↑ Claessen FM, Louwerens JK, Doornberg JN, van Dijk CN, Eygendaal D, van den Bekerom MP. Panner’s disease: literature review and treatment recommendations. Journal of children's orthopaedics. 2015 Feb 1;9(1):9-17.
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
Management / Interventions[edit | edit source]