Vastus Lateralis: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
Abbey Wright (talk | contribs) (spelling mistakes, grammar and general content) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
The vastus lateralis muscle is on the side of the thigh. This muscle is the largest of the quadriceps | The vastus lateralis muscle is located on the lateral side of the thigh. This muscle is the largest of the quadriceps which includes: rectus femoris, vastus intermedius, and vastus medialis. Together, the quadriceps act on the knee and hip to promote movement as well as strength and stability. They provide power for and absorb the impact of daily activities such as walking, running, and jumping.<ref>http://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/vastus-lateralis-muscle</ref> | ||
== Anatomy == | == Anatomy == | ||
=== Origin === | === Origin === | ||
Upper | Upper inter-trochanteric line, base of greater trochanter, lateral linea aspera, lateral supracondylar ridge and lateral intermuscular septum | ||
=== Insertion === | === Insertion === | ||
| Line 24: | Line 22: | ||
=== Blood Supply === | === Blood Supply === | ||
Lateral circumflex femoral artery <ref>http://www.rad.washington.edu/academics/academic-sections/msk/muscle-atlas/lower-body/vastus-lateralis</ref> | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
=== Actions === | === Actions === | ||
1. Extension of the knee | |||
2. Flexion of the hip | |||
=== Functional contributions === | |||
< | In everyday life, the quadriceps muscle group as a whole functions to allow a person to squat, bend backwards, walk up or down stairs, and move from a standing to a seated position (or vice-versa). These muscles are not active while standing with the knees locked, but become active during the heel-strike and toe-off phases of walking.<ref name="www">http://www.triggerpointtherapist.com/blog/knee-pain-trigger-points/vastus-lateralis-trigger-points-quadriceps/</ref> | ||
== | == Assessment == | ||
=== Palpation === | === Palpation === | ||
In supine: | |||
# Place palpating hand distal to greater trochanter | |||
# Get the patient to actively and isometrically contract quadriceps | |||
# Palpate the contracting muscle focusing on the lateral side to target vastus lateralis | |||
# Continue to palpate distally until the quadriceps tendon | |||
=== Length Tension Testing / Stretching === | === Length Tension Testing / Stretching === | ||
| Line 87: | Line 79: | ||
*A tennis ball may be used by a person to treat their TrPs by laying on the side and placing the tennis ball between the outer thigh and the surface of the bed/floor.<ref name="WWW">http://www.triggerpointtherapist.com/blog/knee-pain-trigger-points/vastus-lateralis-trigger-points-quadriceps/</ref> | *A tennis ball may be used by a person to treat their TrPs by laying on the side and placing the tennis ball between the outer thigh and the surface of the bed/floor.<ref name="WWW">http://www.triggerpointtherapist.com/blog/knee-pain-trigger-points/vastus-lateralis-trigger-points-quadriceps/</ref> | ||
*Release by massage | *Release by massage | ||
== References == | |||
== References | |||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] [[Category:Thigh]] [[Category:Muscles]] | [[Category:Anatomy]] | ||
[[Category:Thigh]] | |||
[[Category:Muscles]] | |||
Revision as of 23:11, 18 October 2018
Description[edit | edit source]
The vastus lateralis muscle is located on the lateral side of the thigh. This muscle is the largest of the quadriceps which includes: rectus femoris, vastus intermedius, and vastus medialis. Together, the quadriceps act on the knee and hip to promote movement as well as strength and stability. They provide power for and absorb the impact of daily activities such as walking, running, and jumping.[1]
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Upper inter-trochanteric line, base of greater trochanter, lateral linea aspera, lateral supracondylar ridge and lateral intermuscular septum
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Lateral quadriceps tendon to patella, via ligamentum patellae into tubercle of tibia[2]
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Posterior division of femoral nerve (L3,4)
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
Lateral circumflex femoral artery [3]
Function[edit | edit source]
Actions[edit | edit source]
1. Extension of the knee
2. Flexion of the hip
Functional contributions[edit | edit source]
In everyday life, the quadriceps muscle group as a whole functions to allow a person to squat, bend backwards, walk up or down stairs, and move from a standing to a seated position (or vice-versa). These muscles are not active while standing with the knees locked, but become active during the heel-strike and toe-off phases of walking.[4]
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Palpation[edit | edit source]
In supine:
- Place palpating hand distal to greater trochanter
- Get the patient to actively and isometrically contract quadriceps
- Palpate the contracting muscle focusing on the lateral side to target vastus lateralis
- Continue to palpate distally until the quadriceps tendon
Length Tension Testing / Stretching[edit | edit source]
- Standing [5]
Stand on one leg and pull the other foot up behind your bottom
Keep your knees together and push your hips forwards to increase the stretch
Hold for between 10 and 30 seconds
- Laying
Lay on your front and pull one foot up to meet your buttocks
Hold for between 10 and 30 seconds
Strengthing[edit | edit source]
- Leg extension
Sit on the leg extension machine with your back against the pad and feet under the pads. Place the pads just above the feet.
Curl the legs up until you reach the top position.
Lower weight back to starting position. Lower legs should be vertical to the floor.
- Hack squats
Lay back in the hack squat machine with shoulders place on the pads.
Place feet about shoulder width apart (or where comfortable) with toes pointed out slightly.
Squat down until there is about a 90 degree angle in the knee joint as shown in the illustration.
Push back up until you are back in the starting position.
Repeat for recommended reps.
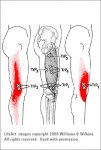
Trigger Point Referral Pattern[edit | edit source]
Pain may be felt over the full length of the lateral anterior (outside and front) thigh as well as behind the knee. Pain is also sometimes reported to feel like explosions up and down the thigh.A person with TrPs in the lateralis may have a stuck patella with pain that wraps up and around the lateral border of the patella and even up the thigh. TrPs in this muscle also make it painful to lie on the affected side and if done so, will disturb sleep.[6]
Management[edit | edit source]
- A tennis ball may be used by a person to treat their TrPs by laying on the side and placing the tennis ball between the outer thigh and the surface of the bed/floor.[7]
- Release by massage
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ http://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/vastus-lateralis-muscle
- ↑ http://www.lumen.luc.edu/lumen/meded/grossanatomy/dissector/mml/vasl.htm
- ↑ http://www.rad.washington.edu/academics/academic-sections/msk/muscle-atlas/lower-body/vastus-lateralis
- ↑ http://www.triggerpointtherapist.com/blog/knee-pain-trigger-points/vastus-lateralis-trigger-points-quadriceps/
- ↑ http://www.teachpe.com/stretching/laying_quads.php
- ↑ http://www.myofascialtherapy.org/symptom-checker/symptomcheck/symptom_leg_lateralis.html
- ↑ http://www.triggerpointtherapist.com/blog/knee-pain-trigger-points/vastus-lateralis-trigger-points-quadriceps/