Spinalis Cervicis: Difference between revisions
Abbey Wright (talk | contribs) (added image) |
Abbey Wright (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
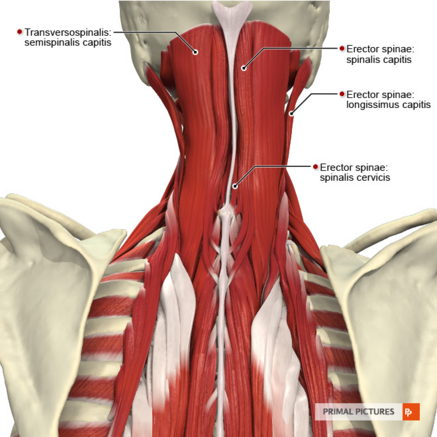
[[File:Muscles of the cervical region intermediate muscles Primal.png|thumb|437x437px]] | [[File:Muscles of the cervical region intermediate muscles Primal.png|thumb|437x437px]] | ||
Spinalis Cervicis belongs to the medial column of the Sacrospinalis group of muscles.<ref name="gray">Gray, Henry. Anatomy of the Human Body. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger, 1918; Bartleby.com, 2000. www.bartleby.com/107/.</ref> | Spinalis Cervicis belongs to the medial column of the [[Erector Spinae|erector spinae]] (Sacrospinalis) group of muscles.<ref name="gray">Gray, Henry. Anatomy of the Human Body. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger, 1918; Bartleby.com, 2000. www.bartleby.com/107/.</ref><ref name=":0">spinalis muscle | anatomy [Internet]. Encyclopedia Britannica. 2021 [cited 30 November 2021]. Available from: https://www.britannica.com/science/spinalis-muscle</ref> | ||
== Origin == | == Origin == | ||
Lower part of ligamentum nuchae (C4 to C6) and spinous process of C7 to T2.<ref name=" | Lower part of ligamentum nuchae (C4 to C6) and spinous process of C7 to T2.<ref name=":0" /><ref name="wh">Spinalis Cervicis : Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics [Internet]. Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics. 2021 [cited 30 November 2021]. Available from: https://www.wheelessonline.com/bones/spine/spinalis-cervicis/</ref> | ||
== Insertion == | == Insertion == | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
== Nerve Supply == | == Nerve Supply == | ||
Posterior rami of cervical and thoracic spinal nerves (C4 to T1). <ref name="wh" /> | |||
== Blood Supply == | == Blood Supply == | ||
Dorsal branches of the posterior intercostal arteries from the thoracic aorta. | Dorsal branches of the posterior intercostal arteries from the thoracic aorta. | ||
== Action == | == Action == | ||
Bilaterally | Bilaterally extend the cervical spine. | ||
Unilaterally laterally flex and rotate the cervical spine to ipsilateral (same) side.<ref name="wh" /> | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Spinalis cervicis works with the other erector spinae muscles to produce extension, lateral flexion and rotation at the cervical spine level. | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 13:08, 30 November 2021
Original Editor Oyemi Sillo
Lead Editors - Abbey Wright, Oyemi Sillo, Kim Jackson, Lucinda hampton, 127.0.0.1 and WikiSysop
Description[edit | edit source]
Spinalis Cervicis belongs to the medial column of the erector spinae (Sacrospinalis) group of muscles.[1][2]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Lower part of ligamentum nuchae (C4 to C6) and spinous process of C7 to T2.[2][3]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
Spinous processes of C2 and sometimes the 3rd and 4th cervical spinous process.[3]
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Posterior rami of cervical and thoracic spinal nerves (C4 to T1). [3]
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
Dorsal branches of the posterior intercostal arteries from the thoracic aorta.
Action[edit | edit source]
Bilaterally extend the cervical spine.
Unilaterally laterally flex and rotate the cervical spine to ipsilateral (same) side.[3]
Function[edit | edit source]
Spinalis cervicis works with the other erector spinae muscles to produce extension, lateral flexion and rotation at the cervical spine level.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Gray, Henry. Anatomy of the Human Body. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger, 1918; Bartleby.com, 2000. www.bartleby.com/107/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 spinalis muscle | anatomy [Internet]. Encyclopedia Britannica. 2021 [cited 30 November 2021]. Available from: https://www.britannica.com/science/spinalis-muscle
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Spinalis Cervicis : Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics [Internet]. Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics. 2021 [cited 30 November 2021]. Available from: https://www.wheelessonline.com/bones/spine/spinalis-cervicis/