Scaphoid: Difference between revisions
Nina Myburg (talk | contribs) (Content changes) |
Nina Myburg (talk | contribs) (Caqtegories and links to other PP pages) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
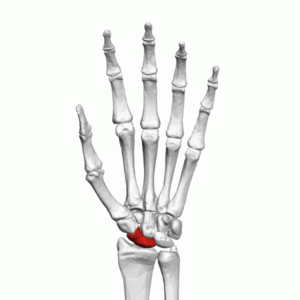
The scaphoid is situated below the radius at the radial (lateral) side of the wrist. It has a boat-like shape with many articulation surfaces. Over 80% of the bone is covered in cartilage. On the palmar surface of the bone, there is a tubercle that can be palpated at the base and medial aspect of the thenar eminence when the hand is extended. <ref name=":1" /> It can also be palpated at the base of the anatomical snuffbox. | The scaphoid is situated below the [[radius]] at the radial (lateral) side of the wrist. It has a boat-like shape with many articulation surfaces. Over 80% of the bone is covered in cartilage. On the palmar surface of the bone, there is a tubercle that can be palpated at the base and medial aspect of the thenar eminence when the hand is extended. <ref name=":1" /> It can also be palpated at the base of the anatomical snuffbox. | ||
[[File:Scaphoid bone (picture of only the bone) - animation1.gif|center|thumb|Scaphoid bone]] | [[File:Scaphoid bone (picture of only the bone) - animation1.gif|center|thumb|Scaphoid bone]] | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
The scaphoid, together with other carpal bones, provide bony structure to the hand and wrist. It is involved in movement of the wrist together with the lunate and distal surfaces of the radius and ulna. It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel and serves as attachment site. | The scaphoid, together with other carpal bones, provide bony structure to the hand and wrist. It is involved in movement of the wrist together with the [[lunate]] and distal surfaces of the [[radius]] and [[ulna]]. It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel and serves as attachment site. | ||
== Articulations == | == Articulations == | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
* Radius (proximally) | * Radius (proximally) | ||
* Trapezoid and trapezium (distally) | * Trapezoid and trapezium (distally) | ||
* Capitate and Lunate (medially) | * [[Capitate]] and [[Lunate]] (medially) | ||
== Soft tissue attachments == | == Soft tissue attachments == | ||
* The transverse carpal ligament attaches to the tubercle of the scaphoid | * The transverse carpal ligament attaches to the tubercle of the [[scaphoid]] | ||
* Sometimes a few fibres of abductor pollicis brevis attaches to the tubercle of the scaphoid | * Sometimes a few fibres of abductor pollicis brevis attaches to the tubercle of the [[scaphoid]] | ||
* The radial collateral ligament attaches to the lateral surface | * The radial collateral ligament attaches to the lateral surface | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
[[Category:Anatomy Project]] | [[Category:Anatomy Project]] | ||
[[Category:Hand and Wrist Anatomy]] | [[Category:Hand and Wrist Anatomy]] | ||
[[Category:Bones of the Wrist]] | |||
Revision as of 14:44, 19 June 2019
Original Editor
Top Contributors - Nina Myburg, Kim Jackson, Chrysolite Jyothi Kommu, Nikhil Benhur Abburi and Vidya Acharya
Description[edit | edit source]
The scaphoid is the largest bone of the proximal row of carpal bones.[1] The word scaphoid is derived from the Greek word skaphos which means "a boat". The name refers to the boat-like shape of the bone. Previously it was called the navicular bone (derived from the Latin word navis which means "boat") of the hand. However, there is a tarsal bone in the foot that is also called navicular due to its boat-like shape. The scaphoid is situated at the radial side of the wrist.[2]
Structure[edit | edit source]
The scaphoid is situated below the radius at the radial (lateral) side of the wrist. It has a boat-like shape with many articulation surfaces. Over 80% of the bone is covered in cartilage. On the palmar surface of the bone, there is a tubercle that can be palpated at the base and medial aspect of the thenar eminence when the hand is extended. [1] It can also be palpated at the base of the anatomical snuffbox.
Function[edit | edit source]
The scaphoid, together with other carpal bones, provide bony structure to the hand and wrist. It is involved in movement of the wrist together with the lunate and distal surfaces of the radius and ulna. It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel and serves as attachment site.
Articulations[edit | edit source]
The scaphoid articulates with five bones:[2]
Soft tissue attachments[edit | edit source]
- The transverse carpal ligament attaches to the tubercle of the scaphoid
- Sometimes a few fibres of abductor pollicis brevis attaches to the tubercle of the scaphoid
- The radial collateral ligament attaches to the lateral surface
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
Clicking of the scaphoid or no anterior translation can indicate scapholunate instability.
See also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Moore KL, Dalley AF. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Fifth edition. Philadelphia: Lippincot Williams & Wilkins; 2006
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Gray H. Anatomy of the Human Body. Twentieth edition. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918 Available from: https://www.bartleby.com/107/54.html [Accessed 19 June 2019]