Sacral Insufficiency Fractures: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
= Examination = | = Examination = | ||
The physical examination shows: | Usually the examination involves: interrogation of the patient, physical examination, sometimes<br>neurological examination, laboratory investigations and finally imaging. (26,27,28)<br>The examination begins with the history of the patient. The patient can report sudden pain in the<br>lower back and pelvic region. This is accompanied with reduction of mobility and independence.<br>Symptoms are worsened by weight bearing activities and are generally improve with rest. These<br>patients usually feel the most comfortable in the supine position. (28)<br>The physical examination shows: [5]<br>● Sacral tenderness (on lateral compression)<br>● SI-joint tests are often positive (this test is not specific for SFI)<br>● Gait is usually slow and antalgic<br>● [http://www.physio-pedia.com/Trendelenburg_Test Trendelenburg test] is usually normal<br>● Sciatic nerve tension test (Lasegue and [http://www.physio-pedia.com/Straight_Leg_Raise_Test Straight Leg Raise (SLR)]) is usually normal<br>Other clinical test that may aid the diagnosis of sacral insufficiency fractures : Hip flexionabduction-external<br>rotation test ([http://www.physio-pedia.com/FABER_Test FABER test]), [http://www.physio-pedia.com/Gaenslen_Test Gaeslen’s test] and Squish test. These tests are not<br>specific for SIF but may indicate a pathology on the sacroiliac joint.(28)<br>The neurological examination is often normal.(28)<br>Laboratory investigations can also be done. Bone alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is a marker of bone<br>formation. The serum levels of ALP are often lightly raised in patients with SIF.<br>(28)<br> | ||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
= Physical Therapy Management = | = Physical Therapy Management = | ||
Revision as of 14:03, 16 May 2016
Search Strategy[edit | edit source]
Keywords:
● Sacral insufficiency fractures
● SIF
● Physical therapy OR Physiotherapy OR Exercise OR Treatment
● Mobilization
● Hydrotherapy OR Aquatherapy
● Medical management AND SIF
● SIF AND examination
Databases:
● Pubmed
● Web of Knowledge
● PEDro
● Google scholar
● Google
Definition/Description[edit | edit source]
Sacral insufficiency fractures (SIFs) are a cause of low back pain.[1]
They are a subtype of stress fractures, resulting from normal stress applied to a bone with reduced
elasticity.[2] [3]
An underlying condition, like osteoporosis or another metabolic bone disease, is often a cause of
SIFs. This is why SIFs are more common with elderly women.[2] [3][4] Bone insufficiency fractures
in general are described first by Laurie in 1982.[3][4]
During the gait, alternating flexion and extension of the lower limbs would impart alternating
twisting forces on the pelvis around its lowest transverse axis. This effect can be shown in a
pretzel-model. When we hold a pretzel in two hands and twist it around its long axis in alternating
directions, the pretzel will snap eventually. This is what happens clinically with the sacrum during
insufficiency fractures.
As previously mentioned, this happens most frequently with elderly women, whose sacroiliac joint
is relatively ankylosed and whose sacrum has been weakend by osteoporosis. Under these
conditions, the torsional stress which is normally buffered by the sacroiliac joint, will be transferred
to the sacrum. Because of the conditions of the weakend sacrum, it fails to buffer the torsional
stress and fractures occur. In most cases, these fractures run vertically through the ala of the
sacrum parallel to the sacroiliac joint.(33)
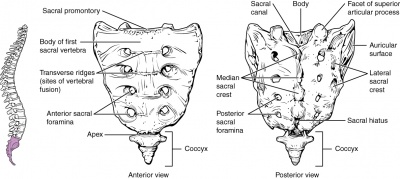
Clinically Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The sacrum is a triangular bone formed by 5 vertebral segments. It is broader on the superior side
than on the inferior, and broader on the anterior side than on the posterior side, allowing the
sacrum to resist shearing from vertical compression (36) as well as transfer loads from the spinal
column to the pelvis.(37)
The sacrum articulates superiorly with the fifth lumbar vertebra and inferiorly with the coccyx. The
lateral surface of the upper part of the lateral masses (auricular surface) articulates with the
ilium.[5]
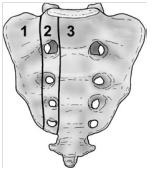
Denis et al classified traumatic sacral fractures by dividing the sacrum into 3 zones (Fig.1).This
classification system is based on the direction, the localisation and the level of the fracture.(36)
These traumatic fractures are not directly related to SIFs, but the classification system of Denis is
very useful for the description of these SIFs.[5]
Zone 1: involves the sacral ala (lateral to the sacral foramina). This is the most common area of SIFs.
Zone 2: involves the sacral (neural) foramina (but the fracture does not enter the central sacral
canal). The fractures in this site are associated with unilateral lumbosacral radiculopathies.
Zone 3: involves the sacral bodies and the transverse central canal.[2] [5]
Epidemiology /Etiology[edit | edit source]
The most important cause of SIF is osteoporosis.[2] [3] [6] [4]
Other risk factors are:
● Pelvic radiation
● Steroid-induced osteopenia [4]
● Rheumatoid arthritis [6]
● Multiple myeloma
● Paget disease [4]
● Renal osteodystrophy (13)
● Hyperparathyroidism [2] [7] [3] [4]
● Corticosteroid medication [2] [3]
● Metastatic disease [2] [3]
● Marrow replacement processes [2] [3]
● Fibrous dysplasia [7]
● Osteogenesis imperfecta [7]
● Osteopetrosis [7]
● Osteomalacia [7]
● Development of osteolysis (12)
● Radiotherapy (13)
● Diabetes mellitus (13)
● Primary biliary cirrhosis (13)
Patients with SIFs are most often women, over the age of 55, where the illness frequently occurs on both sides of the body.(17) The bone strength of these patients is inadequate to withstand normal repetitive stress (19). The average age of these patients suffering from multiple illnesses (of symptoms) (14) is between 70 and 75 years old.
The precise incidence of SIFs is unknown but some studies reported a prevalence of 1% - 5% in
at-risk patient populations. Two-third of the patients were a-traumatic. [2]
SIF can also occur to younger people, for example pregnant women. This type of SIF can be
related to pregnancy-associated osteoporosis. [7]
Characteristics/Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Patients with SIFs may have:
● Tenderness on palpation (lower back and sacral region) [2] [8] [3] [6]
● Pain (at the buttock, low back, hip, pelvic or groin) [9] (12)
● Problems with walking (slowly and painful)
● Nerve damages (unusual) [2] [3]
● Mobility difficulties (12)
● Leg weaknesses (18)
● Parasymphyseal tenderness (suggesting associated pubic ramus fracture) (11)
● Elevated alkaline phosphatase (11)
● Plain radiograph showing pubic ramus fractures or parasymphyseal sclerosis (11)
Patients with this complications generally have a poor prognosis.[11]
Differential Diagnosis
[edit | edit source]
Sacral insufficiency fractures are difficult to diagnose because the signs and symptoms are
vague and non-specific. SIF’s can be mistaken for :
● Metastatic disease [3]
● Radiculopathy [2]
A condition due to a compressed nerve in the spine that can cause pain, numbness,
tingling, or weakness along the course of the nerve. (21)
● Disc disease
● Spinal stenosis
A narrowing of the open spaces within the spine, which can put pressure on the spinal
cord. (24)
● Cauda equina syndrome
Refers to a dysfunction of the cauda equina, the collection of ventral and dorsal lumbar,
sacral and coccygeal nerve roots that surround the filum terminale. (23)
● Osteodegenerative diseases (history of trauma) (13)
Diagnostic Procedures
[edit | edit source]
SIF can be diagnosed using radiology. Bone scintigraphy/scan(16) is the most accurate test to detect SIFs. Another radiographic procedure that can help to diagnose SIF’s is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which is considered as a more sensitive diagnostic tool. (19, 20). There is also single-photon emission-computed tomography with low-dose computed tomography (CT) which
reveals the correct diagnosis. (22)
Difficulties in the diagnostic process and the validity of imaging techniques are highlighted. (18) First of all, the exact locations of sacral insufficiency fractures were catalogued and compared to sacral anatomy. Then, different routine activities were simulated by pelvic models from CT scans of the pelvis and limited element analysis. Analyses were done to correlate areas of stress with activities within the sacrum and pelvis, and these analyses are then compared with patterns of sacral insufficiency fractures. (15)
Examination[edit | edit source]
Usually the examination involves: interrogation of the patient, physical examination, sometimes
neurological examination, laboratory investigations and finally imaging. (26,27,28)
The examination begins with the history of the patient. The patient can report sudden pain in the
lower back and pelvic region. This is accompanied with reduction of mobility and independence.
Symptoms are worsened by weight bearing activities and are generally improve with rest. These
patients usually feel the most comfortable in the supine position. (28)
The physical examination shows: [5]
● Sacral tenderness (on lateral compression)
● SI-joint tests are often positive (this test is not specific for SFI)
● Gait is usually slow and antalgic
● Trendelenburg test is usually normal
● Sciatic nerve tension test (Lasegue and Straight Leg Raise (SLR)) is usually normal
Other clinical test that may aid the diagnosis of sacral insufficiency fractures : Hip flexionabduction-external
rotation test (FABER test), Gaeslen’s test and Squish test. These tests are not
specific for SIF but may indicate a pathology on the sacroiliac joint.(28)
The neurological examination is often normal.(28)
Laboratory investigations can also be done. Bone alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is a marker of bone
formation. The serum levels of ALP are often lightly raised in patients with SIF.
(28)
Physical Therapy Management[edit | edit source]
Early rehabilitation and moderate weight-bearing exercises, within the boundaries of pain tolerance, have been suggested. Earlier rehabilitation will stimulate the bone formation by the osteoblasts and improve muscle tension.
Mobilization is recommended because long periods of immobilization can result in complications (deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolus, loss of muscle strength, etc.). In the earlier stages of fracture healing, mobilization can be assisted by the use of external devices (e.g. walking frames) or hydrotherapy as these are typically tolerated better by many patients. [1]
Resources[edit | edit source]
http://www.artrose-blog.nl/rugaandoeningen/insufficientiefracturen-van-het-sacrum
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedTsiridis