STarT Back Screening Tool: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== PubMed Feed == | == PubMed Feed == | ||
<div class="researchbox"><rss>http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=1Zorz_P_0HTGarrIzdnDmc6Sx7a15bKoJU_UbhbtdqHOkHxshx|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10</rss></div> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 17:43, 17 August 2013
Original Editor - Alistair James
Top Contributors - Alistair James, Kim Jackson, Admin, Simisola Ajeyalemi, Tony Lowe, Elaine Lonnemann, Tarina van der Stockt, WikiSysop, Jess Bell and 127.0.0.1
Images[edit | edit source]
Objective
[edit | edit source]
The Keele STarT Back Screening Tool (SBST) (9-item version) is a brief validated tool, designed to screen primary care patients with low back pain for prognostic indicators that are relevant to initial decision making (Keele University n. d.).
Intended Population
[edit | edit source]
Primary care patients with low back pain (Keele University n. d.).
Method of Use
[edit | edit source]
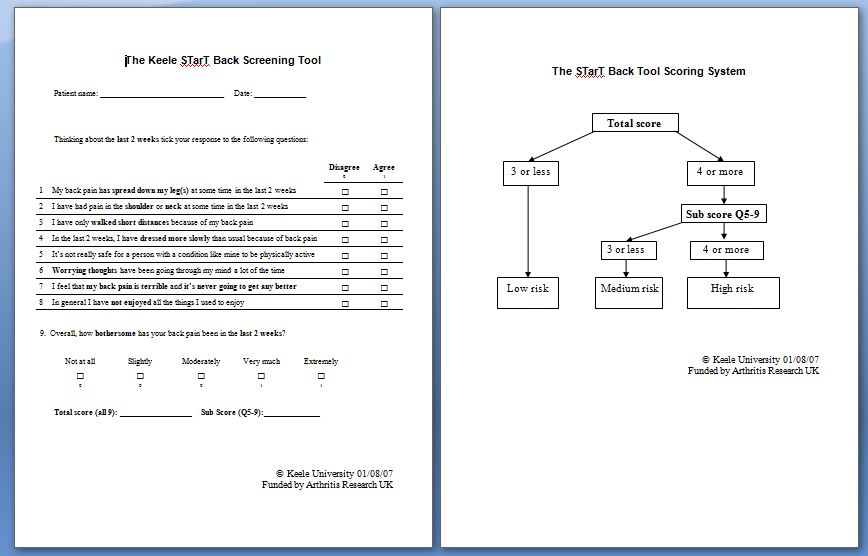
The STarT Back Screening Tool helps primary care clinicans (GPs, physiotherapists etc) to group patients into three categories of risk of poor outcome (persistent disabling symptoms) - low, medium, and high-risk. By being able to categorise patients into these 3 groups, clinicians are then able to target interventions to each sub-group of patients to help outcome (Keele University n.d).
The STarT Back Screening Tool is availalbe in a number of languages including: English, Dutch, French, Spanish, Danish and Welsh (Keele University n.d). The tool produces two scores: overall scores and distress subscale scores (Hill et al. 2008).
- The distress subscale score is used to identify the high-risk subgroup. To score this subscale add the last 5 items; fear, anxiety, catastrophising, depression and bothersomeness (bothersomeness responses are positive for 'very much' or 'extremely' bothersome back pain). Subscale scores range from 0 to 5 with patients scoring 4 or 5 being classified into the high-risk subgroup (Keele University n.d).
- The overall score is used to seperate the low risk patients from the medium-risk subgroups. Scores rnage from 0-9 and are produced by adding all positive items; patients who achieve a score of 0-3 are classified into the low-risk subgroup and those with scores of 4-9 into the medium-risk subgroup (Keele University n.d).
Evidence[edit | edit source]
The STarT Back trial (Hill et al. 2011) compared the clinical and cost effectivness of stratified management approach; allocating patients to different treatment pathways based on thier prognosis (low, medium, or high risk of poor outcome); with that of current best practice. The trial demonstrated that this new model results in greater health benefits, achieved at a lower average health-care cost, with an average saving to health services of £34.39 per patient and societal savings of £675 per patient (Keele University n.d).
Links[edit | edit source]
Keele STarT Back Screening Tool website: http://www.keele.ac.uk/sbst/
Download the Tool: http://www.keele.ac.uk/sbst/downloadthetool/
Related Research[edit | edit source]
- Beneciuk, J. M., Bishop, M. D., Fritz, J. M., Robinson, M. E., Asal, N. R., Nisenzon, A. N. and George, S. Z. (2012) 'The STarT Back Screning Tool and individual psychological measures: evaluation of prognostic capabilities for low back pain clinical outcomes in outpatient physical therapy settings' Physical Therapy
- Bruyere, O., Demoulin, M., Brereton, C., Humblet, F., Flynn, D., Hill, J. C., Maquet, D., Beveren, J. V., Reginster, J., Crielaard, J. and Demoulin, C. (2012) 'Translation validation of a new back pain screening questionnaire (the STarT Back Screening Tool) in French' Archives of Public Health [online] 70, (12). Availalbe form <http://www.archpublichealth.com/content/pdf/0778-7367-70-12.pdf> [29 July 2013]
- del Pozo-Cruz, B., Parraca, J. A., del Pozo-Cruz, J., Adsuar, J. C., Hill, J. C. and Gusi, N. (2012) 'An occupational, internet-based intervnetion to prevent chronicity in subacute lower back pain: a randomized controlled trial' Journal of Rehabilitation Medcine 44, (7) 581-587
- Field, J. and Newell, D. (2012) 'Relationship between STarT Back Screening Tool and prognosis for low back pain patients recieving spinal manipulative therapy' Chiropractic & Manual Therapies 20, (1) 17.
- Foster, N. E., Mullis, R., Young, J., Doyle, C., Lewis, M., Whitehurst, D. and Hay, E. M. (2010) 'Implementation of subgrouping for targeted treatment systems for low back pain patients in primary care: a prospective popualtion-based sequential comparison' BMC Musculoskeletal Disorder 20, (11) 186.
- Fritz, J. M., Beneciuk, J. M. and George, S. Z. (2011) 'Relationship between categorization with the STarT Back Screening Tool and prognosis for people receiving physical therapy for low back pain' Physical Therapy [online] 91, (5) 722-732. Availalbe from <http://ptjournal.apta.org/content/91/5/722
- Foster, N. E. and Delitto, A. (2011) 'Embedding psychological perspectives within clinical management of low back pain: integration of psychosocially informed management principles into physical therapist practice-challenges and opportuities' Physical Therapy [online] 91, (5) 790-803. Availalbe from <http://ptjournal.apta.org/content/91/5/790> [29 July 2013]
- Hay, E., Dunn, K., Hill, J., Lewis, M., Mason, E., Konstantinou, K., Sowden, G., Somerville, S., Vohora, K., Whitehurst, D. and Main, C. (2008) 'A randomised clinical trial of subgrouping and targeted for low back pain compared with best current care. The STarT Back Trail Study Protocol' BMJ Musculoskeletal Disorders [online] 9 58-66. Availalble from <http://www.biomedcentral.com/content/pdf/1471-2474-9-58.pdf> [24 July 2013]
- Hill, J. C., Dunn, K. M., Lewis, M., Mullis, R., Main, C. J., Foster, N. E. and Hay, E. M. (2008) 'A primary care back pain screening tool: identifying patient subgroups for initial treatment' Arthritis Care & Research [online] 59, (5) 632-641. Availalbe from <http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/art.23563/full> [23 July 2013]
- Hill, J. C., Dunn, K. M., Main, C. J. and Hay, E. M. (2012) 'Subgrouping low back pain: a comparison of the STarT Back Tool with the Orebro Musculoskeletal Pain Screening Questionnaire' European Journal of Pain [online] 14, (1) 83-89. Availalbe from <http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1016/j.ejpain.2009.01.003/abstract> [23 July 2013]
- Hill, J. C., Foster, N. E. and Hay, E. M. (2010) 'Cognitive behavioural therapy shown to be an effective and low cost treatment for subacute and chronic low-back pain, improving pain and disability scores in a pragmatic RCT' Evidence Based Medicine 15, (4) 118-119.
- Hill, J. C. and Fritz, J. M. (2011) 'Pschosocial influences on low back pain, disability, and response to treatment'Physical Therapy [online] 91 712-721. Availalbe from <http://ptjournal.apta.org/content/91/5/712.abstract> [24 July 2013]
- Hill, J. C. (2010) 'The early identification of patients with complex back pain problems' The Back Care Journal [online] Spring Availalbe from <http://content.yudu.com/Library/A1ns0p/BackCareSpring2010/resources/index.htm?referrerUrl=http%3A%2%2Fwww.yudu.com%2Fitem%2Fdetails%2F164377%2FBackCare-Spring-2010> [24 July 2013]
- Hill, J. C., Vohora, K., Dunn, K. M., Main, C. J. and Hay, E. M. (2010) 'Comparing the STarT Back Screening Tool's subgroup allocation of individual patients with that of independent clinical experts' Clinical Journal of Pain [online] 26, (9) 783-787. Availalbe from <http://journals.lww.com/clinicalpain/pages/articleviewer.aspx?year=2010&issue=11000&article=00008&type=abstract> [29 July 2013]
- Hill, J. C., Whitehurst, D. G., Lewis, M., Bryan, S., Dunn, K. M., Foster, N. E., Konstantinou, K., Main, C. J., Mason, E., Somerville, S., Sowden, G., Vohora, K. and Hay, E. M. (2011) 'Comparison of stratified primary care management for low back pain with curent best ractice (STarT Back): a randomised controlled trial' Lancet [online] 378, (9802) 1560-1571. Availalbe from <http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21963002> [29 July 2013]
- Kongsted, A., Johannesen, E. and Leboeuf-Yde, C. (2011) 'Feasibility of the STarT Back Screening Tool in chiropractic clinics: a cross-sectional study of patients with low back pain' Chiropractic & Manual Therapies 19, (1) 10.
- Main, C. and George, S. (2011) 'Psychologically informed practice for management of low back pain: future directions in practice and research' Physical Therapy [online] 91, (5) 820-824. Availalbe from <http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21451091> [29 Juy 2013]
- Main, C. J., Sowden, G., Hill, J. C., Watson, P. J. and Hay, E. M. (2012) 'Integrating physical and psychological approaches to treatment in low back pain: the development and content of the STarT Back trial's 'high risk' intervention (StarT Back; ISRCTN 37113406)' Physiotherapy [online] 98, (2) 110-116. Availalbe from <http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031940611004202> [29 July 2013]
- Morso, L., Albert, H., Kent, P., Manniche, C. and Hill, J. (2011) 'Translation and discriminative validation of the STarT Back Screening Tool into Danish' European Spine Journal [online] 20, (12) 2166-2173. Availalbe from <http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs00586-011-1911-6> [29 July 2013]
- Sowden, G., Hill, J. C., Konstantinou, K., Khanna, M., Main, C. J., Salmon, P., Somerville, S., Wathall, S. and Foster, N. E. (2011) 'Subgrouping for targeted treatment in primary care for low back pain: the treatment system and clinical training programmes used in the IMPaCT Back study (ISRCTN 55174281)' Family Practice [online] 0 1-13. Availalbe from <http://fampra.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2011/06/27/fampra.cmr037.full.pdf+html> [29 July 2013]
- Whitehurst, D. G., Bryan, S., Lewis, M., Hill, J. and Hay, E. M. (2012) 'Exploring the cost-utility of stratified primary care management for low back pain compared with current best practice within risk-defined subgroups' Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 71, (11) 1796-1802.
- Widerman, T. H., Hill, J. C., Main, C. J., Lewis, M., Sullivan, M. J. and Hay, E. M. (2012) 'Comparing the responsiveness of a brief, multidimensional risk screening tool for back pain to its unidimensional reference standards: the whole is greater than the sum of its parts' Pain 152 (11) 2182-2191
PubMed Feed[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- Hill, J. C., Dunn, K. M., Lewis, M., Mullis, R., Main, C. J., Foster, N. E. and Hay, E. M. (2008) 'A primary care back pain screening tool: identifying patient subgroups for initial treatment' Arthritis Care & Research [onine] 59, (5) 632-641. Available from <http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/art.23563/full> [29 July 2013]
- Hill, J. C., Whitehurst, D. G., Lewis, M., Bryan, S., Dunn, K. M., Foster, N. E., Konstantinou, K., Main, C. J., Mason, E., Somerville, S., Sowden, G., Vohora, K. and Hay, E. M. (2011) 'Comparison of stratified primary care management for low back pain with current bset practice (STarT Back): a randomised controlled trial' Lancet [online] 378, (9802) 1560-1571. Available from <http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21963002> [29 July 2013]
- Keele University (n. d.) STarT Back Screening Tool Website [online] available from <http://www.keele.ac.uk/sbst/> [23 July 2013]