Partial Knee Replacement: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
[[Image:Pkr 1.jpg|250x250px]][[Image:PKR 2.png|250x250px]][[Image:PKR 3.png|250x250px]][[Image:PKR-4.png|250x250px]]<br> | [[Image:Pkr 1.jpg|250x250px]][[Image:PKR 2.png|250x250px]][[Image:PKR 3.png|250x250px]][[Image:PKR-4.png|250x250px]]<br> | ||
*Unicondylar Knee Replacement is a procedure that replaces only the single affected compartment of the knee, either the medial or lateral compartment. | *Unicondylar Knee Replacement is a procedure that replaces only the single affected compartment of the knee, either the medial or lateral compartment. | ||
*Patellofemoral Knee Replacement is a procedure that replaces the worn patella (the kneecap) and the trochlea (the groove at the end of the thighbone). | *Patellofemoral Knee Replacement is a procedure that replaces the worn patella (the kneecap) and the trochlea (the groove at the end of the thighbone). | ||
*Bicompartmental Knee Replacement is a procedure that replaces two compartments of the knee, the medial and patellofemoral compartments. | *Bicompartmental Knee Replacement is a procedure that replaces two compartments of the knee, the medial and patellofemoral compartments. | ||
Revision as of 18:18, 9 February 2017
Original Editor - Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page.
Top Contributors - Venugopal Pawar, Ahmed Nassef, Kim Jackson, Lucinda hampton, Leana Louw, Lauren Lopez, 127.0.0.1, Admin, Selena Horner, George Prudden and WikiSysop
Description
[edit | edit source]
A partial knee replacement (PKR) is a surgical procedure to replace only one part of a damaged knee. It can replace either the inside (medial) part, the outside (lateral) part, or the kneecap (Patellofemoral) part of the knee.
With PKR, only the damaged area of the knee joint is replaced, which may help to minimize trauma to healthy bone and tissue, and also helps relieve arthritis in on or two of the three compartments of the knee.
Surgery to replace the whole knee joint is called total knee replacement.
Indication
[edit | edit source]
Partial Knee Replacement is intended for use in individuals with joint disease resulting from Degenerative, Rheumatoid and Post traumatic arthritis, and for moderate deformity of the Knee.
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the clinical presentation of the condition
Diagnostic Tests[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to diagnostic tests for the condition
Pre-Op[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the pre-operative advice
Surgical Procedure & Types of Partial Knee Replacement.[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to post-operative rehabilitation
Types:[edit | edit source]
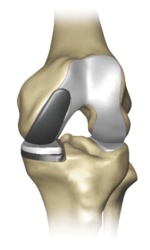
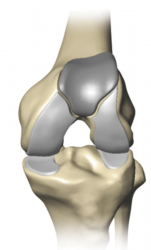
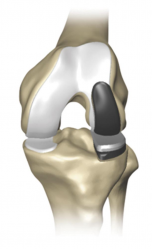
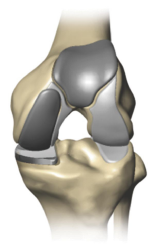
MEDIAL PATELLOFEMORAL LATERAL BICOMAPRMENTAL
- Unicondylar Knee Replacement is a procedure that replaces only the single affected compartment of the knee, either the medial or lateral compartment.
- Patellofemoral Knee Replacement is a procedure that replaces the worn patella (the kneecap) and the trochlea (the groove at the end of the thighbone).
- Bicompartmental Knee Replacement is a procedure that replaces two compartments of the knee, the medial and patellofemoral compartments.
[edit | edit source]
Contra-indications & Common side-effects Key Evidence[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to key evidence with regards to any of the above headings
- Partial Knee EReplacement surgery is not appropriate for patienst with certain types of Infections, any mental or Nueromuscular disorder which would create an unacceptable risk of prosthesis instability, prosthesis fixation failure or complication in postoperative care, skeletal immaturity, severe instability of the knee or Excessive body weight.
- Comom side effects:as with any surgery, PKR has its risks which may be Implant related risks which may lead to a revision include dislocation, loosening, fracture, nerve damage, heterotropic ossification, wear of the implant, metal sensitivity, soft tissue imbalance, osteolysis(localized progressive bone loss) and reaction to particle debris.
- Knee implants may not provide the same feel or performance characteristics experienced with a normal healthy joint.
Resources
[edit | edit source]
add appropriate resources here
Case Studies[edit | edit source]
add links to case studies here (case studies should be added on new pages using the case study template)
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Extension:RSS -- Error: Not a valid URL: Feed goes here!!|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.