Lunate: Difference between revisions
Nina Myburg (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{subst:Bones}}") |
m (link changed to updated page) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | <div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Nina Myburg|Nina Myburg]] '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | ||
'''Original Editor''' | == Description == | ||
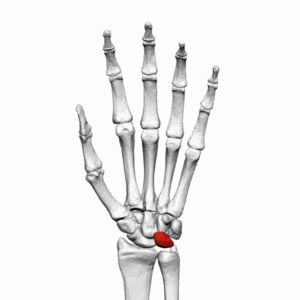
The lunate is one of eight carpal bones that form part of the wrist joint. It is situated in the center of the proximal row of carpal bones. The word lunate is derived from the Latin word ''luna'' which means "crescent-shaped" or ("moon), The bone's shape resembles that of a crescent moon.<ref name=":0">Gray H. ''[https://www.bartleby.com/107/54.html Anatomy of the Human Body].'' Twentieth edition. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918 Available from: https://www.bartleby.com/107/54.html [Accessed 19 June 2019] </ref> | |||
[[File:Lunate bone (left hand) - animation01.gif|center|thumb|Lunate bone (Left hand) - Animation]] | |||
''' | == Structure == | ||
</ | The lunate It is situated in the center of the proximal row of the carpal bones between the [[scaphoid]] and [[triquetrum]].<ref>Moore KL, Dalley AF. ''Clinically Oriented Anatomy.'' Fifth edition. Philadelphia: Lippincot Williams & Wilkins; 2006</ref> It is crescent-shaped with a few articulation surfaces. The lunate is stabilised by a ligament to the [[scaphoid]] and a ligament to the [[triquetrum]]. Ligaments between the [[radius]] and lunate also stabilise the position of the lunate, | ||
[[File:Lunate bone (left hand) - animation02.gif|center|thumb|Lunate Bone - Animation]] | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
The carpal bones function as a unit to provide bony structure to the [[Wrist and Hand|hand and wrist.]] As a proximal carpal bone, the lunate together with the scaphoid, radius and [[ulna]] is also involved in movement of the wrist. | |||
== Articulations == | |||
The lunate articulates with five bones: the [[radius]] proximally, [[capitate]] and [[hamate]] distally, [[scaphoid]] laterally, and [[triquetrum]] medially.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== | == Clinical Relevance == | ||
An infrequent condition which results due to loss of blood supply resulting in avascular necrosis of lunate known as [[Kienbock's Disease|Kienbock's disease]] is identified in some individuals. | |||
== | ==== Signs and symptoms ==== | ||
* Wrist pain | |||
* Tenderness directly over the lunate bone | |||
* Decreased motion or stiffness of the wrist | |||
* Swelling | |||
== | == See also == | ||
* [[Lunate Instability]] | |||
* [[Lunotriquetral Ligament]] | |||
* [[Lunotriquetral dissociation]] | |||
= References = | = References = | ||
| Line 26: | Line 33: | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] [[Category:Bones]] | [[Category:Anatomy]] | ||
[[Category:Wrist - Anatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Wrist - Anatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Bones]] | |||
[[Category:Wrist - Bones]] | |||
[[Category:Wrist]] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:01, 20 December 2022
Description[edit | edit source]
The lunate is one of eight carpal bones that form part of the wrist joint. It is situated in the center of the proximal row of carpal bones. The word lunate is derived from the Latin word luna which means "crescent-shaped" or ("moon), The bone's shape resembles that of a crescent moon.[1]
Structure[edit | edit source]
The lunate It is situated in the center of the proximal row of the carpal bones between the scaphoid and triquetrum.[2] It is crescent-shaped with a few articulation surfaces. The lunate is stabilised by a ligament to the scaphoid and a ligament to the triquetrum. Ligaments between the radius and lunate also stabilise the position of the lunate,
Function[edit | edit source]
The carpal bones function as a unit to provide bony structure to the hand and wrist. As a proximal carpal bone, the lunate together with the scaphoid, radius and ulna is also involved in movement of the wrist.
Articulations[edit | edit source]
The lunate articulates with five bones: the radius proximally, capitate and hamate distally, scaphoid laterally, and triquetrum medially.[1]
Clinical Relevance[edit | edit source]
An infrequent condition which results due to loss of blood supply resulting in avascular necrosis of lunate known as Kienbock's disease is identified in some individuals.
Signs and symptoms[edit | edit source]
- Wrist pain
- Tenderness directly over the lunate bone
- Decreased motion or stiffness of the wrist
- Swelling
See also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Gray H. Anatomy of the Human Body. Twentieth edition. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918 Available from: https://www.bartleby.com/107/54.html [Accessed 19 June 2019]
- ↑ Moore KL, Dalley AF. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Fifth edition. Philadelphia: Lippincot Williams & Wilkins; 2006