Lateral Epicondyle Tendinopathy Toolkit: Section H - Braces, Splints, and Taping: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
== Counterforce Brace == | == Counterforce Brace == | ||
<div class="flex-row row"> | <div class="flex-row row"> | ||
<div class="col-md-8"> | <div class="col-md-8"> | ||
| Line 27: | Line 25: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
A counterforce brace is one of the most conventional treatments. The mechanism of action for this brace is the transferring of stress from the wounded tissue to the unaffected tissues around it. A combined cadaveric and clinical study<ref>Meyer NJ, Walter F, Haines B, Orton D, Daley RA. [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12671861/ Modeled evidence of force reduction at the extensor carpi radialis brevis origin with the forearm support band.] The Journal of hand surgery. 2003 Mar 1;28(2):279-87.</ref> showed a 13-15% force reduction of the [[Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis]] origin with the counterforce brace. | |||
* They are often used for pain relief. | * They are often used for pain relief. | ||
* They are thought to diffuse the load through the tendon to less sensitive areas, thereby decreasing the stress on the area of pathology. | * They are thought to diffuse the load through the tendon to less sensitive areas, thereby decreasing the stress on the area of pathology. | ||
== Wrist Splint == | == Wrist Splint == | ||
<div class="flex-row row"> | <div class="flex-row row"> | ||
<div class="col-md-8"> | <div class="col-md-8"> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 41: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Wrist splints reduces tension and load at the extensor origin, thus promoting tendon repair. | |||
* Wrist splints are less commonly used in the Lateral Epicondyle Tendinopathy. | * Wrist splints are less commonly used in the Lateral Epicondyle Tendinopathy. | ||
* But they do have some support for temporary pain relief in more acute patients. | * But they do have some support for temporary pain relief in more acute patients. | ||
| Line 44: | Line 48: | ||
== Diamond Taping Technique == | == Diamond Taping Technique == | ||
<div class="flex-row row"> | |||
<div class="col-md-8"> | <div class="col-md-8"> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 52: | Line 56: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Taping provides support and stability for the preventing injury as well as it protects the injured anatomical structure during healing. | |||
* The goal is to decrease tension at the epicondyle attachment. | * The goal is to decrease tension at the epicondyle attachment. | ||
* Diamond Taping Technique <ref>Vicenzino B, Brooksbank J, Minto J, Offord S, Paungmali A. [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12918865/ Initial effects of elbow taping on pain-free grip strength and pressure pain threshold.] Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy. Jul 2003; 33(7): 400-7.</ref>consists of four tape strips, repeated twice. | * Diamond Taping Technique <ref>Vicenzino B, Brooksbank J, Minto J, Offord S, Paungmali A. [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12918865/ Initial effects of elbow taping on pain-free grip strength and pressure pain threshold.] Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy. Jul 2003; 33(7): 400-7.</ref>consists of four tape strips, repeated twice. | ||
* The tape is laid in a diamond shape while pulling the soft tissues centrally towards the lateral epicondyle. | * The tape is laid in a diamond shape while pulling the soft tissues centrally towards the lateral epicondyle. | ||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
*Click to go back to the [[Lateral Epicondyle Tendinopathy (Tennis Elbow) Toolkit|Lateral Epicondyle Tendinopathy Toolkit page]] | *Click to go back to the [[Lateral Epicondyle Tendinopathy (Tennis Elbow) Toolkit|Lateral Epicondyle Tendinopathy Toolkit page]] | ||
Revision as of 15:16, 28 October 2022
Original Editor - Vidya Acharya for BC Physical Therapy Tendinopathy Task Force:
Dr. Joseph Anthony, Paul Blazey, Dr. Allison Ezzat, Dr. Angela Fearon, Diana Hughes, Carol Kennedy, Dr. Alex Scott, Michael Yates and Alison Hoens
Top Contributors - Vidya Acharya, Kim Jackson, Evan Thomas, Admin, Wanda van Niekerk, Rishika Babburu and 127.0.0.1
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Various methods have been developed to treat lateral epicondyle tendinopathy that includes brace, splints and taping. It has been found that splinting, bracing, and taping are useful interventions for protecting, stabilising, or immobilising injured or inflamed areas.
Counterforce Brace[edit | edit source]
A counterforce brace is one of the most conventional treatments. The mechanism of action for this brace is the transferring of stress from the wounded tissue to the unaffected tissues around it. A combined cadaveric and clinical study[1] showed a 13-15% force reduction of the Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis origin with the counterforce brace.
- They are often used for pain relief.
- They are thought to diffuse the load through the tendon to less sensitive areas, thereby decreasing the stress on the area of pathology.
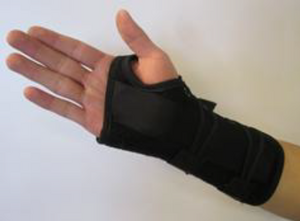
Wrist Splint[edit | edit source]
Wrist splints reduces tension and load at the extensor origin, thus promoting tendon repair.
- Wrist splints are less commonly used in the Lateral Epicondyle Tendinopathy.
- But they do have some support for temporary pain relief in more acute patients.
- The goal is to rest the musculotendinous unit originating at the lateral epicondyle.
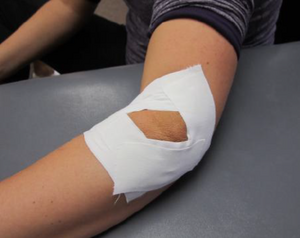
Diamond Taping Technique[edit | edit source]
Taping provides support and stability for the preventing injury as well as it protects the injured anatomical structure during healing.
- The goal is to decrease tension at the epicondyle attachment.
- Diamond Taping Technique [2]consists of four tape strips, repeated twice.
- The tape is laid in a diamond shape while pulling the soft tissues centrally towards the lateral epicondyle.
Resources[edit | edit source]
- Click to go back to the Lateral Epicondyle Tendinopathy Toolkit page
- Click to continue to Section B - Clinical Assessment of LET
- Click to continue to Section C - Outcome Measures
- Click to continue to Section D - Summary of the Evidence
- Click to continue to Section E - Exercise Prescription
- Click to continue to Section G - LASER Dosage Calculation
- Click to continue to Section F - Manual Therapy
- UBC Lateral Epicondyle Tendinopathy (LET) Toolkit
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Meyer NJ, Walter F, Haines B, Orton D, Daley RA. Modeled evidence of force reduction at the extensor carpi radialis brevis origin with the forearm support band. The Journal of hand surgery. 2003 Mar 1;28(2):279-87.
- ↑ Vicenzino B, Brooksbank J, Minto J, Offord S, Paungmali A. Initial effects of elbow taping on pain-free grip strength and pressure pain threshold. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy. Jul 2003; 33(7): 400-7.