First Rib: Difference between revisions
(Content) |
(Content , ref and images) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
The '''first rib''' is the most superior of the twelve ribs. It is an atypical rib and is an important anatomical landmark. It is one of the borders of the superior thoracic aperture. | The '''first rib''' is the most superior of the twelve ribs. It is an atypical rib and is an important anatomical landmark. It is one of the borders of the superior thoracic aperture. | ||
The ribs form the main structure of the thoracic cage that protects the thoracic organs. There are 12 pairs of ribs which are separated by intercostal spaces. The first seven ribs progressively increase in length, the lower five ribs then begin to decrease in length. Ribs are highly vascular and trabecular with a thin outer layer of compact bone. Similar to the first rib, the 11th and 12th ribs are considered atypical ribs due to their anatomical features. The remaining ribs are typical. | The ribs form the main structure of the thoracic cage that protects the thoracic organs. There are 12 pairs of ribs which are separated by intercostal spaces. The first seven ribs progressively increase in length, the lower five ribs then begin to decrease in length. Ribs are highly vascular and trabecular with a thin outer layer of compact bone. Similar to the first rib, the 11th and 12th ribs are considered atypical ribs due to their anatomical features<ref>https://radiopaedia.org/articles/ribs</ref>. The remaining ribs are typical. | ||
[[File:First rib.jpg|thumb|388x388px]] | |||
== Anatomy == | == Anatomy == | ||
| Line 16: | Line 17: | ||
== Blood Supply == | == Blood Supply == | ||
Arterial blood supply arises from the internal thoracic and superior intercostal arteries. The internal thoracic artery supplies the anterior body wall and its associated structures from the clavicles to the umbilicus. It originates from the first part of the subclavian artery in the base of the neck. The superior intercostal arteries are formed as a direct result of the embryological development of the intersegmental arteries. These arteries are paired structures of the upper thorax which normally form to provide blood flow to the first and second intercostal arteries.<ref>https://radiopaedia.org/articles/supreme-intercostal-arteries</ref> | |||
Venous drainage is to the intercostal veins. | |||
== Attaching Structures == | == Attaching Structures == | ||
Revision as of 16:09, 21 January 2018
Original Editor -
Top Contributors - Kim Jackson, Maram Salem, Adam Vallely Farrell, Lucinda hampton, Evan Thomas, Kirenga Bamurange Liliane, Kai A. Sigel, WikiSysop and Mahbubur Rahman
Description[edit | edit source]
The first rib is the most superior of the twelve ribs. It is an atypical rib and is an important anatomical landmark. It is one of the borders of the superior thoracic aperture.
The ribs form the main structure of the thoracic cage that protects the thoracic organs. There are 12 pairs of ribs which are separated by intercostal spaces. The first seven ribs progressively increase in length, the lower five ribs then begin to decrease in length. Ribs are highly vascular and trabecular with a thin outer layer of compact bone. Similar to the first rib, the 11th and 12th ribs are considered atypical ribs due to their anatomical features[1]. The remaining ribs are typical.
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
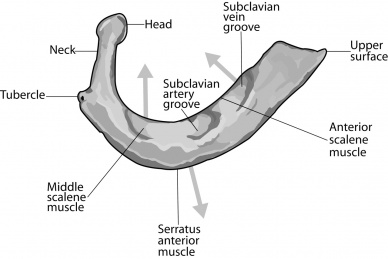
When compared to a typical rib, the first rib is short and thick and only has a single articular facet for the costovertebral joint. The first rib has a head, neck and shaft but lacks a discrete angle. The shaft is indented laterally, the groove for the subclavian artery, which contains the lowest brachial plexus trunk as well as the subclavian artery. Anterior to the scalene tubercle is another groove for the subclavian vein. There is no costal groove on its inferior surface. It has two tubercles:
- transverse tubercle: posterior and lateral to the neck; bears an articular facet for the transverse process of T1
- scalene tubercle: anteriorly between the grooves for the subclavian artery and vein; anterior scalene muscle inserts here
- it is also known as the Lisfranc tubercle, described by Lisfranc in 1815
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
Arterial blood supply arises from the internal thoracic and superior intercostal arteries. The internal thoracic artery supplies the anterior body wall and its associated structures from the clavicles to the umbilicus. It originates from the first part of the subclavian artery in the base of the neck. The superior intercostal arteries are formed as a direct result of the embryological development of the intersegmental arteries. These arteries are paired structures of the upper thorax which normally form to provide blood flow to the first and second intercostal arteries.[2]
Venous drainage is to the intercostal veins.
Attaching Structures[edit | edit source]
Palpation[edit | edit source]
Examination[edit | edit source]
First Rib Assessment on hypomobility in Supine:
First Rib Assessment on hypomobility in Prone:
First Rib Assessment on hypomobility in Sitting:
Pathology/Injury[edit | edit source]
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Extension:RSS -- Error: Not a valid URL: Feed goes here!!
Resources[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ https://radiopaedia.org/articles/ribs
- ↑ https://radiopaedia.org/articles/supreme-intercostal-arteries
- ↑ Physiotutors. First Rib Assessment in Supine | Rib Hypomobility Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dPexFNjZB0Q
- ↑ Physiotutors. First Rib Assessment in Prone | Rib Hypomobility. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gfIy_SZ1KMc
- ↑ Physiotutors. First Rib Assessment in Sitting | Rib Hypomobility. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TTMQh4dZqeg