Extensor carpi radialis longus: Difference between revisions
Rachael Lowe (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "brachial plexus" to "brachial plexus") |
||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | <div class="editorbox"> | ||
'''Original Editor '''- [[User:Wanda van NiekerkWanda van Niekerk]] | '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Wanda van NiekerkWanda van Niekerk|Wanda van Niekerk]] | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
[[File: | [[File:Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus.png|thumb|Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus]] | ||
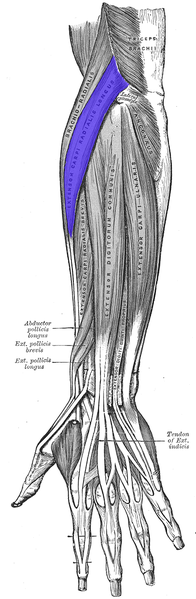
Extensor carpi radialis longus | Extensor carpi radialis longus is a muscle that can be found in the posterior compartment of the forearm. It is partly overlapped by [[brachioradialis]] and these muscles often blend together. As its name suggests it is a wrist extensor and can be palpated infero-posteriorly to the elbow. | ||
== Structure == | |||
Extensor carpi radialis longus is a fusiform muscle that forms a flattened tendon which runs distally over the lateral surface of the radius. In the lower third of the forearm the tendon, together with that of extensor carpi radialis brevis, is crossed by the tendons of abductor pollicis brevis and extensor pollicis brevis. The tendons of extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis pass deep to the extensor retinaculum in a common synovial sheath. Together they groove the posterior surface of the styloid process of the radius.<ref name=":0">Palastanga N, Field D, Soames R. Anatomy and human movement: structure and function. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2006.</ref> | |||
=== Origin === | === Origin === | ||
* Anterior lower third of the lateral supracondylar ridge of the [[humerus]] and adjacent intermuscular septum. Occasionally, there may be an attachment to the lateral epicondyle by the common extensor tendon.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
=== Insertion === | === Insertion === | ||
The | * The radial side of the dorsal surface of the base of the second metacarpal bone .<ref>[https://www.imaios.com/en/e-anatomy/anatomical-structure/extensor-carpi-radialis-longus-1541084744 Extensor carpi radialis longus] [Internet]. Imaios.com. </ref> | ||
=== | === Innervation === | ||
* [[Radial nerve]] (root value C6 and C7) from the posterior cord of the [[Brachial Plexus|brachial plexus]].<ref name=":0" /> | |||
=== | === Blood supply === | ||
Radial artery<ref name=":0" /> | * Radial artery<ref name=":0" /> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
= | * Extensor carpi radialis longus together with extensor carpi radialis brevis produce wrist extension and abduction (radial deviation). | ||
Extensor carpi radialis longus is one of | * In addition extensor carpi radialis longus may help to flex the elbow joint and is active during fist clenching.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
* Extensor carpi radialis longus is one of three primary wrist extensors. It is most effective as a wrist extensor when the elbow is extended and when radial deviation is balanced by the primary ulnar deviator- [[Extensor Carpi Ulnaris|extensor carpi ulnaris]]. | |||
== Clinical Relevance == | |||
Functionally, the wrist extensors work strongly in the action of gripping, together with extensor carpi ulnaris. By maintaining the wrist in an extended position, flexion of the wrist under the action of flexors digitorum superficialis and profundus is prevented, with the result that these muscles act on the fingers. If the wrist is then allowed to flex the flexor tendons cannot shorten sufficiently to produce effective movement at the interphalangeal joints. This therefore becomes a state of active insufficiency. | |||
[[Radial Nerve|Radial nerve]] damage leads to paralysis of the wrist extensors. This leads to a decreased [[Grip Strength|grip strength]]. However, with the wrist splinted in extension, the tendons of flexors digitorum superficialis and profundus act on the fingers and a functional grip can be obtained.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
[[Intersection | [[Intersection Syndrome]] is a bursitis that occurs at the site where the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis tendons cross over the extensor carpi radialis tendons proximal to the extensor retinaculum. This may be due to friction at this site of crossing or it may occur from tenosynovitis of the two extensor tendons within their synovial sheath. This leads to tenderness, swelling and crepitus and can be confused with [[De Quervain's Tenosynovitis|de Quervain's]] syndrome. This condition is often seen in rowers, but also in canoeists and racket sportsmen.<ref name=":1">Brukner P. Khan K. Clinical sports medicine. McGraw-Hill: 2006.</ref> | ||
== Assessment == | == Assessment == | ||
=== Active movements === | |||
* | * Elbow flexion/extension | ||
* | * Supination/pronation | ||
* | * Wrist flexion/extension | ||
* Radial/ulnar deviation | |||
* | |||
== | === Passive movements === | ||
* Elbow flexion/extension | |||
* Supination/pronation | |||
* Wrist flexion/pronation | |||
* Radial/ulnar deviation | |||
[[ | === Resisted movements === | ||
* Wrist extension | |||
* Wrist abduction (radial deviation) | |||
* Wrist extension together with abduction | |||
* Grip test | |||
{{#ev:youtube|rR2dSbH12ig}} <ref>Classroom BOT. MMT Individual Muscle Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus (ECRL) [Internet]. Youtube. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rR2dSbH12ig </ref> | |||
=== Palpation === | |||
* Lateral epicondyle<ref name=":1" /> | |||
* With resisted wrist extension and abduction both extensors carpi radialis longus and brevis can be palpated in the upper lateral aspect of the posterior part of the forearm. The tendons, particularly longus, can be palpated in the floor of the [[anatomical snuff box]] if the same movement of extension and abduction is carried out.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
{{#ev:youtube|Xdinnbur_6w}} <ref>RandaRamnarine. palpating extensor carpi radialis longus [Internet]. Youtube; . Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Xdinnbur_6w </ref> | |||
== See Also == | |||
[[Wrist and Hand Examination|Wrist and hand examination]] | * [[Elbow Examination|Elbow examination]] | ||
* [[Elbow]] | |||
* [[Wrist and Hand Examination|Wrist and hand examination]] | |||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Anatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Anatomy]] [[Category:Muscles]] | [[Category:Elbow - Anatomy]] | ||
[[Category:Wrist - Anatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Hand - Anatomy]] | |||
[[Category:Muscles]] | |||
[[Category:Elbow - Muscles]] | |||
[[Category:Wrist - Muscles]] | |||
[[Category:Hand - Muscles]] | |||
[[Category:Elbow]] | |||
[[Category:Wrist]] | |||
[[Category:Hand]] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:02, 8 March 2024
Original Editor - Wanda van Niekerk
Top Contributors - Wanda van Niekerk, Nina Myburg, Kim Jackson, Rachael Lowe, Amanda Ager and Aya Alhindi
Description[edit | edit source]
Extensor carpi radialis longus is a muscle that can be found in the posterior compartment of the forearm. It is partly overlapped by brachioradialis and these muscles often blend together. As its name suggests it is a wrist extensor and can be palpated infero-posteriorly to the elbow.
Structure[edit | edit source]
Extensor carpi radialis longus is a fusiform muscle that forms a flattened tendon which runs distally over the lateral surface of the radius. In the lower third of the forearm the tendon, together with that of extensor carpi radialis brevis, is crossed by the tendons of abductor pollicis brevis and extensor pollicis brevis. The tendons of extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis pass deep to the extensor retinaculum in a common synovial sheath. Together they groove the posterior surface of the styloid process of the radius.[1]
Origin[edit | edit source]
- Anterior lower third of the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus and adjacent intermuscular septum. Occasionally, there may be an attachment to the lateral epicondyle by the common extensor tendon.[1]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
- The radial side of the dorsal surface of the base of the second metacarpal bone .[2]
Innervation[edit | edit source]
- Radial nerve (root value C6 and C7) from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus.[1]
Blood supply[edit | edit source]
- Radial artery[1]
Function[edit | edit source]
- Extensor carpi radialis longus together with extensor carpi radialis brevis produce wrist extension and abduction (radial deviation).
- In addition extensor carpi radialis longus may help to flex the elbow joint and is active during fist clenching.[1]
- Extensor carpi radialis longus is one of three primary wrist extensors. It is most effective as a wrist extensor when the elbow is extended and when radial deviation is balanced by the primary ulnar deviator- extensor carpi ulnaris.
Clinical Relevance[edit | edit source]
Functionally, the wrist extensors work strongly in the action of gripping, together with extensor carpi ulnaris. By maintaining the wrist in an extended position, flexion of the wrist under the action of flexors digitorum superficialis and profundus is prevented, with the result that these muscles act on the fingers. If the wrist is then allowed to flex the flexor tendons cannot shorten sufficiently to produce effective movement at the interphalangeal joints. This therefore becomes a state of active insufficiency.
Radial nerve damage leads to paralysis of the wrist extensors. This leads to a decreased grip strength. However, with the wrist splinted in extension, the tendons of flexors digitorum superficialis and profundus act on the fingers and a functional grip can be obtained.[1]
Intersection Syndrome is a bursitis that occurs at the site where the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis tendons cross over the extensor carpi radialis tendons proximal to the extensor retinaculum. This may be due to friction at this site of crossing or it may occur from tenosynovitis of the two extensor tendons within their synovial sheath. This leads to tenderness, swelling and crepitus and can be confused with de Quervain's syndrome. This condition is often seen in rowers, but also in canoeists and racket sportsmen.[3]
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Active movements[edit | edit source]
- Elbow flexion/extension
- Supination/pronation
- Wrist flexion/extension
- Radial/ulnar deviation
Passive movements[edit | edit source]
- Elbow flexion/extension
- Supination/pronation
- Wrist flexion/pronation
- Radial/ulnar deviation
Resisted movements[edit | edit source]
- Wrist extension
- Wrist abduction (radial deviation)
- Wrist extension together with abduction
- Grip test
Palpation[edit | edit source]
- Lateral epicondyle[3]
- With resisted wrist extension and abduction both extensors carpi radialis longus and brevis can be palpated in the upper lateral aspect of the posterior part of the forearm. The tendons, particularly longus, can be palpated in the floor of the anatomical snuff box if the same movement of extension and abduction is carried out.[1]
See Also[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Palastanga N, Field D, Soames R. Anatomy and human movement: structure and function. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2006.
- ↑ Extensor carpi radialis longus [Internet]. Imaios.com.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Brukner P. Khan K. Clinical sports medicine. McGraw-Hill: 2006.
- ↑ Classroom BOT. MMT Individual Muscle Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus (ECRL) [Internet]. Youtube. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rR2dSbH12ig
- ↑ RandaRamnarine. palpating extensor carpi radialis longus [Internet]. Youtube; . Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Xdinnbur_6w