Extensor Digitorum Brevis: Difference between revisions
Abbey Wright (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Abbey Wright (talk | contribs) (added links and references videos properly) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:User Name|Ahmed Nasr]] '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | <div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:User Name|Ahmed Nasr]] '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | ||
== Origin == | == Origin == | ||
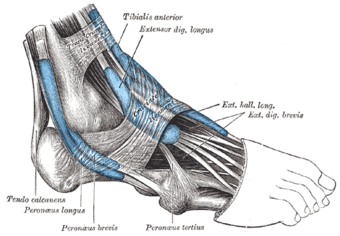
[[File:Extensor digitorum brevis.png|thumb|340x340px]]Extensor Digitorum Brevis is one of the intrinsic muscles on the dorsum of the foot. It arises from the upper and lateral surface of the calcaneous, the floor of tarsal sinus, the talocalcaneal ligament, and the stem of the inferior extensor retinaculum <ref>Anatomy next. Extensor digitorium brevis. Available from<nowiki/>https://www.anatomynext.com/extensor-digitorum-brevis/ accessed at (26july 2019)</ref><ref name=":0">Keith L. , Anne M. R . Clinically Oriented Anatomy . philidephia : Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.Feb 13, 2013</ref> | [[File:Extensor digitorum brevis.png|thumb|340x340px]]Extensor Digitorum Brevis is one of the intrinsic muscles on the dorsum of the [[Ankle and Foot|foot]]. It arises from the upper and lateral surface of the calcaneous, the floor of tarsal sinus, the talocalcaneal ligament, and the stem of the inferior extensor retinaculum <ref>Anatomy next. Extensor digitorium brevis. Available from<nowiki/>https://www.anatomynext.com/extensor-digitorum-brevis/ accessed at (26july 2019)</ref><ref name=":0">Keith L. , Anne M. R . Clinically Oriented Anatomy . philidephia : Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.Feb 13, 2013</ref> | ||
== Insertion == | == Insertion == | ||
Revision as of 09:34, 19 July 2022
Origin[edit | edit source]
Extensor Digitorum Brevis is one of the intrinsic muscles on the dorsum of the foot. It arises from the upper and lateral surface of the calcaneous, the floor of tarsal sinus, the talocalcaneal ligament, and the stem of the inferior extensor retinaculum [1][2]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
It inserts via tendons into the base of the proximal phalanx of the 1st toe, and the middle phalanx of the three medial digits joining with the extensor digitorum longus tendon (toes 2-4)[2][3]
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Deep fibular nerve (S1, S2)[3]
Action[edit | edit source]
Assists Extensor digiorium longus in extending the metatarsophalangeal and interphalangeal joints of the 2nd, 3rd and 4th toes.[2] It also assists extensor hallucis longus and brevis in 1st toe metatarsophalangeal extension.
Palpation[edit | edit source]
EDB can be palpated on the lateral dorsum of the foot. By encouraging extension of the digits of the foot you can palpate and observe what is described as a swelling where the muscle belly of EDB originates.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Anatomy next. Extensor digitorium brevis. Available fromhttps://www.anatomynext.com/extensor-digitorum-brevis/ accessed at (26july 2019)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Keith L. , Anne M. R . Clinically Oriented Anatomy . philidephia : Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.Feb 13, 2013
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Drake RL, Vogl W, Mitchell AWM. Gray's Anatomy for Students. 39th ed. London; Elsevier; 2005. p574-575
- ↑ nabil ebraheim. Extensor Digitorum Brevis - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GQvjwpXdQ38 [last accessed 30/1/2018]
- ↑ C Blake. Extensor Digitorum Brevis. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LVpF_Mk1avM [last accessed 20/11/2012]