Creatine Phosphokinase (CK or CPK)
Original Editor - User Name
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Kirenga Bamurange Liliane and Vidya Acharya
Introduction[edit | edit source]
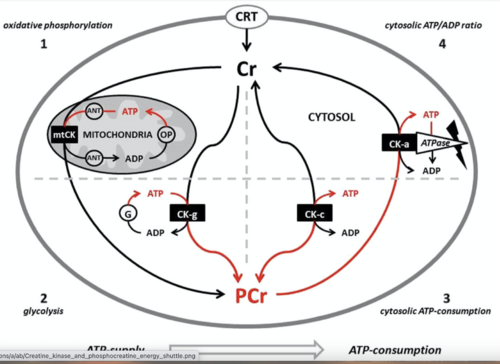
Creatine phosphokinase (CPK) AKA creatine kinase (CK), is the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of creatine and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to phosphocreatine (PCr) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP). It is a reversible enzyme reaction that subsequently produces ATP from PCr and ADP. The PCr made is then used to supply tissues and cells that need substantial amounts of ATP, for instance the brain, skeletal muscles, and the heart, with this much needed ATP. Creatine phosphokinase (CK) is a major controller of homeostasis in cells. Numerous conditions cause disruption of CPK levels, including rhabdomyolysis, heart disease, kidney disease, and certain medications.[1]
Sub Heading 2[edit | edit source]
The appearance of CK in blood is usually considered an indirect marker of muscle damage, especially for diagnosis of medical conditions such as myocardial infarction, muscular dystrophy, and cerebral diseases.
The molecular mechanisms causing CK release from muscle after mild exercise remains unclear. Clarification would help give important information for those concerned about muscle hypertrophy, performance, and the significance of rest periods between periods of exercise.[2]
Sub Heading 3[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Aujla RS, Patel R. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546624/ StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL).Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546624/ (accessed 4.2.2024)
- ↑ Baird MF, Graham SM, Baker JS, Bickerstaff GF. Creatine-kinase-and exercise-related muscle damage implications for muscle performance and recovery. Journal of nutrition and metabolism. 2012 Oct;2012.Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3263635/ (accessed 5.2.2024)