Creatine Phosphokinase (CK or CPK): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
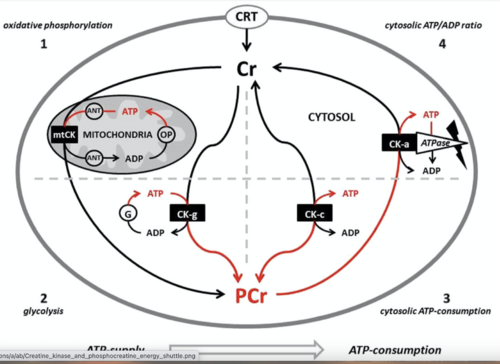
Creatine phosphokinase (CPK) AKA creatine kinase (CK), is the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of [[Creatine and Exercise|creatine]] and [[Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)|adenosine triphosphate]] (ATP) to phosphocreatine (PCr) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP). It is a reversible [[Enzymes|enzyme]] reaction that subsequently produces ATP from PCr and ADP. The PCr made is then used to supply tissues and cells that need substantial amounts of ATP, for instance the brain, skeletal muscles, and the heart, with this much needed ATP. Creatine phosphokinase (CK) is a major controller of homeostasis in cells. Numerous conditions cause disruption of CPK levels, including rhabdomyolysis, heart disease, kidney disease, and certain medications.<ref>Aujla RS, Patel R. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546624/ StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL).Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546624/ (accessed 4.2.2024)</ref> | Creatine phosphokinase (CPK) AKA creatine kinase (CK), is the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of [[Creatine and Exercise|creatine]] and [[Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)|adenosine triphosphate]] (ATP) to phosphocreatine (PCr) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP). It is a reversible [[Enzymes|enzyme]] reaction that subsequently produces ATP from PCr and ADP. The PCr made is then used to supply tissues and cells that need substantial amounts of ATP, for instance the brain, skeletal muscles, and the heart, with this much needed ATP. Creatine phosphokinase (CK) is a major controller of homeostasis in cells. Numerous conditions cause disruption of CPK levels, including rhabdomyolysis, heart disease, kidney disease, and certain medications.<ref>Aujla RS, Patel R. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546624/ StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL).Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546624/ (accessed 4.2.2024)</ref> | ||
[[File:Creatine kinase-phosphocreatine (CK-PCr) energy shuttle..png|center|thumb|500x500px|CKP Energy Shuttle]] | |||
== Sub Heading 2 == | == Sub Heading 2 == | ||
Revision as of 02:33, 5 February 2024
Original Editor - User Name
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Kirenga Bamurange Liliane and Vidya Acharya
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Creatine phosphokinase (CPK) AKA creatine kinase (CK), is the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of creatine and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to phosphocreatine (PCr) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP). It is a reversible enzyme reaction that subsequently produces ATP from PCr and ADP. The PCr made is then used to supply tissues and cells that need substantial amounts of ATP, for instance the brain, skeletal muscles, and the heart, with this much needed ATP. Creatine phosphokinase (CK) is a major controller of homeostasis in cells. Numerous conditions cause disruption of CPK levels, including rhabdomyolysis, heart disease, kidney disease, and certain medications.[1]
Sub Heading 2[edit | edit source]
Sub Heading 3[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Aujla RS, Patel R. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546624/ StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL).Available:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546624/ (accessed 4.2.2024)