Cerebellum: Difference between revisions
(3 templates) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
This article or area is currently under construction and may only be partially complete. Please come back soon to see the finished work! ({{REVISIONDAY}}/{{REVISIONMONTH}}/{{REVISIONYEAR}}) | This article or area is currently under construction and may only be partially complete. Please come back soon to see the finished work! ({{REVISIONDAY}}/{{REVISIONMONTH}}/{{REVISIONYEAR}}) | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User: | <div class="editorbox"> '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Lucinda hampton|Lucinda hampton]] '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}}</div> | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | <div class="editorbox"> | ||
'''Original Editor '''- Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page. | '''Original Editor '''- Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page. | ||
'''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Top Contributors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
[[File:Cerebellum-600x305.jpg|right|frameless|350x350px]] | |||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
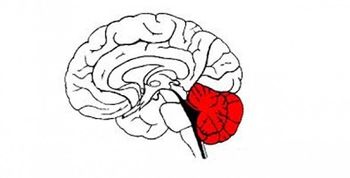
The cerebellum is a vital component in the human brain as it plays a role in motor movement regulation and balance control. The cerebellum <ref>Jimsheleishvili S, Dididze M. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538167/ Neuroanatomy, Cerebellum.] InStatPearls [Internet] 2019 Mar 2. StatPearls Publishing.Available from:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538167/ (last accessed 19.1.2020)</ref> | |||
* coordinates gait | |||
* maintains posture, | |||
* controls muscle tone and voluntary muscle activity | |||
* is unable to initiate muscle contraction. | |||
Damage to this area in humans results in a loss in the ability to control fine movements, maintain posture, and motor learning | |||
== Sub Heading 2 == | == Sub Heading 2 == | ||
| Line 25: | Line 33: | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Neurology]] | |||
[[Category:Anatomy]] | |||
Revision as of 08:07, 19 January 2020
This article or area is currently under construction and may only be partially complete. Please come back soon to see the finished work! (19/01/2020)
Original Editor - Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page.
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Rahma Ahmed Ahmed Bahbah, Rusfid FM, Kim Jackson, Nikhil Benhur Abburi, Khloud Shreif, Mason Trauger and Jonathan Wong
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The cerebellum is a vital component in the human brain as it plays a role in motor movement regulation and balance control. The cerebellum [1]
- coordinates gait
- maintains posture,
- controls muscle tone and voluntary muscle activity
- is unable to initiate muscle contraction.
Damage to this area in humans results in a loss in the ability to control fine movements, maintain posture, and motor learning
Sub Heading 2[edit | edit source]
Sub Heading 3[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Jimsheleishvili S, Dididze M. Neuroanatomy, Cerebellum. InStatPearls [Internet] 2019 Mar 2. StatPearls Publishing.Available from:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538167/ (last accessed 19.1.2020)