Biceps Squeeze Test: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(reference links added, citations added, image edited, info corrected, grammar correction) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
=== Purpose === | === Purpose === | ||
[[File:Biceps tendon tear.jpeg|alt=| | [[File:Biceps tendon tear.jpeg|alt=|thumb|Right distal bicipital [[Tendon Load and Capacity|tendon]] rupture.]] | ||
The | The biceps squeeze test is a diagnostic test for distal [[Biceps Brachii|biceps]] tendon rupture. | ||
* Distal biceps rupture is due to excessive eccentric force as the arm is brought into extension from flexion. Activities that can cause this type of injury include weightlifting, labour-intensive jobs and wrestling. Risk factors include age, [[obesity]] [[Smoking and Exercise|smoking]], [[Overuse Injuries - an Individualised Approach|overuse]] and the use of [[Corticosteroid Medication|corticosteroids]]<ref name=":1" />. | |||
* Distal biceps [[Tendon Biomechanics|tendon]] rupture incidence is about 2.55 per 100,000 patient-years. Most patients (more than 95%) are males, and injury events usually happen during middle age (35 years to 54 years). Rupture of the distal biceps mainly involves the dominant limb.<ref name=":1">1. [Internet]. [cited 2023 Oct 1]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513235/</ref> | |||
* Distal biceps rupture is | <span class="reference" id="cite_ref-:0_1-0"></span>Related Tests | ||
* | |||
Related Tests | |||
# [[Elbow Hook Test]] | # [[Elbow Hook Test]] | ||
| Line 18: | Line 16: | ||
# [[Flexion Initiation Test]] | # [[Flexion Initiation Test]] | ||
=== Technique === | === Technique<ref name=":0">Ruland CR, Bowen CJ. [https://www.researchgate.net/publication/7690169_The_Biceps_Squeeze_Test_for_Diagnosis_of_Distal_Biceps_Tendon_Ruptures/link/5b355cbe4585150d23e07f73/download The biceps squeeze test for diagnosis of distal biceps tendon ruptures]. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research (1976-2007). 2005 Aug 1;437:128-31. </ref> === | ||
'''Step 1.''' Patient position in sitting with the forearm comfortably supported on the patient's lap. | '''Step 1.''' Patient position in sitting with the forearm comfortably supported on the patient's lap. The examiner stands on the same side as the limb that is being tested. | ||
'''Step | '''Step 2.''' Elbow is flexed approximately 60-80 degrees (Stress on the brachialis minimises in this range and helps isolate the biceps brachii). | ||
'''Step | '''Step 3.''' The forearm is slightly pronated (to put tension on the biceps brachii tendon). | ||
'''Step 4.''' The examiner then squeezes the biceps brachii firmly with both hands, one hand on the distal [[Myotendinous Junction|myotendinous junction]] and the other around the muscle belly. When the biceps brachii is squeezed, the belly of the muscle is drawn away from the humerus leading to an anterior bowing of the muscle. | |||
'''Step 5''' | '''Step 5''': The absence of supination of the forearm is considered a positive test and can indicate a biceps brachii tendon or muscle belly rupture | ||
<div class="row"> | <div class="row"> | ||
Latest revision as of 13:48, 1 October 2023
Original Editor - Anas Mohamed
Top Contributors - Anas Mohamed, Lucinda hampton, Wendy Snyders and Kim Jackson
Purpose[edit | edit source]
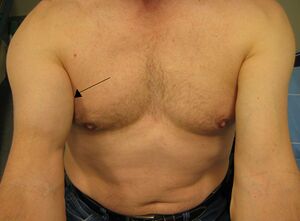
The biceps squeeze test is a diagnostic test for distal biceps tendon rupture.
- Distal biceps rupture is due to excessive eccentric force as the arm is brought into extension from flexion. Activities that can cause this type of injury include weightlifting, labour-intensive jobs and wrestling. Risk factors include age, obesity smoking, overuse and the use of corticosteroids[1].
- Distal biceps tendon rupture incidence is about 2.55 per 100,000 patient-years. Most patients (more than 95%) are males, and injury events usually happen during middle age (35 years to 54 years). Rupture of the distal biceps mainly involves the dominant limb.[1]
Related Tests
Technique[2][edit | edit source]
Step 1. Patient position in sitting with the forearm comfortably supported on the patient's lap. The examiner stands on the same side as the limb that is being tested.
Step 2. Elbow is flexed approximately 60-80 degrees (Stress on the brachialis minimises in this range and helps isolate the biceps brachii).
Step 3. The forearm is slightly pronated (to put tension on the biceps brachii tendon).
Step 4. The examiner then squeezes the biceps brachii firmly with both hands, one hand on the distal myotendinous junction and the other around the muscle belly. When the biceps brachii is squeezed, the belly of the muscle is drawn away from the humerus leading to an anterior bowing of the muscle.
Step 5: The absence of supination of the forearm is considered a positive test and can indicate a biceps brachii tendon or muscle belly rupture
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1. [Internet]. [cited 2023 Oct 1]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513235/
- ↑ Ruland CR, Bowen CJ. The biceps squeeze test for diagnosis of distal biceps tendon ruptures. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research (1976-2007). 2005 Aug 1;437:128-31.
- ↑ BICEPS SQUEEZE TEST. Patras Orthopaedics Clinical Examination. Available from: https://youtu.be%7CUIi8eLbSqQI
- ↑ Squeeze Test In Orthopaedics - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim. Available from: https://youtu.be%7CEiFS5okDTHA






