Diaphragmatic Breathing and Ventilator-Induced Diaphragmatic Dysfunction
Top Contributors - Ewa Jaraczewska, Carin Hunter, Jess Bell, Kim Jackson and Wanda van Niekerk
Effects of Diaphragmatic Breathing[edit | edit source]
- Detoxifies and releases toxins:
- Our body is designed to release 70% of its toxins through breathing. At least 3x times per day for 39 seconds
- Anti-stress:[1]
- When a body experiences stress, the brain releases cortisol, which is often known as the "stress hormone". Cortisol increases heartrate and blood pressure.
- If an individual takes a few diaphragmatic breaths, the result is slowing of the heart rate which allows more oxygen to enter the bloodstream which causes the brain calm.
- Deep breathing can increase our endorphins as well.
- Relaxation and mood elevation:[2]
- Diaphragmatic breathing stimulates the vagus nerve which is parasympathetic, thus inducing relaxation.
- Deep breathing relieves pain:
- Breathing into pain will increase circulation to that specific area, relieves tension and increase oxygenation. This triggers the release of endorphins, thus affecting pain relief.
- Deep breathing enhances the immune system:
- Deep breathing enhances the body’s ability to metabolize nutrients and vitamins. Deep breathing aids in digestion which helps strengthen immunity.
- Lowers blood pressure:
- With relaxation blood vessels dilate, which improves circulation and lowers blood pressure. Deep breathing also slows and regulates the heart rate, which also helps with lowering BP.
- Deep breathing improves cellular regeneration:
- With deep breathing the body is better oxygenated and has better circulation which enhances the body’s efforts of cellular regeneration.
- Helps support correct posture:
- Inspiration lengthens the spine, facilitates lumbopelvic movements, activates core muscles.[3]
Evidence Based Practice[edit | edit source]
- Allison et al.[7] reported that during lumbopelvic motion control tests, diaphragmatic activity increases in healthy subjects.
- O’Sullivan and Beales[8] concluded in their case studies that lumbopelvic movements decrease in patients with diaphragmatic injuries.
- Moreover, patients with chronic lower back pain have often been reported to have defects in posture and motor control.[8][9]
Effect of Mechanical Ventilation on Diaphragm[edit | edit source]
- Ventilator-induced diaphragmatic dysfunction(VIDD):
- Loss of diaphragmatic force-generating capacity as a consequence to use of mechanical ventilation due to suppressed inspiratory effort.[10][11]
- Mechanical ventilatory assistance contributes to diaphragm muscle inactivity and unloading thus leading to diaphragmatic atrophy and fatigue.[12]
- Diaphragm weakness is a leading cause of difficult weaning from mechanical ventilation[13] and loss of thickness of diaphragm muscle, however, if there is insufficient ventilatory support and the diaphragm is not unloaded adequately this can lead to load-induced inflammation and injury.[14]
- Diaphragm atrophy developing during mechanical ventilation strongly impacts clinical outcomes. Targeting an inspiratory effort level similar to that of healthy subjects at rest might accelerate liberation from ventilation.[15]
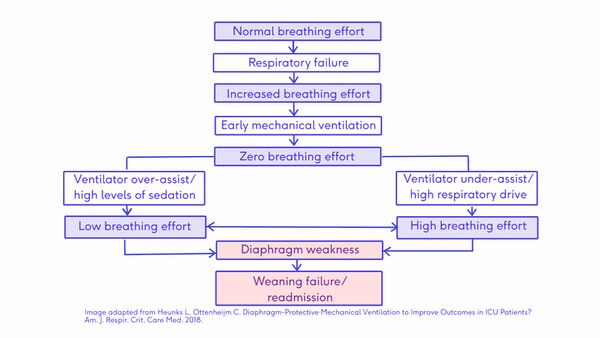 Ventilator-Induced Diaphragmatic Dysfunction Flow chart [16]
Ventilator-Induced Diaphragmatic Dysfunction Flow chart [16]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Hunt MG, Rushton J, Shenberger E, Murayama S. Positive effects of diaphragmatic breathing on physiological stress reactivity in varsity athletes. Journal of Clinical Sport Psychology. 2018 Mar 1;12(1):27-38.
- ↑ Hamasaki H. Effects of Diaphragmatic Breathing on Health: A Narrative Review. Medicines. 2020 Oct;7(10):65.
- ↑ Stephens RJ, Haas M, Moore III WL, Emmil JR, Sipress JA, Williams A. Effects of diaphragmatic breathing patterns on balance: a preliminary clinical trial. Journal of manipulative and physiological therapeutics. 2017 Mar 1;40(3):169-75.
- ↑ Harvard Vanguard Medical Associates. Diaphragmatic Breathing Part 1 of 3 - Intro to Diaphragmatic Breathing Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gAkjx25o4eI&t=3s [last accessed 10 November 2021]
- ↑ Harvard Vanguard Medical Associates. Diaphragmatic Breathing Part 2 of 3 - Breathing While Lying Down. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BckGYBfN5e0&t=64s [last accessed 10 November 2021]
- ↑ Harvard Vanguard Medical Associates. Diaphragmatic Breathing Part 3 of 3 - Seated or Upright Position. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1vXlTkrNxyw&t=18s [last accessed 10 November 2021]
- ↑ Allison G, Kendle K, Roll S, Schupelius J, Scott Q, Panizza J. The role of the diaphragm during abdominal hollowing exercises. Australian Journal of Physiotherapy. 1998 Jan 1;44(2):95-102.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 O’Sullivan P. Diagnosis and classification of chronic low back pain disorders: maladaptive movement and motor control impairments as underlying mechanism. Manual therapy. 2005 Nov 1;10(4):242-55.
- ↑ Hodges PW, Moseley GL. Pain and motor control of the lumbopelvic region: effect and possible mechanisms. Journal of electromyography and kinesiology. 2003 Aug 1;13(4):361-70.
- ↑ Kim WY, Lim CM. Ventilator-induced diaphragmatic dysfunction: diagnosis and role of pharmacological agents. Respiratory care. 2017 Nov 1;62(11):1485-91.
- ↑ Peñuelas O, Keough E, López-Rodríguez L, Carriedo D, Gonçalves G, Barreiro E, Lorente JÁ. Ventilator-induced diaphragm dysfunction: translational mechanisms lead to therapeutical alternatives in the critically ill. Intensive care medicine experimental. 2019 Jul;7(1):1-25.
- ↑ Vassilakopoulos T, Petrof BJ. Ventilator-induced diaphragmatic dysfunction. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 2004 Feb 1;169(3):336-41.
- ↑ Dres M, Dubé BP, Mayaux J, Delemazure J, Reuter D, Brochard L, Similowski T, Demoule A. Coexistence and impact of limb muscle and diaphragm weakness at the time of liberation from mechanical ventilation in medical intensive care unit patients. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 2017 Jan 1;195(1):57-66.
- ↑ Orozco-Levi M, Lloreta J, Minguella J, Serrano S, Broquetas JM, Gea J. Injury of the human diaphragm associated with exertion and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 2001 Nov 1;164(9):1734-9.
- ↑ Lipson DA, Barnacle H, Birk R, Brealey N, Locantore N, Lomas DA, Ludwig-Sengpiel A, Mohindra R, Tabberer M, Zhu CQ, Pascoe SJ. FULFIL trial: once-daily triple therapy for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 2017 Aug 15;196(4):438-46.
- ↑ Schepens T, Dres M, Heunks L, Goligher EC. Diaphragm-protective mechanical ventilation. Current opinion in critical care. 2019 Feb 1;25(1):77-85.






