Facet Arthrosis: Difference between revisions
Niha Mulla (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Niha Mulla (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Definition == | == Definition == | ||
[[File:Facet Joints.png|thumb|150x150px]] | |||
Facet arthrosis is a painful arthritis-like condition of the spine caused by degeneration of the joints between the spinal bones. | |||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
[[File:Facet Joints Anatomy.jpeg|thumb|200x200px]] | |||
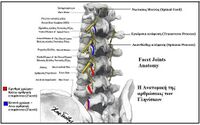
The spine is made up of vertebrae and between each vertebra are two facet joints cushioned by cartilage and lubricated by synovial fluid. These facet joints run alongside the vertebrae posteriorly and and help with twisting and turning motions of the spine. | |||
== Clinical relevance == | == Clinical relevance == | ||
[[File:Facet-joints.png|border|thumb|195x195px]] | |||
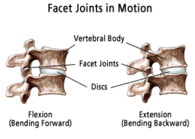
Facet joints degenerate, wear down with age, leading to facet arthrosis. The cartilage of the facet joints, wears down and gets damaged due to trauma or/and aging causing friction in-between joints leading to inflammation, swelling and stiffness; which further causes discomfort and extreme pain. | |||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
Revision as of 23:46, 10 May 2022
This article is currently under review and may not be up to date. Please come back soon to see the finished work! (10/05/2022)
Original Editor - Niha Mulla
Top Contributors - Niha Mulla
Definition[edit | edit source]
Facet arthrosis is a painful arthritis-like condition of the spine caused by degeneration of the joints between the spinal bones.
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The spine is made up of vertebrae and between each vertebra are two facet joints cushioned by cartilage and lubricated by synovial fluid. These facet joints run alongside the vertebrae posteriorly and and help with twisting and turning motions of the spine.
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
Facet joints degenerate, wear down with age, leading to facet arthrosis. The cartilage of the facet joints, wears down and gets damaged due to trauma or/and aging causing friction in-between joints leading to inflammation, swelling and stiffness; which further causes discomfort and extreme pain.
Causes[edit | edit source]
Risk factors[edit | edit source]
Signs and symptoms[edit | edit source]
Evaluation[edit | edit source]
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Treatment and prognosis[edit | edit source]
Complications[edit | edit source]
Physical therapy interventions[edit | edit source]
Prevention[edit | edit source]
- x
or
- numbered list
- x