Autonomic Dysreflexia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
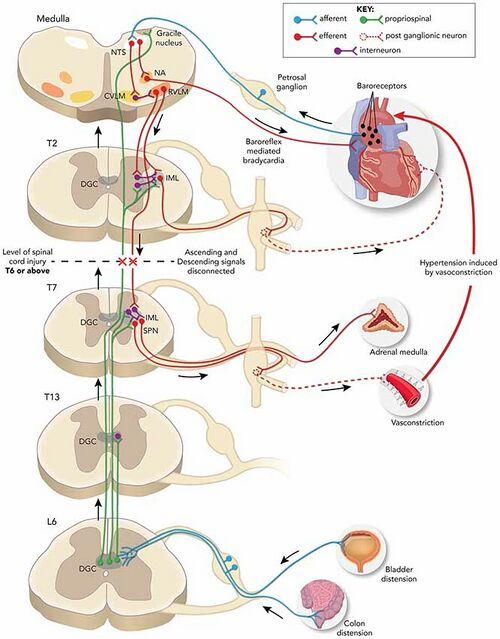
Autonomic dysreflexia is a condition that emerges soon after a [[Spinal Cord Injury]], usually when the damage has occurred at or above the T6 level. It is generally defined as a syndrome in susceptible Spinal Cord injured patients that incorporates a sudden, exaggerated reflexive increase in blood pressure in response to a stimulus, usually bladder or bowel distension, originating below the level of the neurological injury. It is also sometimes known as autonomic hyperreflexia, hypertensive autonomic crisis, sympathetic hyperreflexia, autonomic [[Spasticity]], paroxysmal hypertension, mass reflex, and viscero-autonomic stress syndrome. (Autonomic dysfunction, autonomic neuropathy, and dysautonomia refer to general dysfunction of the [[Autonomic Nervous System]], which is a distinctly different entity.)<ref>Allen KJ, Leslie SW. [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29494041/ Autonomic dysreflexia]. InStatPearls [Internet] 2022 Feb 14. StatPearls publishing.</ref> | Autonomic dysreflexia is a condition that emerges soon after a [[Spinal Cord Injury]], usually when the damage has occurred at or above the T6 level. It is generally defined as a syndrome in susceptible Spinal Cord injured patients that incorporates a sudden, exaggerated reflexive increase in blood pressure in response to a stimulus, usually bladder or bowel distension, originating below the level of the neurological injury. It is also sometimes known as autonomic hyperreflexia, hypertensive autonomic crisis, sympathetic hyperreflexia, autonomic [[Spasticity]], paroxysmal hypertension, mass reflex, and viscero-autonomic stress syndrome. (Autonomic dysfunction, autonomic neuropathy, and dysautonomia refer to general dysfunction of the [[Autonomic Nervous System]], which is a distinctly different entity.)<ref>Allen KJ, Leslie SW. [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29494041/ Autonomic dysreflexia]. InStatPearls [Internet] 2022 Feb 14. StatPearls publishing.</ref> | ||
[[File:AutoDys2019.jpeg|center|thumb|639x639px|Autonomic Dysreflexia]] | |||
== Etiology == | == Etiology == | ||
Revision as of 03:10, 24 April 2022
Top Contributors -
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Autonomic dysreflexia is a condition that emerges soon after a Spinal Cord Injury, usually when the damage has occurred at or above the T6 level. It is generally defined as a syndrome in susceptible Spinal Cord injured patients that incorporates a sudden, exaggerated reflexive increase in blood pressure in response to a stimulus, usually bladder or bowel distension, originating below the level of the neurological injury. It is also sometimes known as autonomic hyperreflexia, hypertensive autonomic crisis, sympathetic hyperreflexia, autonomic Spasticity, paroxysmal hypertension, mass reflex, and viscero-autonomic stress syndrome. (Autonomic dysfunction, autonomic neuropathy, and dysautonomia refer to general dysfunction of the Autonomic Nervous System, which is a distinctly different entity.)[1]
Etiology[edit | edit source]
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the clinical presentation of the condition
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to diagnostic tests for the condition
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
add links to outcome measures here (see Outcome Measures Database)
Management / Interventions
[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to management approaches to the condition
Differential Diagnosis
[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the differential diagnosis of this condition
Resources[edit | edit source]
add appropriate resources here
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Allen KJ, Leslie SW. Autonomic dysreflexia. InStatPearls [Internet] 2022 Feb 14. StatPearls publishing.