Infrared Therapy: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
== Application == | == Application == | ||
Non-luminous lamp has to be switched on up to 15 mins before application to allow maximum emission. | |||
== Contraindication == | == Contraindication == | ||
Revision as of 09:55, 22 June 2021
Original Editor - User Name
Top Contributors - Vidya Acharya, Cindy John-Chu, Kim Jackson and Sai Kripa
This article or area is currently under construction and may only be partially complete. Please come back soon to see the finished work! (22/06/2021)
Introduction[edit | edit source]
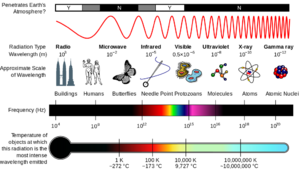
Thermal radiation or Infrared is a band of energy in the complete electromagnetic spectrum and it has been used effectively for millennia to treat/ease certain maladies and discomforts. Infrared are the radiations of longer wavelength than the red end of the visible spectrum and extending to the microwave region, i.e. from 760 nm to 1 mm.[1]
Infrared (IR) is a type of electromagnetic radiation, including wavelengths between the 780 nm to 1000 μm. IR is divided into different bands: Near-Infrared (NIR, 0.78~3.0 μm), Mid-Infrared (MIR, 3.0~50.0 μm) and Far-Infrared (FIR, 50.0~1000.0 μm) as defined in standard ISO 20473:2007 Optics and photonics -- Spectral bands.[2]
Classification
The classification of the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) has three sub-divisions for the IR radiation[3]
| Type | Wavelength |
|---|---|
| IR A (Near IR) | 700-1400nm |
| IR B (Mid-IR) | 1400-3000nm |
| IR C (Far-IR) | 3000 nm– 0.1 mm |
An alternative classification provided in ISO 20473 [3]
Infrared radiations are produced by various kinds vibrations in the molecules; the molecular movement causes infrared emission of different wavelengths[1]. The Near infrared are also known as 'luminous' as they have some visible light with wavelength of 770 to 1500 nanometers.[4] The Far infrared also called as non-luminous are within 1500nm to 0.1 mm.
Production of Infrared
Different kinds of lamps are used for production of therapeutic infrared. One type is similar to electric fire; in these heater the wire glows red thus giving some radiation in the visible region with peak emission in the near infrared.
Physiological Effects[edit | edit source]
Infrared radiations cause[1]:
- local cutaneous vasodilation due to the release of chemical vasodilator (histamine) as well as possible effect on the blood vessels, occurs after 1-2 mins
- evident erythema the rate and intensity of erythema depends on rate and degree of heating.
- reflex dilation of other cutaneous vessels occurs to maintain normal heat balance
- prolonged heating leads to sweating leading to cooling
Therapeutic Uses[edit | edit source]
Infrared is used for the following purposes[1]:
- pain relief
- decreases muscle spasm
- increases the sensory nerve conduction velocity, increase in endorphins influencing the pain gate mechanism
- acceleration of healing and tissue repair- pressure sores
- used prior to electrical stimulation/testing or biofeedback to make the skin a better conductor
Application[edit | edit source]
Non-luminous lamp has to be switched on up to 15 mins before application to allow maximum emission.
Contraindication[edit | edit source]
Precautions[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Infrare dand visible radiations. Electrotherapy Explained principles and practice. John Low & Ann Reed. 2nd edition.
- ↑ Tsai SR, Hamblin MR. Biological effects and medical applications of infrared radiation. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology. 2017 May 1;170:197-207.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Vatansever F, Hamblin MR. Far infrared radiation (FIR): its biological effects and medical applications. Photonics & lasers in medicine. 2012 Nov 1;1(4):255-66.
- ↑ Thermal agents in rehabilitation. Chapter 5 Biophysical Principles of heating.