Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis and Back Pain: Difference between revisions
Man Nok Tam (talk | contribs) (Created page with "== Content == == Aims == This article aims to discuss the relationship between adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) and back pain, and the management plan for it. == Object...") |
Man Nok Tam (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Aims == | == Aims == | ||
[[File:Cobb angle (Greiner, 2002).png|thumb|'''Fig. 1''' [[Cobb's angle|Cobb angle]] (Greiner, 2002)]] | |||
This article aims to discuss the relationship between adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) and back pain, and the management plan for it. | This article aims to discuss the relationship between adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) and back pain, and the management plan for it. | ||
== Objectives == | == Objectives == | ||
* To introduce AIS | |||
* To discuss the relationship between AIS and back pain, with considering of dysfunctional breathing | |||
* To discuss the potential treatments for back pain in AIS | |||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
Scoliosis is where the spine twists and curves to the side (NHS, 2017). See [[Scoliosis]] for full details. | |||
The common outcome measure for the curvature of scoliosis is the [[Cobb's angle|Cobb angle]] (Fig.1). | |||
[[Category:Pain]] | |||
[[Category:Paediatrics]] | |||
Revision as of 19:27, 24 May 2019
Aims[edit | edit source]
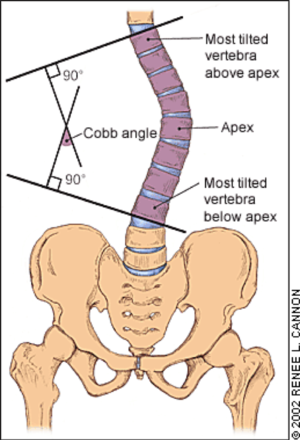
This article aims to discuss the relationship between adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) and back pain, and the management plan for it.
Objectives[edit | edit source]
- To introduce AIS
- To discuss the relationship between AIS and back pain, with considering of dysfunctional breathing
- To discuss the potential treatments for back pain in AIS
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Scoliosis is where the spine twists and curves to the side (NHS, 2017). See Scoliosis for full details.
The common outcome measure for the curvature of scoliosis is the Cobb angle (Fig.1).






