Chorea: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
* '''Randomness''' | * '''Randomness''' | ||
* '''Flowing Quality''' | * '''Flowing Quality''' | ||
* '''Parakinesia'''-Patients blend their chorea induced movements with their own normal movements. | * '''Parakinesia'''-Patients blend their chorea-induced movements with their own normal movements. | ||
* '''Motor impersistence'''- patient is unable to perform sustained motor activities. | * '''Motor impersistence'''- the patient is unable to perform sustained motor activities. | ||
* '''Ballism'''- Variant of chorea which shows large-amplitude flinging movements involving proximal extremities. | * '''Ballism'''- Variant of chorea which shows large-amplitude flinging movements involving proximal extremities. | ||
* '''Athetosis'''-Slow writhing movements involving distal limbs sometimes may be | * '''Athetosis'''-Slow writhing movements involving distal limbs sometimes may be facing. | ||
* '''Varying velocity of movements'''-quick velocity and low- amplitude movements accompanied by jerks. | * '''Varying velocity of movements'''-quick velocity and low-amplitude movements accompanied by jerks. | ||
{{#ev:youtube|RxWEilu-Mf4}} | {{#ev:youtube|RxWEilu-Mf4}} | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
== Management == | == Management == | ||
1.Dopamine depleting agents | 1. Dopamine-depleting agents | ||
2.Dopamine D2 receptor-blocking agents | 2. Dopamine D2 receptor-blocking agents | ||
3. Anticonvulsants | 3. Anticonvulsants | ||
Revision as of 13:24, 23 August 2022
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The word Chorea has Greek origins meaning "to dance". It has a dance-like appearance due to the random and flowing quality of the movement. Chorea is a type of hyperkinetic movement disorder. The involuntary movements flow from one body area to another which cannot be predicted beforehand.
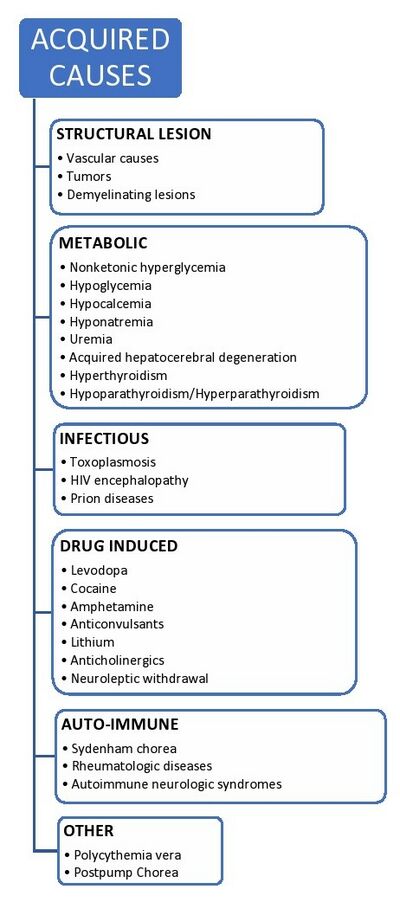
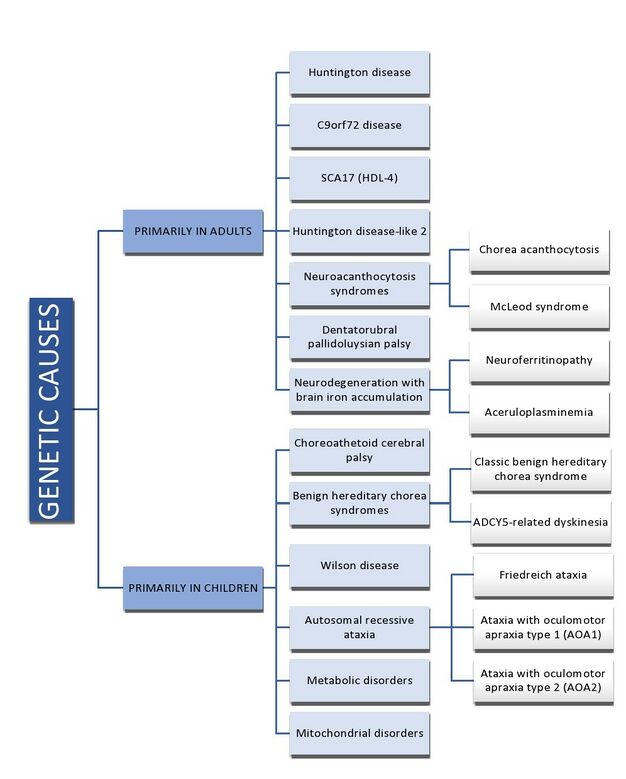
Causes[edit | edit source]
They are predominantly of 2 types
- Acquired Causes
- Genetic Causes
Phenomenological Features[edit | edit source]
- Randomness
- Flowing Quality
- Parakinesia-Patients blend their chorea-induced movements with their own normal movements.
- Motor impersistence- the patient is unable to perform sustained motor activities.
- Ballism- Variant of chorea which shows large-amplitude flinging movements involving proximal extremities.
- Athetosis-Slow writhing movements involving distal limbs sometimes may be facing.
- Varying velocity of movements-quick velocity and low-amplitude movements accompanied by jerks.
This video displays the dance-like movements performed by a patient.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Management[edit | edit source]
1. Dopamine-depleting agents
2. Dopamine D2 receptor-blocking agents
3. Anticonvulsants
4. Anti-glutamatergic agents
5. Cannabinoids
6. Deep Brain Stimulation
7. Physiotherapy