Implementation Science: Sustainment Stage: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
Thinking about sustainment needs to start in the pre-implementation planning stage, specifically, identifying the: determinants or predictors of sustainment as related to organizational and contextual factors and strategies) and the outcomes of sustainment of intervention use. To learn more about the pre-implementation stage, please review [[Implementation Science: Pre-Implementation Stage|this article]]. | Thinking about sustainment needs to start in the pre-implementation planning stage, specifically, identifying the: determinants or predictors of sustainment as related to organizational and contextual factors and strategies) and the outcomes of sustainment of intervention use. To learn more about the pre-implementation stage, please review [[Implementation Science: Pre-Implementation Stage|this article]]. | ||
During the Sustainment Phase, the intervention is engrained in the organisation, including stable funding and ongoing monitoring and or quality assurance processes. | During the Sustainment Phase, the intervention is engrained in the organisation, including stable funding and ongoing monitoring and or quality assurance processes. Sustainment can be influenced by multiple contextual factors, specifically inner and outer contextual factors, that influence the adoption and implementation of interventions. '''Box 14''' provides several key implementation facilitator questions key to the inner and outer context of sustainment. | ||
[[File:Implementation science box 14.png|center|thumb|800x800px|The questions in Box 14 have been informed by the EPIS, a popular Implementation Science framework.]] | |||
For more information about the Exploration, Preparation, Implementation, Sustainment (EPIS) framework, please review the EPIS Implementation Framework [https://episframework.com website]. | |||
== Implementation Facilitation Capacity Building == | |||
Effective implementation of interventions requires: | |||
# Tailoring implementation processes to individual settings | |||
# Involving multiple stakeholders | |||
# Applying diverse implementation strategies | |||
Implementation facilitation capacity, ie: knowledge and skills, when applied to implementation science can create supportive environments to implement evidence-based rehabilitation interventions. However, implementation facilitation capacity building is also a process (not a single event) that needs to occur in individuals, organisations and systems. In practice, implementation facilitation capacity building is a long-term and iterative process, as much an organisational change process as a technical skill building process. Implementation efforts need to be authorised and supported on an ongoing basis if interventions are to be successfully adopted, implemented and sustained in routine practice. | |||
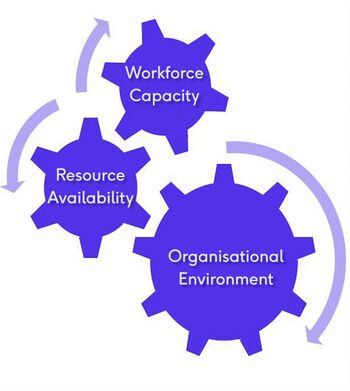
Recognizing the multiple organisational determinants of capacity building can help to build a strong implementation science culture within an organisation. Implementation science evaluators and specialists identify three key determinants of capacity building. | |||
[[File:Key determinants of capacity building.jpg|thumb|391x391px|The three determinants of capacity building]] | |||
'''The three key determinants of capacity building:''' | |||
# '''Organisational environment''': the motivations to develop and plan pre-implementation, implementation, evaluation and sustainment; leadership and trust; conduct and use the implementation evidence; and the existence of a culture of implementation inquiry and learning | |||
# '''Workforce capacity''': the staff skills, abilities and involvement in the design, conduct and evaluation of implementation efforts | |||
# '''Resource availability''': the available and dedicated funding, time and tools to plan, conduct and use implementation evidence to inform adoption, implementation and sustainment of rehabilitation interventions | |||
== Implementation Science Overview '''(KEEP IN?)''' == | |||
This training was developed for rehabilitation professionals working in diverse rehabilitation clinical and strategic leadership sections and roles. The goal is to build implementation science knowledge and skills that can be applied in diverse rehabilitation work environments. <blockquote>'''These specific implementation science skills will enable you to:''' | |||
== Implementation Science Overview == | |||
This training was developed for rehabilitation professionals working in diverse rehabilitation clinical and strategic leadership sections and roles. | |||
* formulate appropriate implementation science questions | * formulate appropriate implementation science questions | ||
| Line 57: | Line 58: | ||
* identify appropriate implementation strategies | * identify appropriate implementation strategies | ||
* identify appropriate implementation process and outcome evaluation questions | * identify appropriate implementation process and outcome evaluation questions | ||
* identify approaches to support the sustainment of your implementation facilitation efforts an interventions | * identify approaches to support the sustainment of your implementation facilitation efforts an interventions | ||
</blockquote><blockquote>'''Overall these implementation science skills will enable you to:''' | |||
Overall these implementation science skills will enable you to: | |||
* inform the design and development of implementation | * inform the design and development of implementation | ||
* review the alignment of implementation efforts with intervention, context and stakeholders needs & experiences | * review the alignment of implementation efforts with intervention, context and stakeholders needs & experiences | ||
* improve the design of rehabilitation intervention implementation processes & activities | * improve the design of rehabilitation intervention implementation processes & activities | ||
* assess the merit, worth and value of implementation efforts | * assess the merit, worth and value of implementation efforts | ||
</blockquote>Implementation is a continuous process with four key stages: [[Implementation Science: Pre-Implementation Stage|pre-implementation]], [[Implementation Science: Implementation Stage|implementation]], [[Implementation Science: Evaluation Stage|evaluation]] and sustainment. | |||
The field of implementation science is rapidly growing, it would be beneficial to review the many additional journals, references and websites that can support an ever more important implementation science facilitation roles and capability. Please see the Resources section below for some suggested references. | |||
The field of implementation science is rapidly growing, | |||
== Summary == | == Summary == | ||
Planning for the sustainment stage needs to start in the pre-implementation planning stage. This includes identifying the determinants or predictors of sustainment as related to organizational and contextual factors and strategies and the outcomes of sustainment of intervention use. Given that sustainment can be influenced by multiple factors, implementation facilitation efforts should be focussed on inner and outer organisational contextual factors that can either enable or hinder implementation sustainment efforts. | |||
== Resources | == Recommended Additional Learning Resources == | ||
'''Online Journals:''' | |||
Journals | |||
* Implementation Science Journal provides a unique, multidisciplinary platform for research on implementation strategies, including their development, outcomes, economics, process by which effects are achieved, and factors associated with implementation outcomes.- [[/implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/|https://implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/]] | * Implementation Science Journal provides a unique, multidisciplinary platform for research on implementation strategies, including their development, outcomes, economics, process by which effects are achieved, and factors associated with implementation outcomes.- [[/implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/|https://implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/]] | ||
* Implementation Research and Practice - is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal publishing interdisciplinary research that advances the implementation of effective approaches to assess, prevent, and treat mental health, substance use, or other addictive behaviors, in the general population or among those at-risk or suffering from these disorders. [[/journals.sagepub.com/home/irp|https://journals.sagepub.com/home/irp]] | * Implementation Research and Practice - is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal publishing interdisciplinary research that advances the implementation of effective approaches to assess, prevent, and treat mental health, substance use, or other addictive behaviors, in the general population or among those at-risk or suffering from these disorders. [[/journals.sagepub.com/home/irp|https://journals.sagepub.com/home/irp]] | ||
'''Journal Articles:''' | |||
* Eccles MP & Mittman BS. (2006). Welcome to Implementation Science. Implementation Science 2006, 1:1 doi:10.1186/1748-5908-1-1. [[/implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/track/pdf/10.1186/1748-5908-1-1.pdf|https://implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/track/pdf/10.1186/1748-5908-1-1.pdf]] | * Eccles MP & Mittman BS. (2006). Welcome to Implementation Science. Implementation Science 2006, 1:1 doi:10.1186/1748-5908-1-1. [[/implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/track/pdf/10.1186/1748-5908-1-1.pdf|https://implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/track/pdf/10.1186/1748-5908-1-1.pdf]] | ||
| Line 107: | Line 88: | ||
* Proctor et al (2012). Writing implementation research grant proposals: ten key ingredients. Implementation Science. 2012; 7:96. [[/www.implementationscience.com/content/7/1/96|http://www.implementationscience.com/content/7/1/96]] | * Proctor et al (2012). Writing implementation research grant proposals: ten key ingredients. Implementation Science. 2012; 7:96. [[/www.implementationscience.com/content/7/1/96|http://www.implementationscience.com/content/7/1/96]] | ||
* Wensing et al. (2020). Implementation Science in time of COVID-19. Implementation Science 15:42 [[/doi.org/10.1186/s13012-020-01006-x|https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-020-01006-x]] | * Wensing et al. (2020). Implementation Science in time of COVID-19. Implementation Science 15:42 [[/doi.org/10.1186/s13012-020-01006-x|https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-020-01006-x]] | ||
Websites | '''Websites:''' | ||
# [[/implementationscience-gacd.org/implementation-science-overview/|https://implementationscience-gacd.org/implementation-science-overview/]] | # [[/implementationscience-gacd.org/implementation-science-overview/|https://implementationscience-gacd.org/implementation-science-overview/]] | ||
Revision as of 04:52, 14 May 2022
Top Contributors - Stacy Schiurring, Kim Jackson and Jess Bell
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Individual, organisational and system readiness and capacity for change are recognised precursors to the successful implementation of complex changes in rehabilitation settings. While implementation science has focused mainly on the initial uptake and use of evidence-based practices, there has been less attention to sustainment of new evidence-based rehabilitation intervention.
Sustainment: the continuous use of these practices, as intended, over time in ongoing operations, often involving adaptation to dynamic contexts. [1]
This article is dedicated to sustaining successful implementation of innovative systems-level rehabilitation interventions using implementation science, to strengthen rehabilitation inclusive health systems.
Sustainability[edit | edit source]
While the concept of sustainability is still maturing across the discipline of implementation science, work in this area has recently acknowledged a useful distinction between sustainability and sustainment:
Sustainability which generally refers to the extent to which an evidence-based intervention can deliver its intended benefits over an extended period of time after external support from the donor agency is terminated. Sustainment which refers to the continued enactment of processes, practices, or work routines that are conveyed and learned through an intervention.
The term ‘sustainment’ will be used here as it keeps with an implementation facilitation practice approach.
Challenges to Implementation Sustainment[edit | edit source]
There are multiple challenges to adopting and implementing evidence-based rehabilitation intervention in lower-middle income countries (LMICs), sustainment of any intervention efforts remains difficult.
Examples of challenges to successful implementation in LMICs:
- cultural differences
- cost barriers
- accessibility
- quality ???
Evidence from LMICs also reveals that the complexity of interventions, inadequate program familiarity, limited human resource, and lack of workplace support for the new interventions, and high staff turnover are key barriers to sustainment.[2] Furthermore, the limited health system capacity, poor application of evidence-based interventions, inadequate involvement of local implementers, and high staff turnover also were reported to hinder the use of public health interventions.[3]
Thinking about sustainment needs to start in the pre-implementation planning stage, specifically, identifying the: determinants or predictors of sustainment as related to organizational and contextual factors and strategies) and the outcomes of sustainment of intervention use. To learn more about the pre-implementation stage, please review this article.
During the Sustainment Phase, the intervention is engrained in the organisation, including stable funding and ongoing monitoring and or quality assurance processes. Sustainment can be influenced by multiple contextual factors, specifically inner and outer contextual factors, that influence the adoption and implementation of interventions. Box 14 provides several key implementation facilitator questions key to the inner and outer context of sustainment.
For more information about the Exploration, Preparation, Implementation, Sustainment (EPIS) framework, please review the EPIS Implementation Framework website.
Implementation Facilitation Capacity Building[edit | edit source]
Effective implementation of interventions requires:
- Tailoring implementation processes to individual settings
- Involving multiple stakeholders
- Applying diverse implementation strategies
Implementation facilitation capacity, ie: knowledge and skills, when applied to implementation science can create supportive environments to implement evidence-based rehabilitation interventions. However, implementation facilitation capacity building is also a process (not a single event) that needs to occur in individuals, organisations and systems. In practice, implementation facilitation capacity building is a long-term and iterative process, as much an organisational change process as a technical skill building process. Implementation efforts need to be authorised and supported on an ongoing basis if interventions are to be successfully adopted, implemented and sustained in routine practice.
Recognizing the multiple organisational determinants of capacity building can help to build a strong implementation science culture within an organisation. Implementation science evaluators and specialists identify three key determinants of capacity building.
The three key determinants of capacity building:
- Organisational environment: the motivations to develop and plan pre-implementation, implementation, evaluation and sustainment; leadership and trust; conduct and use the implementation evidence; and the existence of a culture of implementation inquiry and learning
- Workforce capacity: the staff skills, abilities and involvement in the design, conduct and evaluation of implementation efforts
- Resource availability: the available and dedicated funding, time and tools to plan, conduct and use implementation evidence to inform adoption, implementation and sustainment of rehabilitation interventions
Implementation Science Overview (KEEP IN?)[edit | edit source]
This training was developed for rehabilitation professionals working in diverse rehabilitation clinical and strategic leadership sections and roles. The goal is to build implementation science knowledge and skills that can be applied in diverse rehabilitation work environments.
These specific implementation science skills will enable you to:
- formulate appropriate implementation science questions
- understand the proposed evidence-based intervention through an implementation lens
- understand the context within which the new intervention is to be implemented
- identify and engage key stakeholders in your implementation efforts
- identify appropriate implementation strategies
- identify appropriate implementation process and outcome evaluation questions
- identify approaches to support the sustainment of your implementation facilitation efforts an interventions
Overall these implementation science skills will enable you to:
- inform the design and development of implementation
- review the alignment of implementation efforts with intervention, context and stakeholders needs & experiences
- improve the design of rehabilitation intervention implementation processes & activities
- assess the merit, worth and value of implementation efforts
Implementation is a continuous process with four key stages: pre-implementation, implementation, evaluation and sustainment.
The field of implementation science is rapidly growing, it would be beneficial to review the many additional journals, references and websites that can support an ever more important implementation science facilitation roles and capability. Please see the Resources section below for some suggested references.
Summary[edit | edit source]
Planning for the sustainment stage needs to start in the pre-implementation planning stage. This includes identifying the determinants or predictors of sustainment as related to organizational and contextual factors and strategies and the outcomes of sustainment of intervention use. Given that sustainment can be influenced by multiple factors, implementation facilitation efforts should be focussed on inner and outer organisational contextual factors that can either enable or hinder implementation sustainment efforts.
Recommended Additional Learning Resources[edit | edit source]
Online Journals:
- Implementation Science Journal provides a unique, multidisciplinary platform for research on implementation strategies, including their development, outcomes, economics, process by which effects are achieved, and factors associated with implementation outcomes.- https://implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/
- Implementation Research and Practice - is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal publishing interdisciplinary research that advances the implementation of effective approaches to assess, prevent, and treat mental health, substance use, or other addictive behaviors, in the general population or among those at-risk or suffering from these disorders. https://journals.sagepub.com/home/irp
Journal Articles:
- Eccles MP & Mittman BS. (2006). Welcome to Implementation Science. Implementation Science 2006, 1:1 doi:10.1186/1748-5908-1-1. https://implementationscience.biomedcentral.com/track/pdf/10.1186/1748-5908-1-1.pdf
- Peters et al (2013). Implementation research: what it is and how to do it. BMJ. 2013; 347:f6753. https://www.bmj.com/content/bmj/347/bmj.f6753.full.pdf
- Nilsen (2015). Making sense of implementation theories, models and frameworks. Implementation Science (2015) 10:53 DOI 10.1186/s13012-015-0242-0
- Smith et al (2020). The Implementation Research Logic Model: a method for planning, executing, reporting, and synthesizing implementation projects. Implementation Science (2020) 15:84 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-020-01041-8
- Proctor et al (2012). Writing implementation research grant proposals: ten key ingredients. Implementation Science. 2012; 7:96. http://www.implementationscience.com/content/7/1/96
- Wensing et al. (2020). Implementation Science in time of COVID-19. Implementation Science 15:42 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13012-020-01006-x
Websites:
- https://implementationscience-gacd.org/implementation-science-overview/
- https://impsciuw.org/implementation-science/learn/implementation-science-overview/
- https://cfirguide.org/
- MAC implementation science seminar series https://machaustralia.org/news/implementation-science-series/
- Global Implementation Society. https://globalimplementation.org/
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Birken SA, Haines ER, Hwang S, Chambers DA, Bunger AC, Nilsen P. Advancing understanding and identifying strategies for sustaining evidence-based practices: a review of reviews. Implementation Science. 2020 Dec;15(1):1-3.
- ↑ Hodge LM, Turner KM. Sustained implementation of evidence‐based programs in disadvantaged communities: A conceptual framework of supporting factors. American journal of community psychology. 2016 Sep;58(1-2):192-210.
- ↑ Yamey G. What are the barriers to scaling up health interventions in low and middle income countries? A qualitative study of academic leaders in implementation science. Globalization and health. 2012 Dec;8(1):1-1.