Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Oyemi Sillo (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (194 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | |||
'''Original Editors '''- [http://www.physio-pedia.com/Pathophysiology_of_Complex_Patient_Problems Students from Bellarmine University's Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems project.] | |||
'''Original Editors '''- | |||
'''Top Contributors''' - | '''Top Contributors''' - [http://www.physio-pedia.com/User:Carly_McArtor Carly McArtor] [http://www.physio-pedia.com/User:Krista_Polanin Krista Polanin] and [http://www.physio-pedia.com/User:Elaine_Lonnemann Elaine Lonneman]<br> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Definition/Description == | == Definition/Description == | ||
Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva is a rare, genetic disorder | [[Image:Victor McKusick.jpg|thumb|left|150x200px|Dr. Victor McKusick]] | ||
Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva is a rare, genetic disorder that transforms ligaments, muscles and tendons into bone outside the skeleton that impairs movement.<ref name="Lak" /> It was first described in 1692 and is characterized by progressive heterotropic ossification in anatomic structures. <ref name="IFOP">International Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva Association. 2009. Available at: http://www.ifopa.org/. Accessed March 22, 2016.</ref>At first it was given the name Myositis Ossificans Progressiva which means "muscle that turns to bone." <ref name="IFOP" />The name was later changed to Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva indicating "soft tissue that turns to bone." <ref name="IFOP" />The name Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva means that ligaments and tendons are also turning to bone not just muscle which differentiates it from Myositis Ossificans Progressiva.<ref name="IFOP" />This difference was discovered by Dr. Victor McKusick of Johns Hopkins University in the 1970's. <ref name="IFOP" /><br> | |||
<br> | |||
<br> | |||
== Prevalence == | == Prevalence == | ||
One in every two million people are diagnosed with Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva<ref name="Lak" />. The disease mostly begins in childhood, usually diagnosed before age ten. <ref name="IFOP" /> Nearly 90% of the time the disease is misdiagnosed and mismanaged by physicians or other health care providers.<ref name="Lak" /> However, there have been 800 confirmed cases in the world and 285 in the United States.<ref name="IFOP" /> 67% undergo invasive procedures for diagnosis and treatment such as, an osteotomy, blood sample, or an MRI.<ref name="Lak" /> Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva has not been shown to be linked with any specific gender, ethnicity or race<ref name="IFOP" />. | |||
== Characteristics/Clinical Presentation == | == Characteristics/Clinical Presentation == | ||
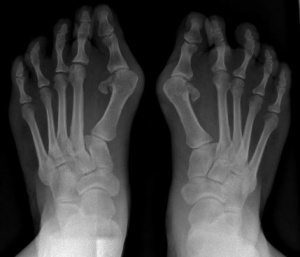
*'''''Congenital hallux valgus with microdactyly and monophalangeal great toe are early signs& | *'''''Congenital hallux valgus with microdactyly and monophalangeal great toe are early signs that are often visible at birth.<ref name="Lak">Lakkireddy M, Chilakamarri V, Ranganath P, Arora A, Vanaja M. Clinical and Genetic Analysis of Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva: A Case Report and Literature Review. Journal Of Clinical & Diagnostic Research [serial online]. August 2015;9(8):1-3. Available from: Academic Search Complete, Ipswich, MA. Accessed March 19, 2016.</ref>'''''[[Image:Hallux valgus.jpg|thumb|Hallux Valgus|alt=]] | ||
*< | *FOP primarily starts at the neck and shoulders then progressively moves to the trunk, back and extremities once the extra bone begins to form.<ref name="Lak" /> | ||
*Ossification of intercostal muscles<ref name="Pig" /> | |||
*Kyphoscoliosis and lordosis<ref name="Abhishek" /> | |||
*Ossification of intercostal muscles | *Severe weight loss <ref name="Lak" /> | ||
*Kyphoscoliosis and lordosis | *Torticollis <ref name="Kap" /> | ||
*Severe weight loss | *[[TMJ Anatomy|TMJ]] complications <ref name="Abhishek" /> | ||
*Torticollis | |||
*TMJ complications< | |||
Flare-ups are usually sporadic and unpredictable. It is impossible to predict duration and severity of the flare-ups even though there has been some | Flare-ups are usually sporadic and unpredictable. It is impossible to predict duration and severity of the flare-ups even though there has been some characteristic patterns described in some research. It is also possible that flare-ups can occur from trauma.<ref name="Pig" /> | ||
'''Acute flare-ups due to:''' intramuscular immunizations, mandibular blocks for dental work, muscle fatigue, blunt muscle trauma from bumps, bruises, falls, influenza-like viral illnesses<ref name="Pig" /> | |||
< | == Prognosis == | ||
The average lifespan of these patients is approximately 40 years. Death is usually caused by respiratory infections or complications with thoracic insufficiency syndrome.<ref name="IFOP" /> Most individuals with FOP are confined to a wheelchair by the second decade of life and require lifelong assistance with performing activities of daily living and more than 50% of people diagnosed with Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva will experience lifelong disabilities.<ref name="Abhishek">Abhishek K, Jain S, Khadgawat R. A case of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva: 20 years of follow-up. Neurology India [serial online]. March 2016;64(2):354-356. Available from: Academic Search Complete, Ipswich, MA. Accessed March 22, 2016.</ref> | |||
== Medications == | == Medications == | ||
There is no proven treatment or medication that will change the history of the disease for people with Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva. Controlling progression of the disease and flare-ups are to be managed by the following: | |||
'''''For acute flare-ups:''''' | '''''For acute flare-ups:''''' | ||
* | *Short term high does corticosteroids<ref name="Lak" /> | ||
*NSAIDS | *NSAIDS<ref name="Lak" /> | ||
*Biophosphonates<br> | *Biophosphonates<ref name="Lak" /><br> | ||
*Radiotherapy | *Radiotherapy<ref name="Lak" /> | ||
'''''For chronic discomfort and ongoing flare-ups:''''' | '''''For chronic discomfort and ongoing flare-ups:''''' | ||
*Cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitors | *Cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitors<ref name="Pig" /> | ||
*Leukotreine inhibitors | *Leukotreine inhibitors<ref name="Pig" /> | ||
*Mast Cell Stabilizers | *Mast Cell Stabilizers<ref name="Pig" /> | ||
== Diagnostic Tests/Lab Tests/Lab Values == | == Diagnostic Tests/Lab Tests/Lab Values == | ||
Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva can be misdiagnosed easily, but can be avoided by examining the individual's toes for the hallux valgus and the short great toe feature, along with a thorough clinical examination and a positive test for the ACVR1 gene.<ref name="Kap" /> Genetic testing can now be done to confirm the diagnosis of FOP before the appearance of heterotropic ossification, which may avoid possible invasive treatments and diagnostic testing.<ref name="Pig" /> <br> | |||
'''Blood Samples''' | '''Blood Samples''' | ||
<div> | |||
*<span style="background-color: rgb(249, 249, 249);">Positive for heterozygous R206H mutation of the ACVR1 gene.<ref name="Lak" /></span> | |||
'''Computed Tomography<ref name="Lak" />''' | |||
''' | '''Magnetic Resonance Imaging<ref name="Lak" />'''<br> | ||
''' | '''Bone Scans<ref name="Lak" />''' | ||
'''ESR elevated during acute flare-ups<ref name="Lak" />''' | |||
</div> | |||
'''ESR elevated during acute flare-ups''' | |||
== Etiology/Causes == | == Etiology/Causes == | ||
*Genetic R206H mutation of the ACVR1 gene | *Genetic R206H mutation of the ACVR1 gene<ref name="Lak" /> | ||
*ACVR1 gene is a bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) type1 receptor signaling endochondral ossification | *ACVR1 gene is a bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) type1 receptor signaling endochondral ossification<ref name="Lak" /> | ||
*R206H mutation leads to an increase in enhanced BMP signaling | *R206H mutation leads to an increase in enhanced BMP signaling<ref name="Lak" /> | ||
*Confirmation of a heterozygous gene mutation of the ACVR1 gene< | *Confirmation of a heterozygous gene mutation of the ACVR1 gene<ref name="Lak" /> | ||
== Systemic Involvement == | == Systemic Involvement == | ||
| Line 76: | Line 81: | ||
'''<u>Cardiopulmonary system</u>''' | '''<u>Cardiopulmonary system</u>''' | ||
* | *Respiratoy problems caused by thoracic insufficiencies (i.e. decreased chest wall expansion)<ref name="Kap" /> | ||
*Restrictive pulmonary diseases< | *Throacic Insufficieny Syndrome, a possible life-threating complication that can cause right sided heart failure and pneumonia. Maximizing pulmonary function and minimizing respiratory complications may be beneficial for these people.<ref name="Pig" /> | ||
*Restrictive pulmonary diseases (i.e. pneumonia)<ref name="Kap">Kaplan FS, Le merrer M, Glaser DL, et al. Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2008;22(1):191-205.</ref> | |||
'''<u> | '''<u>Auditory System</u>'''[[Image:Ossification lower ribs.jpg|thumb|right|223x271px|'''Ossification lower ribs''']] | ||
*Middle ear ossifications | *Middle ear ossifications<ref name="Kap" /> | ||
*Hearing impairments | *Hearing impairments<ref name="Kap" /> | ||
Hearing loss occurs in about half of the people diagnosed with FOP.<ref name="Pig" /> | |||
'''<u>Immune system</u>''' | '''<u>Immune system</u>''' | ||
*Flare-ups following viral infections can occur | *Flare-ups following viral infections can occur<ref name="Kap" /> | ||
*Inflammation | *Inflammation of joints and other structures<ref name="Kap" /> | ||
< | Macrophages, lymphocytes, and mast cells will be present in early lesions of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva.<ref name="Pig">Pignolo RJ, Shore EM, Kaplan FS. Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva: diagnosis, management, and therapeutic horizons. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2013;10 Suppl 2:437-48.</ref> | ||
*Individuals with FOP are 2 times more likely to get kidney stones | <u>'''Renal system'''</u> | ||
*Individuals with FOP are 2 times more likely to get kidney stones<ref name="Pig" /> | |||
*History of UTI, low fiber diet, and decreased water intake may also increase the risk of developing kidney stones in people with FOP.<ref name="Pig" /> | |||
<u>'''Integumentary system<ref name="Ulusoy" />'''</u> | |||
*These individuals are at risk for pressure sores due to the decrease in soft tissue and the increase in bone. | |||
== Medical Management (current best evidence) == | == Medical Management (current best evidence) == | ||
'''''Medications ''''' | '''''Medications<ref name="Pig" /> ''''' | ||
*Reduces the pain and severity of flare-ups<br> | *Reduces the pain and severity of flare-ups, chronic or acute<br> | ||
'''''Surgical release of joint contractures''''' | '''''Surgical release of joint contractures<ref name="Pig" />''''' | ||
*Usually unsuccessful<br> | *Usually unsuccessful and may cause trauma-induced heterotrophic ossificans<br> | ||
'''''Osteotomy of heterotropic bone''''' | '''''Osteotomy of heterotropic bone<ref name="Pig" />''''' | ||
*Mobilizes joints | *Mobilizes joints | ||
*Usually counterproductive because new heterotrophic ossificans can form at the site<br> | *Usually counterproductive because new heterotrophic ossificans can form at the site<br> | ||
'''''Repositioned surgically''''' | '''''Repositioned surgically<ref name="Pig" />''''' | ||
*Improves the patients overall functional status | *Improves the patients overall functional status | ||
*Rare | *Rare<br> | ||
<br> | <u>'''Ultimately, there is not much that can be done to cure this disease. Surgical interventions are associated with numerous complications.<ref name="Pig" />'''</u><br> | ||
[http://clementiapharma.com/ Clementia Pharmaceuticals Inc]. is currently working on a Phase II randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled study that looks at the effect of different doses of palovarotene on bone formation during a flare up and after a flare up. Palovarotene may prevent abnormal bone growth by disrupting the systems in the bone morphogenetic protein path, which allows for new bone formation. The trial uses three outcomes to obtain results from the effect of the drug on people with FOP: imaging for new bone formation, assessments of function, and patient-reported outcomes. | |||
== Physical Therapy Management | == Physical Therapy Management == | ||
Physical therapy has been shown in some cases to make the condition worse in individuals with FOP because it tends to cause flare-ups which eventually leads to further ossification of the ligaments, tendons and muscle.<ref name="IFOP" /> Aquatic therapy, however has been shown to be beneficial in maintaining ROM, pain relief, and aerobic endurance.<ref name="IFOP" /> Aquatic therapy provides low impact and resistance created by the water which ultimately, enhances the ease of activities of daily living, makes functional activities as easy as possible, and implements fall prevention precautions.<ref name="IFOP" /> | |||
== Differential Diagnosis == | == Differential Diagnosis == | ||
Myositis | Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva has been commonly misdiagnosed by physicians with the following diseases: | ||
*'''Myositis Ossficians Progressiva''' | |||
*'''Juvenile Fibromatosis '''connective tissues cells called fibroblasts that invade ligaments, tendons and muscles causing swelling.<ref name="IFOP" /> | |||
*'''[[Lymphoedema]]''' | |||
*'''Soft tissue sarcomas/neoplasms''' there are many doctors that misdiagnose FOP for neoplasms due to the recurrence of soft tissue flare-ups.<ref name="IFOP" /> | |||
== Case Reports/ Case Studies == | == Case Reports/ Case Studies == | ||
*4 year old boy with FOP | |||
Clinical and Genetic Analysis of Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva: A Case Report and Literature Review<ref name="Lak" /><br> | |||
*20 year follow-up of a 23 year old female | |||
A case of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva: 20 years of follow‑up<ref name="Abhishek" /><br> | |||
*29 year old man with onset of sypmtoms at age 9 | |||
<br> | Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva without characteristic Skeletal anomalies<ref name="Ulusoy">Ulusoy H. Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva without characteristic skeletal anomalies. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(5):1379-82.</ref><br> | ||
== Resources == | |||
[[Image:Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva.jpg|left|179x269px|Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva]]'''International Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva Association ''' | |||
== | There is a support group offered to individuals diagnosed with this disorder <span style="line-height: 1.5em; font-size: 13.28px;">called Internation Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva Association. It discusses the latest research, what it is like to live with FOP, and clinical trials. It was founded by Jeannie</span><span style="font-size: 13.28px; line-height: 1.5em;"> Peeper who has FOP. She wanted to end social isolation.<ref name="IFOP" /> IFOPA's "Mission of Hope" http://www.ifopa.org/component/content/article/33/105.html | ||
</span> | |||
<br> | |||
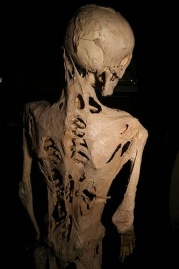
'''Henry Eastlack Skeleton '''<br> Henry Eastlack was a gentlemen who suffered and died from FOP. His <span style="line-height: 1.5em; font-size: 13.28px;">skeleton is now on display at The Mutter Museum of The College of </span>Physicians in Philadelphia. When individuals die their skeleton falls apart because the connective tissue, ligaments and tendons are no longer holding their skeleton together. When a skeleton is put on display at a museum it has to meticulously be rearticulated with wires and glue. Henry's skeleton never had to be rearticulated because of the extra bone created by FOP. His skeleton truly shows the harsh reality of FOP and the dysfunctions it can create.<ref name="IFOP" /> | |||
<br> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | |||
[[Category:Musculoskeletal/Orthopaedics]] | |||
[[Category:Genetic Disorders]] | |||
[[Category:Conditions]] | |||
Latest revision as of 03:28, 24 April 2022
Original Editors - Students from Bellarmine University's Pathophysiology of Complex Patient Problems project.
Top Contributors - Carly McArtor Krista Polanin and Elaine Lonneman
Definition/Description[edit | edit source]
Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva is a rare, genetic disorder that transforms ligaments, muscles and tendons into bone outside the skeleton that impairs movement.[1] It was first described in 1692 and is characterized by progressive heterotropic ossification in anatomic structures. [2]At first it was given the name Myositis Ossificans Progressiva which means "muscle that turns to bone." [2]The name was later changed to Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva indicating "soft tissue that turns to bone." [2]The name Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva means that ligaments and tendons are also turning to bone not just muscle which differentiates it from Myositis Ossificans Progressiva.[2]This difference was discovered by Dr. Victor McKusick of Johns Hopkins University in the 1970's. [2]
Prevalence[edit | edit source]
One in every two million people are diagnosed with Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva[1]. The disease mostly begins in childhood, usually diagnosed before age ten. [2] Nearly 90% of the time the disease is misdiagnosed and mismanaged by physicians or other health care providers.[1] However, there have been 800 confirmed cases in the world and 285 in the United States.[2] 67% undergo invasive procedures for diagnosis and treatment such as, an osteotomy, blood sample, or an MRI.[1] Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva has not been shown to be linked with any specific gender, ethnicity or race[2].
Characteristics/Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
- Congenital hallux valgus with microdactyly and monophalangeal great toe are early signs that are often visible at birth.[1]
- FOP primarily starts at the neck and shoulders then progressively moves to the trunk, back and extremities once the extra bone begins to form.[1]
- Ossification of intercostal muscles[3]
- Kyphoscoliosis and lordosis[4]
- Severe weight loss [1]
- Torticollis [5]
- TMJ complications [4]
Flare-ups are usually sporadic and unpredictable. It is impossible to predict duration and severity of the flare-ups even though there has been some characteristic patterns described in some research. It is also possible that flare-ups can occur from trauma.[3]
Acute flare-ups due to: intramuscular immunizations, mandibular blocks for dental work, muscle fatigue, blunt muscle trauma from bumps, bruises, falls, influenza-like viral illnesses[3]
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The average lifespan of these patients is approximately 40 years. Death is usually caused by respiratory infections or complications with thoracic insufficiency syndrome.[2] Most individuals with FOP are confined to a wheelchair by the second decade of life and require lifelong assistance with performing activities of daily living and more than 50% of people diagnosed with Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva will experience lifelong disabilities.[4]
Medications[edit | edit source]
There is no proven treatment or medication that will change the history of the disease for people with Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva. Controlling progression of the disease and flare-ups are to be managed by the following:
For acute flare-ups:
- Radiotherapy[1]
For chronic discomfort and ongoing flare-ups:
Diagnostic Tests/Lab Tests/Lab Values[edit | edit source]
Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva can be misdiagnosed easily, but can be avoided by examining the individual's toes for the hallux valgus and the short great toe feature, along with a thorough clinical examination and a positive test for the ACVR1 gene.[5] Genetic testing can now be done to confirm the diagnosis of FOP before the appearance of heterotropic ossification, which may avoid possible invasive treatments and diagnostic testing.[3]
Blood Samples
- Positive for heterozygous R206H mutation of the ACVR1 gene.[1]
Computed Tomography[1]
Magnetic Resonance Imaging[1]
Bone Scans[1]
ESR elevated during acute flare-ups[1]
Etiology/Causes[edit | edit source]
- Genetic R206H mutation of the ACVR1 gene[1]
- ACVR1 gene is a bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) type1 receptor signaling endochondral ossification[1]
- R206H mutation leads to an increase in enhanced BMP signaling[1]
- Confirmation of a heterozygous gene mutation of the ACVR1 gene[1]
Systemic Involvement[edit | edit source]
Cardiopulmonary system
- Respiratoy problems caused by thoracic insufficiencies (i.e. decreased chest wall expansion)[5]
- Throacic Insufficieny Syndrome, a possible life-threating complication that can cause right sided heart failure and pneumonia. Maximizing pulmonary function and minimizing respiratory complications may be beneficial for these people.[3]
- Restrictive pulmonary diseases (i.e. pneumonia)[5]
Auditory System
Hearing loss occurs in about half of the people diagnosed with FOP.[3]
Immune system
Macrophages, lymphocytes, and mast cells will be present in early lesions of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva.[3]
Renal system
- Individuals with FOP are 2 times more likely to get kidney stones[3]
- History of UTI, low fiber diet, and decreased water intake may also increase the risk of developing kidney stones in people with FOP.[3]
Integumentary system[6]
- These individuals are at risk for pressure sores due to the decrease in soft tissue and the increase in bone.
Medical Management (current best evidence)[edit | edit source]
Medications[3]
- Reduces the pain and severity of flare-ups, chronic or acute
Surgical release of joint contractures[3]
- Usually unsuccessful and may cause trauma-induced heterotrophic ossificans
Osteotomy of heterotropic bone[3]
- Mobilizes joints
- Usually counterproductive because new heterotrophic ossificans can form at the site
Repositioned surgically[3]
- Improves the patients overall functional status
- Rare
Ultimately, there is not much that can be done to cure this disease. Surgical interventions are associated with numerous complications.[3]
Clementia Pharmaceuticals Inc. is currently working on a Phase II randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled study that looks at the effect of different doses of palovarotene on bone formation during a flare up and after a flare up. Palovarotene may prevent abnormal bone growth by disrupting the systems in the bone morphogenetic protein path, which allows for new bone formation. The trial uses three outcomes to obtain results from the effect of the drug on people with FOP: imaging for new bone formation, assessments of function, and patient-reported outcomes.
Physical Therapy Management[edit | edit source]
Physical therapy has been shown in some cases to make the condition worse in individuals with FOP because it tends to cause flare-ups which eventually leads to further ossification of the ligaments, tendons and muscle.[2] Aquatic therapy, however has been shown to be beneficial in maintaining ROM, pain relief, and aerobic endurance.[2] Aquatic therapy provides low impact and resistance created by the water which ultimately, enhances the ease of activities of daily living, makes functional activities as easy as possible, and implements fall prevention precautions.[2]
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva has been commonly misdiagnosed by physicians with the following diseases:
- Myositis Ossficians Progressiva
- Juvenile Fibromatosis connective tissues cells called fibroblasts that invade ligaments, tendons and muscles causing swelling.[2]
- Lymphoedema
- Soft tissue sarcomas/neoplasms there are many doctors that misdiagnose FOP for neoplasms due to the recurrence of soft tissue flare-ups.[2]
Case Reports/ Case Studies[edit | edit source]
- 4 year old boy with FOP
Clinical and Genetic Analysis of Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva: A Case Report and Literature Review[1]
- 20 year follow-up of a 23 year old female
A case of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva: 20 years of follow‑up[4]
- 29 year old man with onset of sypmtoms at age 9
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva without characteristic Skeletal anomalies[6]
Resources[edit | edit source]
International Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva Association
There is a support group offered to individuals diagnosed with this disorder called Internation Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva Association. It discusses the latest research, what it is like to live with FOP, and clinical trials. It was founded by Jeannie Peeper who has FOP. She wanted to end social isolation.[2] IFOPA's "Mission of Hope" http://www.ifopa.org/component/content/article/33/105.html
Henry Eastlack Skeleton
Henry Eastlack was a gentlemen who suffered and died from FOP. His skeleton is now on display at The Mutter Museum of The College of Physicians in Philadelphia. When individuals die their skeleton falls apart because the connective tissue, ligaments and tendons are no longer holding their skeleton together. When a skeleton is put on display at a museum it has to meticulously be rearticulated with wires and glue. Henry's skeleton never had to be rearticulated because of the extra bone created by FOP. His skeleton truly shows the harsh reality of FOP and the dysfunctions it can create.[2]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 Lakkireddy M, Chilakamarri V, Ranganath P, Arora A, Vanaja M. Clinical and Genetic Analysis of Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva: A Case Report and Literature Review. Journal Of Clinical & Diagnostic Research [serial online]. August 2015;9(8):1-3. Available from: Academic Search Complete, Ipswich, MA. Accessed March 19, 2016.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 International Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva Association. 2009. Available at: http://www.ifopa.org/. Accessed March 22, 2016.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 3.13 3.14 3.15 3.16 Pignolo RJ, Shore EM, Kaplan FS. Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva: diagnosis, management, and therapeutic horizons. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2013;10 Suppl 2:437-48.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Abhishek K, Jain S, Khadgawat R. A case of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva: 20 years of follow-up. Neurology India [serial online]. March 2016;64(2):354-356. Available from: Academic Search Complete, Ipswich, MA. Accessed March 22, 2016.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 Kaplan FS, Le merrer M, Glaser DL, et al. Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2008;22(1):191-205.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Ulusoy H. Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva without characteristic skeletal anomalies. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(5):1379-82.