Dopamine: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
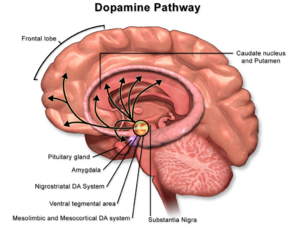
[[File:Dopamine Pathway.png|thumb|Dopamine pathway]] | Dopamine is a neurotransmitter associated with movement, attention, learning, and the brain’s pleasure and reward system<ref>Wiktionary Dopamine Available: https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/dopamine<nowiki/>(accessed 16.4.2022)</ref>. Dopamine works by primarily by inhibiting the transmission of nerve impulses in the substantia nigra, basal ganglia, and corpus striatum of the brain. | ||
A deficiency of dopamine associated with cellular death in the substantia nigra results in Parkinson disease. Dopamine-receptor agonists, which bind to dopamine receptors on dopamine-producing neurons in the neurotransmitter’s absence, can increase dopaminergic activity in the brain, helping to lessen Parkinson symptoms<ref name=":0">Britannice Dopamine Available:https://www.britannica.com/science/dopamine (accessed 16.4.2022)</ref>. | |||
Abnormalities in dopamine transmission, including hyperactive dopamine transmission in certain parts of the brain, have been linked to psychotic syndromes such as schizophrenia. Dopaminergic structures within the brain, such as the striatum and nucleus accumbens, have also been implicated in reward-related behaviour.<ref name=":0" />[[File:Dopamine Pathway.png|thumb|Dopamine pathway]] | |||
== Sub Heading 2 == | == Sub Heading 2 == | ||
Revision as of 01:53, 16 April 2022
Original Editor - Lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Nikhil Benhur Abburi and Tolulope Adeniji
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter associated with movement, attention, learning, and the brain’s pleasure and reward system[1]. Dopamine works by primarily by inhibiting the transmission of nerve impulses in the substantia nigra, basal ganglia, and corpus striatum of the brain.
A deficiency of dopamine associated with cellular death in the substantia nigra results in Parkinson disease. Dopamine-receptor agonists, which bind to dopamine receptors on dopamine-producing neurons in the neurotransmitter’s absence, can increase dopaminergic activity in the brain, helping to lessen Parkinson symptoms[2].
Abnormalities in dopamine transmission, including hyperactive dopamine transmission in certain parts of the brain, have been linked to psychotic syndromes such as schizophrenia. Dopaminergic structures within the brain, such as the striatum and nucleus accumbens, have also been implicated in reward-related behaviour.[2]
Sub Heading 2[edit | edit source]
Sub Heading 3[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Wiktionary Dopamine Available: https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/dopamine(accessed 16.4.2022)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Britannice Dopamine Available:https://www.britannica.com/science/dopamine (accessed 16.4.2022)