Adipose Tissue: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
[[File:AdiposeTissue.png|right|frameless]] | [[File:AdiposeTissue.png|right|frameless|alt=|399x399px]] | ||
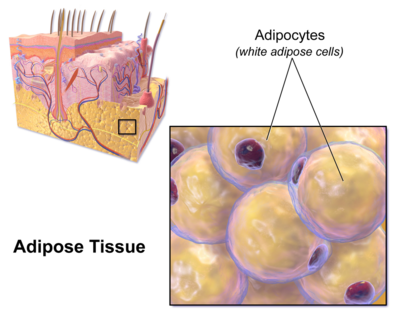
The more technical term for body fat is adipose tissue, with individual cells being called adipocytes. | The more technical term for body fat is adipose tissue. It is a loose connective tissue composed of fat cells, with individual cells being called adipocytes. <ref>Body Composition [https://bodyrecomposition.com/fat-loss/what-is-body-fat What is body fat] Available: https://bodyrecomposition.com/fat-loss/what-is-body-fat (accessed 12.11.2021)</ref> | ||
'''Image 1: Adipose tissue''' | |||
Adipocytes contain lipid droplets of stored triglycerides. These cells swell as they store fat and shrink when the fat is used for energy. | |||
Adipose tissue helps to store energy in the form of fat, cushion internal organs, and insulate the body. | |||
There are three types of adipose tissue: white, brown, and beige adipose. | |||
# White adipose stores energy and helps to insulate the body. | |||
# Brown and beige adipose tissue burn energy and generate heat. Their colour is derived from the abundance of [[Arteries|blood vessels]] and [[mitochondria]] in the tissue. | |||
Adipose tissue also produces [[hormones]], such as adiponectin, which help to burn fat and reduce body weight.<ref>Thought co [https://www.thoughtco.com/adipose-tissue-373191 Adipose tissue] Available: https://www.thoughtco.com/adipose-tissue-373191<nowiki/>(accessed 12.11.2021)</ref> | |||
== Sub Heading 2 == | == Sub Heading 2 == | ||
Revision as of 05:41, 12 November 2021
Original Editor - lucinda hampton
Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton, Kim Jackson, Vidya Acharya and Sai Kripa
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The more technical term for body fat is adipose tissue. It is a loose connective tissue composed of fat cells, with individual cells being called adipocytes. [1]
Image 1: Adipose tissue
Adipocytes contain lipid droplets of stored triglycerides. These cells swell as they store fat and shrink when the fat is used for energy.
Adipose tissue helps to store energy in the form of fat, cushion internal organs, and insulate the body.
There are three types of adipose tissue: white, brown, and beige adipose.
- White adipose stores energy and helps to insulate the body.
- Brown and beige adipose tissue burn energy and generate heat. Their colour is derived from the abundance of blood vessels and mitochondria in the tissue.
Adipose tissue also produces hormones, such as adiponectin, which help to burn fat and reduce body weight.[2]
Sub Heading 2[edit | edit source]
Sub Heading 3[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- bulleted list
- x
or
- numbered list
- x
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Body Composition What is body fat Available: https://bodyrecomposition.com/fat-loss/what-is-body-fat (accessed 12.11.2021)
- ↑ Thought co Adipose tissue Available: https://www.thoughtco.com/adipose-tissue-373191(accessed 12.11.2021)