Obstructed Defecation Syndrome: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<div class="noeditbox">This article or area is currently under construction and may only be partially complete. Please come back soon to see the finished work! ({{REVISIONDAY}}/{{REVISIONMONTH}}/{{REVISIONYEAR}})</div> | <div class="noeditbox">This article or area is currently under construction and may only be partially complete. Please come back soon to see the finished work! ({{REVISIONDAY}}/{{REVISIONMONTH}}/{{REVISIONYEAR}})</div> | ||
== Clinically Relevant Anatomy == | == Clinically Relevant Anatomy == | ||
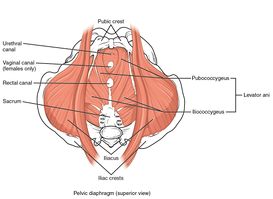
[[File:1115 Muscles of the Pelvic Floor.jpg|thumb]] | [[File:1115 Muscles of the Pelvic Floor.jpg|thumb|273x273px]] | ||
The [[Levator Ani Muscle|levator ani]] muscles as a component of pelvic floor diaphragm ( the iliococcygeus, the pubococcygeal, and the puborectalis muscles) in addition to its role as a supportive structure and keeping visceral and internal organs in place. levator ani muscles specifically puborectalis have a role to maintain the urinary and fecal continence, contraction, and relaxation of puborectalis, lower abdominal muscles, and anal sphincter work synchronically for normal and smooth defecation. | The [[Levator Ani Muscle|levator ani]] muscles as a component of pelvic floor diaphragm ( the iliococcygeus, the pubococcygeal, and the puborectalis muscles) in addition to its role as a supportive structure and keeping visceral and internal organs in place. levator ani muscles specifically puborectalis have a role to maintain the urinary and fecal continence, contraction, and relaxation of puborectalis, lower abdominal muscles, and anal sphincter work synchronically for normal and smooth defecation. | ||
[[File:Pudendal Nerve.png|thumb| | [[File:Pudendal Nerve.png|thumb|270x270px|Pudendal nerve]] | ||
The pudendal nerve innervates the external anal sphincter and part of the puborectalis muscle, with frequent and prolonged straining that may stretch the pudendal nerve causing [[Pudendal Neuralgia|pudendal neuropathy]]. | The pudendal nerve innervates the external anal sphincter and part of the puborectalis muscle, with frequent and prolonged straining that may stretch the pudendal nerve causing [[Pudendal Neuralgia|pudendal neuropathy]]. | ||
<br> | While we have voluntary control over the external anal sphincter the internal anal sphincter muscles are involuntary muscles affected by the rectum, it is relaxed if the rectum filled with stool and vice versa, so the sensitivity of the rectum is important for normal physiology.<br> | ||
== Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process == | == Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process == | ||
Revision as of 00:04, 21 April 2021
Top Contributors - Khloud Shreif, Temitope Olowoyeye, Kim Jackson and Aminat Abolade
Clinically Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The levator ani muscles as a component of pelvic floor diaphragm ( the iliococcygeus, the pubococcygeal, and the puborectalis muscles) in addition to its role as a supportive structure and keeping visceral and internal organs in place. levator ani muscles specifically puborectalis have a role to maintain the urinary and fecal continence, contraction, and relaxation of puborectalis, lower abdominal muscles, and anal sphincter work synchronically for normal and smooth defecation.
The pudendal nerve innervates the external anal sphincter and part of the puborectalis muscle, with frequent and prolonged straining that may stretch the pudendal nerve causing pudendal neuropathy.
While we have voluntary control over the external anal sphincter the internal anal sphincter muscles are involuntary muscles affected by the rectum, it is relaxed if the rectum filled with stool and vice versa, so the sensitivity of the rectum is important for normal physiology.
Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the mechanism of injury and/or pathology of the condition
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the clinical presentation of the condition
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to diagnostic tests for the condition
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
add links to outcome measures here (see Outcome Measures Database)
Management / Interventions[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to management approaches to the condition
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
add text here relating to the differential diagnosis of this condition
Resources[edit | edit source]
add appropriate resources here