The emerging role of Microsoft Kinect in physiotherapy rehabilitation for stroke patients: Difference between revisions
Nicole Bell (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Karen Feeney (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br>Virtual Reality, is a clinically validated physical rehabilitation system based on video games and motion capture technology. It was developed to treat patients suffering from various conditions and pathologies. Neurodegenerative disease (Multiple Sclerosis & Parkinson's disease) Neuromuscular disorders ( Dystrophies, myopathies) and Neurovascular disorders/Trauma (Stroke and traumatic brain injuries) also to improve mobility of the elderly.<br> <br>The result was a game developed in 2012 in Virtual Rehab to test out the possibilities of using video games as a complementary rehabilitation tool. The patient interacts with the system in a 3D environment, where they perform multiple movement combinations without the need of an attached device or a controller thanks to the Kinect.<br> <br>VirtualRehab is tackling major issues related to rehabilitation. Not only is it providing a rehabilitation service which improves adherence to treatment by adding fun and entertaining features, but it also reduces the high cost associated with traditional rehabilitation making it more affordable and accessible to everyone.<ref name="Microsoft Developers">Microsoft. UK Developers. 2014 [cited 05 Nov 2015]. Available from: http://www.microsoft.com/en-gb/developers/articles/week05may14/how-the-kinect-azure-and-gamification-are-helping-virtualrehab-to-rehabilitate-patients-worldwide/</ref><br> <br>Ideally, all stroke rehabilitation exercises would be performed with a therapist in a clinical setting on a daily basis with a recommended session of 45min per patient. However, this demand within hospitals is becoming increasing difficult and logistically impractical.<ref name="NICE">National Institute for Health and Care Excelance. NICE. 2013 [cited 05 Nov 2015]. Available from:(https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG162/chapter/Key-priorities-for-implementation#the-core-multidisciplinary-stroke-team)</ref><br> <br>Microsoft Kinect is the forerunner in commercially available hardware in which development of these new technologies can be built. Information on how it works? What is does? And an insight into Virtual Rehab developed by Microsoft Kinect for the use of stroke patients will be discussed.<ref name="Microsoft Developers" /><br> | <br>Virtual Reality, is a clinically validated physical rehabilitation system based on video games and motion capture technology. It was developed to treat patients suffering from various conditions and pathologies. Neurodegenerative disease (Multiple Sclerosis & Parkinson's disease) Neuromuscular disorders ( Dystrophies, myopathies) and Neurovascular disorders/Trauma (Stroke and traumatic brain injuries) also to improve mobility of the elderly.<br> <br>The result was a game developed in 2012 in Virtual Rehab to test out the possibilities of using video games as a complementary rehabilitation tool. The patient interacts with the system in a 3D environment, where they perform multiple movement combinations without the need of an attached device or a controller thanks to the Kinect.<br> <br>VirtualRehab is tackling major issues related to rehabilitation. Not only is it providing a rehabilitation service which improves adherence to treatment by adding fun and entertaining features, but it also reduces the high cost associated with traditional rehabilitation making it more affordable and accessible to everyone.<ref name="Microsoft Developers">Microsoft. UK Developers. 2014 [cited 05 Nov 2015]. Available from: http://www.microsoft.com/en-gb/developers/articles/week05may14/how-the-kinect-azure-and-gamification-are-helping-virtualrehab-to-rehabilitate-patients-worldwide/</ref><br> <br>Ideally, all stroke rehabilitation exercises would be performed with a therapist in a clinical setting on a daily basis with a recommended session of 45min per patient. However, this demand within hospitals is becoming increasing difficult and logistically impractical.<ref name="NICE">National Institute for Health and Care Excelance. NICE. 2013 [cited 05 Nov 2015]. Available from:(https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG162/chapter/Key-priorities-for-implementation#the-core-multidisciplinary-stroke-team)</ref><br> <br>Microsoft Kinect is the forerunner in commercially available hardware in which development of these new technologies can be built. Information on how it works? What is does? And an insight into Virtual Rehab developed by Microsoft Kinect for the use of stroke patients will be discussed.<ref name="Microsoft Developers" /><br> | ||
| Line 201: | Line 192: | ||
== Performing Rehabilitation at Home == | == Performing Rehabilitation at Home == | ||
== Skills and Knowledge Required == | == Skills and Knowledge Required == | ||
=== Continuous Professional Development === | |||
= Assessment of stroke patients for the use of Microsoft Kinect = | = Assessment of stroke patients for the use of Microsoft Kinect = | ||
Revision as of 19:50, 17 November 2015
Original Editor - Karen Feeney, Kate Reidy, Nicole Bell, Sally Wood and Joanne Knowles as part of the QMU Current and Emerging Roles in Physiotherapy Practice Project
Top Contributors - Sally Wood, Kate Reidy, Nicole Bell, Karen Feeney, Hannah Meredith, Leana Louw, Kim Jackson, Joanne Knowles, Naomi O'Reilly, 127.0.0.1, Admin, Chee Wee Tan, Evan Thomas and Michelle Lee
Introduction:Where it all began[edit | edit source]
1.0 Introduction
The median age of the general population is projected to significantly rise in upcoming years. This causes much added stress for clinics and hospitals. Stroke is a significant risk factor with age and the need for new rehabilitation is on demand. Technology and its advanced methods are continuously being assessed so that they can be used in a private, home-based setting while still providing rehabilitation instructions and progress tracking. This area of rehabilitation technology is expected to expand and will do so over the current year's [1]
(Levac et al., 2014).[2]
Virtual Reality, is a clinically validated physical rehabilitation system based on video games and motion capture technology. It was developed to treat patients suffering from various conditions and pathologies. Neurodegenerative disease (Multiple Sclerosis & Parkinson's disease) Neuromuscular disorders ( Dystrophies, myopathies) and Neurovascular disorders/Trauma (Stroke and traumatic brain injuries) also to improve mobility of the elderly.
The result was a game developed in 2012 in Virtual Rehab to test out the possibilities of using video games as a complementary rehabilitation tool. The patient interacts with the system in a 3D environment, where they perform multiple movement combinations without the need of an attached device or a controller thanks to the Kinect.
VirtualRehab is tackling major issues related to rehabilitation. Not only is it providing a rehabilitation service which improves adherence to treatment by adding fun and entertaining features, but it also reduces the high cost associated with traditional rehabilitation making it more affordable and accessible to everyone.[3]
Ideally, all stroke rehabilitation exercises would be performed with a therapist in a clinical setting on a daily basis with a recommended session of 45min per patient. However, this demand within hospitals is becoming increasing difficult and logistically impractical.[4]
Microsoft Kinect is the forerunner in commercially available hardware in which development of these new technologies can be built. Information on how it works? What is does? And an insight into Virtual Rehab developed by Microsoft Kinect for the use of stroke patients will be discussed.[3]
Words: Microsoft Kinect, Virtual Rehab, Rehabilitation, Stroke
Audience[edit | edit source]
This resource is designed to provide physiotherapists with an insight into Microsoft Kinect and its use in stroke rehabilitation.
Learning outcomes [edit | edit source]
L1 - Identify and justify the knowledge and reasoning behind the use of motion sensor technology in physiotherapy practice for the rehabilitation of stroke patients.
L2 - Critically evaluate the evidence behind motion sensor technology in the rehab of stroke patients
L3 - Justify the use of Microsoft Kinect and how this benefits patient outcomes.
L4 - Outline the key knowledge physiotherapists will need to work with motion sensor technology in the rehab of stroke patients in the future
Why sensors in healthcare are about to have their moment[edit | edit source]
What is Microsoft Kinect [edit | edit source]
Kinect derived from the meaning of the word kinetic (meaning to produce movement).
Microsoft's Kinect is described as a "controller-free gaming and entertainment experience" and is commonly sold bundled with the Xbox 360. However, to see it as only a way to play games would underestimate its significance and brilliance.[5]
A computer based gaming systems such as Microsoft Kinect (Kinect), can facilitate complex task practice, enhance sensory and motor feedback, and provide visually observed technique for the user.
The Kinect is currently the hardware that provides developers with the greatest opportunities for innovative programs - for both games and applications.
Essentially this hardware is a box with some cameras that makes use of infra-red (IR) illumination to obtain depth data, colour images and sound. The Kinect system can identify players through face and voice recognition. Kinect can "see" in 3-D and creates a skeleton image of the player and a motion sensor detects movement.[6]
Recap of Stroke and Current stroke Rehab
[edit | edit source]
Demands placed on physiotherapy rehabilitation services [edit | edit source]
Stroke occurs approximately 152,000 times a year in the UK; that is one every 3 minutes 27 seconds (State Association., 2015). As people are living longer the number of sufferers will continue to increase, making cost effective community rehabilitation a higher priority. Stroke is the largest cause of complex disability with half of stroke survivors being left with residual disability. Globally the challenge of providing quality, affordable health care has never been so crucial in stroke rehabilitation. The number of sessions that stroke survivors attend are limited to the availability of a clinic close to their residence and the amount of time friends and family can devote to help them commute, as most are incapable of driving.With the high prevalence rate of stroke this puts increased demand on physiotherapists to treat each patient both in hospital and after discharge. Although many people with stroke receive early rehabilitation, many are left dissatisfied with the way they are followed up and the level of rehabilitation provided in the year following the stroke. Due to time restraints and prioritisation of patients they can be pushed further down the rehabilitation follow up list. Another challenge to effective rehabilitation is insufficient completion of rehabilitation exercises by patients which severely reduces the potential outcome of overall motor recovery. Exercises are often unpleasant, and tedious leading to patient's tolerance for exercise to decline. Patients are often dependent on one-to-one rehabilitation services provided by physiotherapists to help regain their functional ability. It is widely recognised that a strong rehabilitation service is the most effective and efficient way of addressing these growing issues which can be addressed through technologically advanced methods.
How Microsoft kinect can help
[edit | edit source]
Microsoft kinect can: :
- Provide flexibility in delivering individualised physiotherapy in the patient's home.
- Involve carers more within the rehabilitative process.
- Help the NHS meet National Clinical Guidelines on physiotherapy interventions for stroke suffers (45 minutes per day of treatment during the acute phase).
- Improve patient engagement through stimulating rehabilitation.
- Be a low cost rehabilitation tool.
- Reduce the need for expensive one-to-one clinical contact.
- Provide a range of indirect savings due to improved rehabilitation of patient.
Question Time
[edit | edit source]
- Name three ways in which Microsoft Kinect can help in the rehabilitation of stroke patients
- What are the main contributing factors which increase demands on the healthcare system at present?
- What is the recommended daily treatment time for patients in the acute phase of stroke rehabilitation?
Stroke and the need for intensive rehabilitation[edit | edit source]
Physiotherapy plays a key role in the rehabilitation of those affected by stroke and is needed in order to aid patients through their journey of recovery. Physiotherapy in stroke rehabilitation typically aims to strengthen and retrain muscles to regain lost limb function and improve quality of life.
Through studies of motor learning and motor control evidence shows that for effective learning and muscle re-education to take place practice of exercises needs to be intensive and frequent (McBean et al 2013). The most rapid recovery occurs within the first 3 months post stroke and therefore during this time frame patients need intensive rehabilitation therapy. Unfortunately, currently in most NHS hospitals stroke patients receive approximately 7.5hours of physiotherapy rehabilitation per week and when discharged patients receive on average 1-2 hours of community rehabilitation per week. Additionally, the current Early supported discharge (ESD) plan, for stroke patients with mild to moderate disability, only runs for on average 6 weeks (Stroke Association, 2015). Due to the current economic status of the NHS this is not likely to improve therefore more intensive rehabilitation strategies need to be introduced in order to improve outcomes for stroke patients.
Patients are being discharged from hospital earlier and earlier as there is a need to free up hospital beds which often leaves patients with fewer hours of physiotherapy rehabilitation. There is therefore a need for cost effective, intensive home based physiotherapy programmes which retrain and re-educate muscles in stroke patients.
Is Microsoft Kinect the answer?
Microsoft Kinect allows intensive stroke rehabilitation to take place in the home environment as well as taking pressure off health providers as patients can perform this type of rehabilitation on there own.
Stroke and Microsoft Kinect: Background[edit | edit source]
The demand for technologically advanced home-based rehabilitation which allows therapists to track progression is expected to expand. Microsoft Kinect is the leading commercially available hardware which can be developed to meet these needs while simultaneously maintaining affordability.
In an ideal world, stroke rehabilitation would take place with one to one therapist-patient interaction on a daily basis, however, as mentioned previously the demands on both the NHS and physiotherapists makes this dream difficult to achieve. Through guided interactive rehabilitation and the ability for therapists to track progress, the Kinect-based stroke rehabilitation programmes potentially reduce these difficulties on demand. The accuracy of the Kinect for clinical use in stroke rehabilitation is strong, allowing therapist assisted home-based rehab to become a reality. The Kinects ability to allow therapists to track progress and give feedback may not only enhance rehabilitation, but also improve medical record keeping (Webster et al 2014).
Some useful statistics as well as facts and current care pathway information can be found here:
www.stroke.org.uk/sites/default/files/stroke_statistics_2015.pdf
Question Time:[edit | edit source]
- Using the Stroke Association link above find out how many hospital beds on average are taken up by stroke patients
- Using the Stroke Association link above find out what percentage hospitals have access to ESD service
a.What do you think the implications of this are?
b.How do you think microsoft kinect could help?
Microsoft Kinect[edit | edit source]
What is Microsoft Kinect?[edit | edit source]
VirtualRehab[edit | edit source]
How does it work?[edit | edit source]
Pros[edit | edit source]
VirtualRehab in action[edit | edit source]
Did you know?[edit | edit source]
Jintronix
[edit | edit source]
Pros for clinicians[edit | edit source]
Jintronix in action[edit | edit source]
Using video games for better medical rehabilitation: Justin Tan at TEDxMontreal[edit | edit source]
Question time:[edit | edit source]
Key points[edit | edit source]
Research available
[edit | edit source]
Advantages and disadvantages of Microsoft Kinect[edit | edit source]
Advantages[edit | edit source]
- Intensive therapy that has high potential in rehabilitation of stroke – rehab can be carried out at home
- Inexpensive tool compared to long term rehabilitation sessions - retails at £ 129.99 for xbox and £199.99 for Microsoft.
- The accuracy of Kinect for clinical use is strong (Obdrzalek et al., 2012).
- Provides instant feedback to both patients and physiotherapists
- Kinect is an acceptable and affordable depth sensor for rehabilitation purposes- good accuracy and reliability (Kurillo et al. 2013 and Bonnechere et al. 2014).
- Can increase motivation levels to complete home exercise programmes since they can be viewed as a fun activity (Chang 2011).
- Does not require the use of any devices attached to the body or held onto by hand (i.e. motion sensors, hand-held remotes, standing on an object, etc.)
Disadvantages[edit | edit source]
- From a patient's perspective they may be reluctant to change and use this device.
- Games targeted at rehabilitation may be prone to “cheating” (e.g. excessive, unnatural and counter-productive trunk-based compensation).
- The current benefits of Kinect-based gaming have only tentatively been studied with mainly short term and small sample sized studies.
- Not all clinics or patients will have a Kinect available for use ( required to purchase one)
- Software is still in development
- Physiotherapists we will require training to learn how to use the Kinect (especially how to develop a patient’s home exercise programme through the Kinect).
- Social problem – patients may become house bound with their rehabilitation programme and become excluded from society.
Question time[edit | edit source]
- Name 3 advantages and 3 disadvantages of Microsoft Kinect.
- From a physiotherapist's perspective can you think of any other potential advantages / disadvantages that may be of concern?
- As a physiotherapist would you be willing to increase your knowledge about Microsoft Kinect's potential use in rehabilitation? Does its use appeal to you?
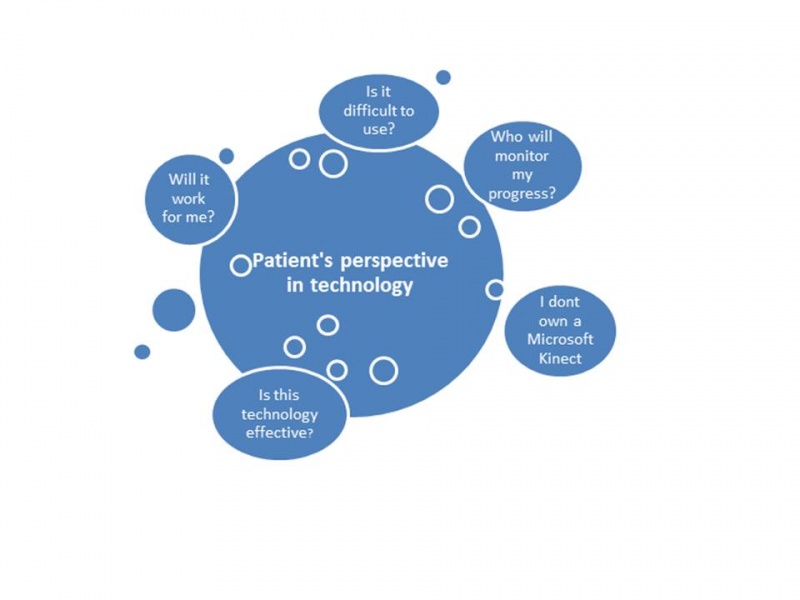
Patient's perspective on Microsoft Kinect[edit | edit source]
Examples of patient experiences[edit | edit source]
How can Microsoft Kinect benefit me?[edit | edit source]
Key points[edit | edit source]
Fun facts[edit | edit source]
Considering microsoft kinect’s potential future in stroke rehabilitation: Emerging evidence
[edit | edit source]
The Kinect has shown much potential for use in stroke rehabilitation but evolving evidence highlights its prospective use into specific areas of rehab for stroke.
Facial paralysis rehabilitation[edit | edit source]
Emerging evidence suggests that Microsoft kinect can be a useful device for use in facial paralysis rehabilitation. Patients can use kinect to complete physiotherapy regimes by copying on-screen exercises, while doing so the system will monitor and measure the patient's face. Feedback will be provided to the patient on how well they completed the exercises (NHS, National Institute for Health Research., 2014).
Upper extremity rehabilitation[edit | edit source]
A system was developed using kinect for upper limb rehabilitation. The use of therapy using Kinect-based systems maintained or improved the patient's motor performance (Acosta, I.P., 2012). Other studies that have used kinect emphasised that its use was particularly beneficial to those who had recovered significant amounts of motor functionality leading to question its effectiveness in the use with patients at different levels of recovery. Kinect provides opportunities for gross arm movements exercises but fine motor control movements of the hand and fingers are more difficult to track (Shires et al., 2014).
Balance rehabilitation[edit | edit source]
The patient stands in front of a screen while his/her movements are monitored using kinect. A pair of virtual shoes is displayed on the monitor following the patient's feet movements. The results of this study showed significant improvements in balance recovery as measured by the Berg Balance Scale. (Lloréns et al., 2012).
Assessment of gait[edit | edit source]
Other possibilities[edit | edit source]
As identified by Microsoft Research (2015), long term plans for stroke recovery with Kinect include integrating social networking into the system so that stroke patients can connect with one another and participate jointly in the rehabilitation programme. This could offer patients emotional and psychological support and motivation. Within the community, patients would have the opportunity to communicate about their condition and receive encouragement as they advance towards recovery. Possible functionality could include guided exercises with both correctional and encouraging feedback, with variable difficulty levels, and performance reports and summaries for physiotherapy use. Future updates could make it possible for physiotherapists to monitor the patient’s rehabilitation from their office, and to communicate with the patient regarding their treatment and progress.
From the research gathered Microsoft Kinect could be used in a variety of settings that include hospital, home and community and would be a successful rehabilitation tool for stroke patients. More research needs to be conducted to enhance the knowledge about the devices capabilities and limitations.
Key points[edit | edit source]
- Emerging evidence suggests that Microsoft kinect has high potential in rehabilitation of stroke suffers through its effectiveness in facial, balance,and upper limb rehabilitation.
- Microsoft Kinect can play a key part in rehabilitation in diverse setting to include hospitals, communities and in patient's home thus increasing patient's independence in performing their rehabilitation programme. .
- Further research on Microsoft kinect and its use in stroke rehabilitation needs to carried out to develop our knowledge about its abilities and limits.
Physiotherapist Role[edit | edit source]
Patient Assessment[edit | edit source]
Rehabilitation Programme Design[edit | edit source]
Performing Rehabilitation at Home[edit | edit source]
Skills and Knowledge Required[edit | edit source]
Continuous Professional Development[edit | edit source]
Assessment of stroke patients for the use of Microsoft Kinect[edit | edit source]
What you need to know as a physiotherapist
[edit | edit source]
References [edit | edit source]
- ↑ Webster, David, and Ozkan Celik. "Systematic review of Kinect applications in elderly care and stroke rehabilitation." J. Neuroeng. Rehabil 11.1 (2014): 108.
- ↑ Levac et al. (2014)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Microsoft. UK Developers. 2014 [cited 05 Nov 2015]. Available from: http://www.microsoft.com/en-gb/developers/articles/week05may14/how-the-kinect-azure-and-gamification-are-helping-virtualrehab-to-rehabilitate-patients-worldwide/
- ↑ National Institute for Health and Care Excelance. NICE. 2013 [cited 05 Nov 2015]. Available from:(https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG162/chapter/Key-priorities-for-implementation#the-core-multidisciplinary-stroke-team)
- ↑ TechTarget.2009 [cited 03 Nov 2015]. Available from: http://searchhealthit.techtarget.com/definition/Kinect
- ↑ Fairhead.H All about Kinect. 2015 [cited 03 Nov 2015]. Available from: http://www.i-programmer.info/babbages-bag/2003-kinect-the-technology-.html