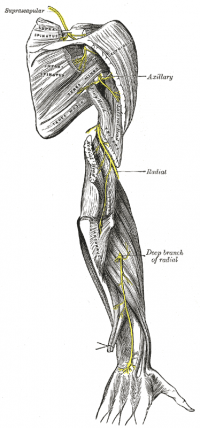
Radial Nerve
Original Editor - George Prudden
Top Contributors - George Prudden, Kim Jackson, WikiSysop, Vidya Acharya, 127.0.0.1, Joao Costa and Naomi O'Reilly;
Description[edit | edit source]
The radial nerve is a major nerve of the posterior cord and one of its terminal branches. In the axilla, it lies behind the axillary and upperbrachial arteries, it then passes anterior to the tendons of teres minor, latissimus dorsi and subscapularis. It then enters the posterior compartment of the arm passing through the triangular space, formed by the lateral humerus, long head of triceps and teres minor. Through this space, the nerve enters the spiral groove of the humerus and descends obliquely between lateral and medial heads of triceps where it reaches ther lateral border of the humerus in the distal third of the arm. The nerve enters the anterior compartment by piercing through the lateral intermuscular septum where it continues between brachialis and brachioradialis. Anterior to the lateral epicondyle the nerve splits into its terminal superficial and deep branches.
The posterior cutaneous nerve of the arm arises in the axilla, peiercing the deep fascia nerar the posterior axillary fold. The lower lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm arises before the radial nerve, pierces the intermuscular septum and becomes cuntaneous below the deltoid.
The superior branch of the radial nerve directly continues from the radial nerve anterior to the lateral epicondyle. It travels along the anterolateral side of the forearm. It is only function is sensory. It is superior to supinator, pronator teres, flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor pollicis longus and inferior to brachioradialis. In the distal third of the forearm, the nerve rises posteriorly from below the tendon of brachioradialis and pierces the deep fascia to become superior. It the further divides into the digital nerves
The deep branch of the radial nerve or posterior interosseous nerve, is entirely motor. It begins anterior to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and enters the posterior compartment of the forearm through the two heads of supinator where it curves around the lateral and posterior surfaces of the radius. It descends between the deep and superficial extensor muscles and lies on the interosseous membrane and ends in a flattened expansion.
Root[edit | edit source]
C5, 6, 7, 8 (T1)
From[edit | edit source]
Posterior cord of brachial plexus
Branches[edit | edit source]
Superficial branch of the radial nerve
Deep branch of the radial nerve (posterior interosseous nerve)
Function[edit | edit source]
Motor[edit | edit source]
- Triceps (all 3 heads)
- Anconeus
- Brachialis (lateral third)
- Extensor carpi radialis longus
Deep branch
- Supinator
- Extensor carpi radialis brevis
- Extensor digitorum
- Extensor digitorum
- Extensor carpi ulnaris
- Extensor pollicis longus
- Extensor pollicis brevis
- Extensor indicis
- Abductor pollicis longus
Sensory[edit | edit source]
Cutaneous braches supply the skin on the back of the arm and forearm
Posterior cutaneous nerve of the arm Posterior surface of the proximal third of the arm Lower lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm
- Lower lateral part of the arm
- Small area of skin on the forearm
Superficial branch
- Dorsum of the wrist
- Lateral dorsal surface of the hand
- Dorsum of the thumb
- Dorsum of the index and middle fingers
- Dorsum of the lateral aspect of ring finger