Pectoralis major: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
[[Image:Gray410 pectoralis major.png|right|200x200px]] | [[Image:Gray410 pectoralis major.png|right|200x200px]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
== Anatomy == | |||
<br> | === Origin === | ||
Origin of the upper fibers of pectoralis major is anterior surface of the sternal 1/2 of the clavicle. Anterior surface of the sternum, cartilages of first six or seven ribs and aponeurosis of the external oblique is the origin of the lower fibers of pectoralis major.<ref name=":0">Kendall F, McCreary E, Provance P,Rodgers M,Romani W. Muscles:Testing and function with posture and pain. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2005. </ref><br> | |||
=== | === Insertion === | ||
The upper and lower fibers of pectoralis major insert to the crest of greater tubercle of the humerus. Upper fibers are more anterior and caudal on the crest, while posterior fibers twist on themselves and are more posterior and cranial than the upper fibers.<ref name=":0" /> <br> | |||
=== | === Nerve supply === | ||
Nerve of the upper fibers: Lateral pectoral, C5,6,7. | |||
= | Nerves to the lower fibers: Lateral and medial pectoral, C6, 7,8, T1. <ref name=":0" /><br> | ||
=== | === Function === | ||
With the origin fixed, the pectoralis major adducts and medially rotates the humerus. With the insiortion fixed, it may assist in elevating thorax, as in forced inspiration. In cruntch-walking or parallel-bar work, it will assist in supporting the weight of the body. <ref name=":0" /><br> | |||
== | == Clinical relevance == | ||
< | === Weakness === | ||
Decrease the ability to draw the arm in horizontal adduction across the chest, making it difficult to touch the hand to the opposite shoulder. Decreases the strength of shoulder flexion and medial rotation.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== | === Shortness === | ||
The range of motion in horizontal abduction and lateral rotation of the shoulder is decreased. Shortness of the pectoralis holds the humerus in medial rotation and adduction and, secondarily, results in abduction of the scapula from the spine. <ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Assessment == | == Assessment == | ||
=== Palpation === | |||
=== Power === | |||
=== Length === | |||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Revision as of 18:11, 30 June 2018
Original Editor - Kudzanayi Ronald Muzenda
Top Contributors - Ilona Malkauskaite, Shaimaa Eldib, Kim Jackson, Lucinda hampton, Kudzanayi Ronald Muzenda, Pierre Beunardeau, Joao Costa, Wendy Walker, Oyemi Sillo, George Prudden and WikiSysop
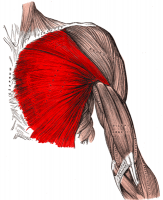
Description[edit | edit source]
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Origin of the upper fibers of pectoralis major is anterior surface of the sternal 1/2 of the clavicle. Anterior surface of the sternum, cartilages of first six or seven ribs and aponeurosis of the external oblique is the origin of the lower fibers of pectoralis major.[1]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
The upper and lower fibers of pectoralis major insert to the crest of greater tubercle of the humerus. Upper fibers are more anterior and caudal on the crest, while posterior fibers twist on themselves and are more posterior and cranial than the upper fibers.[1]
Nerve supply[edit | edit source]
Nerve of the upper fibers: Lateral pectoral, C5,6,7.
Nerves to the lower fibers: Lateral and medial pectoral, C6, 7,8, T1. [1]
Function[edit | edit source]
With the origin fixed, the pectoralis major adducts and medially rotates the humerus. With the insiortion fixed, it may assist in elevating thorax, as in forced inspiration. In cruntch-walking or parallel-bar work, it will assist in supporting the weight of the body. [1]
Clinical relevance[edit | edit source]
Weakness[edit | edit source]
Decrease the ability to draw the arm in horizontal adduction across the chest, making it difficult to touch the hand to the opposite shoulder. Decreases the strength of shoulder flexion and medial rotation.[1]
Shortness[edit | edit source]
The range of motion in horizontal abduction and lateral rotation of the shoulder is decreased. Shortness of the pectoralis holds the humerus in medial rotation and adduction and, secondarily, results in abduction of the scapula from the spine. [1]
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Palpation[edit | edit source]
Power[edit | edit source]
Length[edit | edit source]
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]