Ottawa Ankle Rules: Difference between revisions
Evan Thomas (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Evan Thomas (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Purpose: == | == Purpose: == | ||
To see if there is an indication for X-rays after an acute ankle injury. | To see if there is an indication for X-rays after an acute ankle injury.<ref name="Emparanza et al">Emparanza JI, Aginaga JR, Estudio Multicéntro en Urgencias de Osakidetza: Reglas de Ottawa (EMUORO) Group. Validation of the Ottawa Knee Rules. Ann Emerg Med. 2001 Oct;38(4):364-8.</ref> | ||
== Variables:<ref name="Stiell et al 1994">Stiell IG, McKnight RD, Greenberg GH, McDowell I, Nair RC, Wells GA, Johns C, Worthington JR. Implementation of the Ottawa Ankle Rules. JAMA 1994;271:827-32.</ref> == | == Variables:<ref name="Stiell et al 1994">Stiell IG, McKnight RD, Greenberg GH, McDowell I, Nair RC, Wells GA, Johns C, Worthington JR. Implementation of the Ottawa Ankle Rules. JAMA 1994;271:827-32.</ref> == | ||
Revision as of 00:31, 29 March 2013
Original Editor - Jill Nicole Hickey
Lead Editors - Your name will be added here if you are a lead editor on this page. Read more.
Purpose:[edit | edit source]
To see if there is an indication for X-rays after an acute ankle injury.[1]
Variables:[2][edit | edit source]
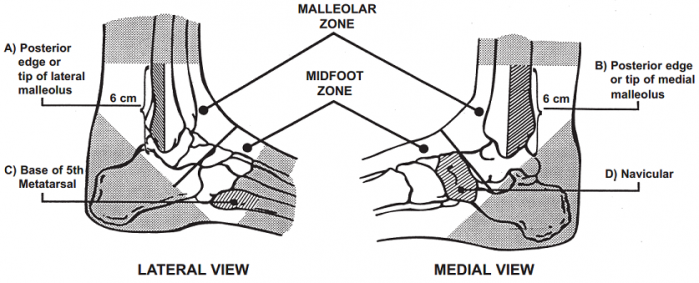
Figure 1. Palpation locations within the malleolar and midfoot zones. (Image from CDR Ankle Poster[3])
1. Bony tenderness along distal 6 cm of posterior edge of tibia/tip of medial malleolus
2. Bony tenderness along distal 6 cm of posterior edge of fibula or tip of lateral malleolus
3. Bony tenderness at the base of 5th metatarsal
4. Bony tenderness at the navicular
5. Inability to bear weight both immediately after injury and for 4 steps during intial evaluation
Method of Use:[edit | edit source]
http://www.ohri.ca/emerg/cdr/ankle_rule_flash.html
An ankle x-ray series is only required if there is pain in the malleolar zone AND any of variables 1 OR 2 OR 5.[2]
A foot x-ray series is only required if there is pain in the midfoot zone AND any of variables 3 OR 4 OR 5.[2]
Recommendations:[2][edit | edit source]
Ensure to apply the Ottawa Ankle Rules accurately by...
1. Palpating the entire distal 6cm of the tibia and fibula
2. Not neglecting the importance of medial malleolar tenderness
3. Using the rules only on those over the age of 18
Be sure to give written instructions and encourage follow-up in 5-7 days if pain and walking ability have not improved.
Evidence:[edit | edit source]
A systematic review of 27 studies by Bachmann et al 2003 found the pooled sensitivity of the Ottawa Ankle Rules to be 97.6%, with a median specificty of 31.5%. Pooled negative likelihood ratios was determined to be 0.10.[4]
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed):[edit | edit source]
Failed to load RSS feed from http://eutils.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=1Vy-VINwlaUmvVLdQopxCRbome4n8hgucX4pU4cvolrwOqUkR|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10: Error parsing XML for RSS
References:[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Emparanza JI, Aginaga JR, Estudio Multicéntro en Urgencias de Osakidetza: Reglas de Ottawa (EMUORO) Group. Validation of the Ottawa Knee Rules. Ann Emerg Med. 2001 Oct;38(4):364-8.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Stiell IG, McKnight RD, Greenberg GH, McDowell I, Nair RC, Wells GA, Johns C, Worthington JR. Implementation of the Ottawa Ankle Rules. JAMA 1994;271:827-32.
- ↑ http://www.ohri.ca/emerg/cdr/docs/cdr_ankle_poster.pdf
- ↑ Bachmann LM, Kolb E, Koller MT, Steurer J, ter Riet G. Accuracy of Ottawa ankle rules to exclude fractures of the ankle and mid-foot: Systematic review. BMJ 2003;326:417-23.