Middle Scalene: Difference between revisions
Wendy Walker (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div class="editorbox"> | <div class="editorbox"> | ||
'''Original Editor '''- | '''Original Editor '''- [[User:Wendy Walker|Wendy Walker]] | ||
'''Lead Editors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | '''Lead Editors''' - {{Special:Contributors/{{FULLPAGENAME}}}} | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
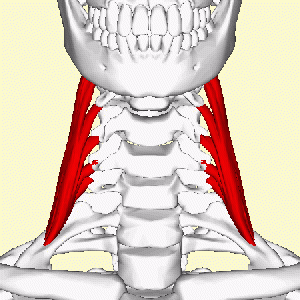
Middle Scalene, AKA Scalenus Medius, is the largest and longest muscle in the Scalene group of lateral neck muscles. Often penetrated by the dorsal scapular and long thoracic nerves, it is deeply placed, lying behind [[Sternocleidomastoid|Sternocleidomastoid]].<br> | Middle Scalene, AKA Scalenus Medius, is the largest and longest muscle in the Scalene group of lateral neck muscles. Often penetrated by the dorsal scapular and long thoracic nerves, it is deeply placed, lying behind [[Sternocleidomastoid|Sternocleidomastoid]].<br> | ||
[[Image:Scalenus medius muscle - animation02.gif]] | [[Image:Scalenus medius muscle - animation02.gif|center|300px]] | ||
== Origin == | == Origin == | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
== Action == | == Action == | ||
Middle scalene acts with [[ | Middle scalene acts with [[Anterior Scalene|anterior]] and [[Posterior Scalene|posterior scalene]] muscles. | ||
<span> </span>Acting from above: elevation of 1st rib | <span> </span>Acting from above: elevation of 1st rib | ||
Revision as of 13:24, 27 January 2014
Original Editor - Wendy Walker
Lead Editors - Wendy Walker, Kim Jackson, Milijana Delevic, Admin, WikiSysop, Wendy Snyders and Evan Thomas
Description[edit | edit source]
Middle Scalene, AKA Scalenus Medius, is the largest and longest muscle in the Scalene group of lateral neck muscles. Often penetrated by the dorsal scapular and long thoracic nerves, it is deeply placed, lying behind Sternocleidomastoid.
Origin[edit | edit source]
Insertion[edit | edit source]
1st Rib
Superior surface of the 1st rib, posterior to the subclavian groove
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Cervical nerves 5 to 3 & 4
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
Mscular branches of the ascending cervical artery
Action[edit | edit source]
Middle scalene acts with anterior and posterior scalene muscles.
Acting from above: elevation of 1st rib
Acting from below: cervical side flexion and rotation[1]; if bilateral action, small degree of cervical flexion
Function[edit | edit source]
Acting from above: accessory muscle of inspiration
Acting from below: cervical side flexor and rotator
Resources[edit | edit source]
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
Failed to load RSS feed from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/erss.cgi?rss_guid=1pEhTjOZGNUGUm-7rbxUkZq-IjYd8dzBK83PvdsWZriE_BbkdQ|charset=UTF-8|short|max=10: Error parsing XML for RSS
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.
- ↑ J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2002 Oct;32(10):488-96.fckLRActions of the scalene muscles for rotation of the cervical spine in macaque and human.fckLRBuford JA, Yoder SM, Heiss DG, Chidley JV.