Knee Extension Resistance Test: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Clinically Relevant Anatomy == | == Clinically Relevant Anatomy == | ||
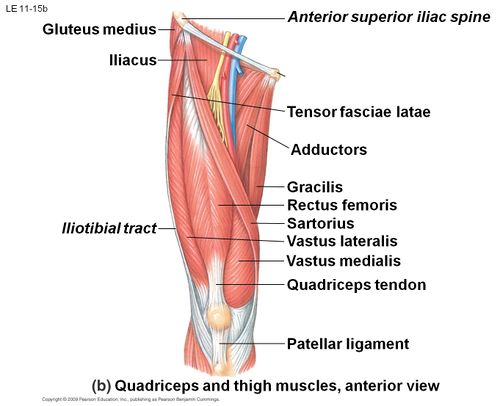
[[File:Quadriceps muscle.jpg|right|frameless|500x500px]] | |||
[[Quadriceps Muscle|Quadriceps femoris]] | |||
| | |||
== Purpose == | == Purpose == | ||
The extension resistance test is used to perform a maximal provocation on the muscle-tendon mechanism of the extensor muscles.<br> | The extension resistance test is used to perform a maximal provocation on the muscle-tendon mechanism of the extensor muscles. Tests muscle strength from grade 3 to 5, not applicable for lesser grade.<br> | ||
The extension resistance test is positive when the affected knee shows less power to hold the pressure. If positive we can say the extensor mechanism of the knee is disturbed.<ref name="Hagen">Hagen, K., ‘Anterieure Kniepijn’, Afstudeeropdracht fysiotherapie HvU, 2005, p. 1-8. (Level of Evidence 2A)</ref> | The extension resistance test is positive when the affected knee shows less power to hold the pressure. If positive we can say the extensor mechanism of the knee is disturbed.<ref name="Hagen">Hagen, K., ‘Anterieure Kniepijn’, Afstudeeropdracht fysiotherapie HvU, 2005, p. 1-8. (Level of Evidence 2A)</ref> | ||
| Line 33: | Line 26: | ||
|} | |} | ||
Knee Extension ( tests grade 3-thru 5) | |||
1. Ask patient to sit up straight and support trunk with arms propped with no greater | |||
than 20 degree of trunk extension. 2. The therapist may put their hand or a rolled towel | |||
under the distal end of the thigh to cushion it. | |||
3. Ask patient to extend the knee. | |||
4. Place the knee in 20° of flexion from full extension to avoid mechanical locking of the | |||
joint. | |||
5. Apply resistance just proximal to the ankle. | |||
NB. For a grade of 3 the patient should be able to actively extend the knee from 90o of flexion without a swinging motion secondary to flexing the knee and creating momentum<ref>kumc.ed [http://www.kumc.edu/Documents/fshd/ManualMuscleTesting.pdf MANUAL MUSCLE TESTING (MMT)] Available from:http://www.kumc.edu/Documents/fshd/ManualMuscleTesting.pdf (last accessed 3.9.2020)</ref>. This test is not appropriate for a grades 0-2. <br>In the video (R), resisted testing of knee starts at 4m30s.<br> | |||
<br> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 07:06, 3 September 2020
This article is currently under review and may not be up to date. Please come back soon to see the finished work! (3/09/2020)
Original Editors - Yelena Gesthuizen
Top Contributors - Laura Ritchie, Lucinda hampton, Admin, Yelena Gesthuizen, Kim Jackson, Evan Thomas, WikiSysop and Wanda van Niekerk
Clinically Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Purpose[edit | edit source]
The extension resistance test is used to perform a maximal provocation on the muscle-tendon mechanism of the extensor muscles. Tests muscle strength from grade 3 to 5, not applicable for lesser grade.
The extension resistance test is positive when the affected knee shows less power to hold the pressure. If positive we can say the extensor mechanism of the knee is disturbed.[1]
Technique[edit | edit source]
| [2] |
Knee Extension ( tests grade 3-thru 5)
1. Ask patient to sit up straight and support trunk with arms propped with no greater
than 20 degree of trunk extension. 2. The therapist may put their hand or a rolled towel
under the distal end of the thigh to cushion it.
3. Ask patient to extend the knee.
4. Place the knee in 20° of flexion from full extension to avoid mechanical locking of the
joint.
5. Apply resistance just proximal to the ankle.
NB. For a grade of 3 the patient should be able to actively extend the knee from 90o of flexion without a swinging motion secondary to flexing the knee and creating momentum[3]. This test is not appropriate for a grades 0-2.
In the video (R), resisted testing of knee starts at 4m30s.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Hagen, K., ‘Anterieure Kniepijn’, Afstudeeropdracht fysiotherapie HvU, 2005, p. 1-8. (Level of Evidence 2A)
- ↑ drjabbour. Knee Physical Examination - Flexion and Extension - Dr. Tony Jabbour. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fCiD3FwvwIA [last accessed 21/09/14]
- ↑ kumc.ed MANUAL MUSCLE TESTING (MMT) Available from:http://www.kumc.edu/Documents/fshd/ManualMuscleTesting.pdf (last accessed 3.9.2020)