Kinesio Taping: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 98: | Line 98: | ||
# Tape cut (Y, I, X, Fan, Web, Donut, Jelly Fish, Snowflake, EDF) | # Tape cut (Y, I, X, Fan, Web, Donut, Jelly Fish, Snowflake, EDF) | ||
[[Image:KT y tape.jpg|thumb|alt=|left|100x100px|Y cut]]<br> | |||
# Tension on the tape | # Tension on the tape | ||
# Tape direction | # Tape direction | ||
| Line 109: | Line 112: | ||
*Should be 2 inches longer than the target muscle | *Should be 2 inches longer than the target muscle | ||
==== 'I' tape application is generally used for: ==== | ==== 'I' tape application is generally used for: ==== | ||
Revision as of 01:56, 12 November 2021
Original Editor - Karina Leahy
Top Contributors - Karina Leahy, Ewa Jaraczewska, Vanessa Rhule, Admin, Kim Jackson, Naomi O'Reilly, George Prudden, WikiSysop, Candace Goh, Shaimaa Eldib and Wanda van Niekerk
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Kinesio Taping Method is a therapeutic tool utilised by the rehabilitation specialists in all programs (paediatric,[1] geriatric, orthopaedic,[2] neurological, oncology and others) and levels of care (acute care,[3] inpatient rehabilitation,[4] outpatient, home care and Day Rehab). The idea of using elastic tape to mimic the therapist's hands was first presented by Dr Kenzo Kase in the 1970s. Since then it became the modality used in pain management[5], soft tissue injury[6], tissues and joints malalignment[1], oedema[7], and more. Kinesio Taping Method utilises four types of Kinesio Tex Tapes, each one with specific properties designed to use on fragile skin, sensitive skin or applied with higher tensions. Kinesio Taping Method has also been found effective in treating animals[8] and two special tapes are used: Kinesio Equine and Kinesio Canine.
Properties[edit | edit source]
Kinesio Tex Tape contains either 100% cotton and elastic fibres or it can be a blend of polyester and cotton with elastic fibres. The latter is a preferable choice for Kinesio Taping application on sensitive skin when higher tensions on the tape are needed for the desired outcome. The tape is applied on the paper backing using an acrylic adhesive and with 10-15% stretch. This amount of stretch is used with some Kinesio Taping techniques and is referred to as "paper off tension". Other characteristics of Kinesio Tex Tape include[9]:
- Ability to stretch to 120-140% of its original length
- Recoil back to the anchor that is applied without stretch
- Heat activated adhesive
- Hypoallergenic dyes that make the tape safe for most users
- Latex-free
- Drying time after being wet is about 5-10 minutes
- Can be worn for several days
Type of Kinesio Tex Tapes[edit | edit source]
Currently, there are 4 types of tapes available for Kinesio Taping Method applications for humans and 2 types of tapes for animals. Each clinician can choose the most appropriate type of tape, based on the desired outcome and the client's skin condition. When taping is considered by an untrained individual it is suggested to use Classic or Performance+ Tape.
The following are tape types and their characteristic:
- Kinesio Tex Classic: the original tape that received several upgrades over time, the most universal as it can be used for all applications and ideally on healthy skin
- Kinesio Tex Performance+: different, looser pattern on the tread, polyester and cotton blend best for sensitive skin when higher tensions on the tape are desired
- Kinesio Tex Gold: special distribution of adhesive allowing good attachment without requiring large surface area, good for low tension applications and available only for trained professionals
- Kinesio Tex Gold Light Touch Plus: adhesive distributed to allow gentle grip, does not last as long as other types so it is used for short term applications and usually for children and older adults with fragile skin
- Kinesio Equine: developed to allow Kinesio Taping method to be used on horses, can be applied directly on horses hair and its taste prevents animals from chewing it
- Kinesio Canine: used on dogs and it works well with dogs' hair
Theory[edit | edit source]
Kinesio Taping theory is based on the neurophysiological mechanisms and the effect of mechanical stimuli on various systems in the body:
Central Nervous System (CNS): Kinesio Tex Tape applied on the skin with varying degrees of stretch creates a mechanical stimulus and activates an afferent pathway to CNS
Skin: Kinesio Tex Tape applied on the skin with a low degree of stretch changes the density and the concentration of the tissue in the dermis and epidermis.[11] This mechanical stimulus produces cell movement.[12][13]Kinesio Tex Tape produces pressure and stretch on the skin that may be able to stimulate mechanoreceptors. This stimulus interacts with CNS and modulates pain responses.[14]
Fascia: the application of Kinesio Tex Tape changes the tension elements in tissues to encourage homeostasis. The tension imposed from the tape frees the fascia of any movement limitations through the movement of the skin relative to the target tissue.[15] [9]
Lymphatic and Circulatory System: the application of Kinesio Tex Tape facilitates the opening of microvalves due to a dynamic pressure variation as a result of alteration in skin density. This decompression activates lymphatics in the dermis and improves lymphatic flow. The end result is tissue inflammation and swelling reduction.[14]It is also theorised that lifting the skin detaches filaments that attach the skin to endothelial cells of the lymphatic and capillary beds. This is proposed to create channels that allow for lymph to drain, thus reducing swelling and allowing increased blood flow to the area.[17]
Basics of Application[edit | edit source]
- Complete patient's assessment to identify the most appropriate application. Include Kinesio Taping Method specific assessment tools.
- Follow contraindications and precautions when choosing Kinesio Taping Method
- Apply the tape on dry skin, free of oils and lotion
- Remove body hair if possible by trimming or shaving the area
- Follow the tension guidelines
- Round all the edges of the tape to prevent premature peeling
- Avoid touching the adhesive side of the tape after removing the backing as this may decrease the adhesive strength on the skin
- Once the tape is applied, activate the heat-sensitive adhesive by rubbing the surface of the tape for a few seconds
- Inform the patient to defer activities that cause perspiration for one hour if possible
- Inform the patient to remove the tape if itching or burning sensation has occurred or if the pain has increased
- Teach the patient and caregiver how to remove the tape if needed
- Provide the patient with informed consent and an information sheet with a description including:
- sign and symptoms of skin irritation and skin allergy
- instruction on tape removal
- how long to wear the tape
- physiotherapist contact information
Contraindications and Precautions[edit | edit source]
It is up to each physiotherapist to use their judgement when choosing Kinesio Taping Method. The decision needs to be based on the physiotherapist's clinical experience and experience with taping gained by attending Kinesio Taping Method certification courses.
General contraindications are:
- Malignancy
- Infection, cellulitis
- Open wound
- DVT
- Previous allergic reaction to Kinesio Tex Tape
General precautions are:
- Diabetes
- Congestive heart failure (CHF)
- Patient receiving dialysis/Kidney disease
- Organ transplants
- Pregnancy
Types of Applications[edit | edit source]
Each physiological system is targeted with a specific application that can be described by:
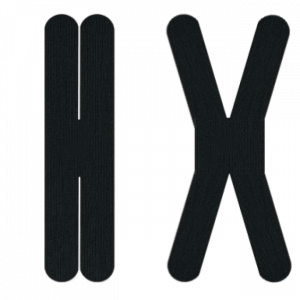
- Tape cut (Y, I, X, Fan, Web, Donut, Jelly Fish, Snowflake, EDF)
- Tension on the tape
- Tape direction
'Y' tape application is generally used to:[edit | edit source]
- Surround the target muscle
- Inhibit or facilitate muscle stimuli
- Should be 2 inches longer than the target muscle
'I' tape application is generally used for:[edit | edit source]
- Acute injuries in place of 'Y' tape
- Oedema and pain (primary purpose)
- Alignment correction
'X' tape application is generally used when:[edit | edit source]
- The origin and insertion of the target muscle change depending on movement e.g. the Rhomboids
'Fan/Web' tape application is used for:[edit | edit source]
- Oedema (web is different because the ends remain intact)
'Donut' tape application is generally used for:[edit | edit source]
- Oedema (use overlapping strips and the center is cut out over the area of focus)
[edit | edit source]
Insertion to Origin: [edit | edit source]
- Used to inhibit overused or stretched muscles
- Light stretch used to achieve goal
Origin to Insertion:[edit | edit source]
- Used to facilitate weak or underperforming muscles
- Light to moderate stretch required
Type of Application Stretch[edit | edit source]
The target muscle should be elongated prior to stretch. KT requires none to partial stretch to be applied on tape.
- Full - 100%
- Severe - 75%
- Moderate - 50%
- Light - 15-25%
- None - 0%
For percentage stretch refer to percentage of available stretch.
Line of pull of the tape is key
- Facilitate: proximal to distal (15-50% tension)
- Inhibit: distal to proximal (15-25%) [18]
Kinesio Tape Instruction Video's[edit | edit source]
http://www.kinesiotaping.hk/how-to-use-Kinesio-Tapes.html[19]
Clinical Implications[edit | edit source]
- Level of evidence - weak
- What does the evidence support?
-Increase ROM
-Increase in Function
-Decrease Oedema/Swelling
Pros[edit | edit source]
- Some evidence proves theories
- Provides a treatment
- Applicable to multiple patient populations
- Feeling of treatment encourages movement
- Versatile
Cons[edit | edit source]
- Small body of evidence to prove theories
- Expensive
- Requires practice
- Skin irritation
Patient After-Care Advice[edit | edit source]
- If the tape makes symptoms worse then take it off
- If the tape starts to come off then rub it to re-activate the tape adhesive
- Do NOT dry it with a hairdryer
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Dixit J, Roy S.Effect of Neuromuscular Taping Along with Reactive Postural Adjustment and Anticipatory Postural Adjustment in Improving Sitting Balance in Children with Spastic Diplegic Cerebral Palsy. IJHSR 2018;8(11):116-125.
- ↑ Arrebola LS, Teixeira de Carvalho R, Yan Lam Wun P, Rizzi de Oliveira P, Firmo dos Santos J, Gonçalves Coutinho de Oliveira V, Pinfildi CE. Investigation of different application techniques for Kinesio Taping® with an accompanying exercise protocol for improvement of pain and functionality in patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome: A pilot study. Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies 2020, 24 (1):47-55,
- ↑ Brockmann R, Klein HM. Pain-diminishing effects of Kinesio® taping after median sternotomy. Physiotherapy Theory and Practice 2018; 34(6): 433-441.
- ↑ Gallagher J. Anterior and posterior diaphragm Kinesio taping for intractable hiccups after ischemic stroke: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Aug;97(34):e11934.
- ↑ Donec V, Kubilius R. The effectiveness of Kinesio Taping® for pain management in knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trial. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2019 Aug 29;11:1759720X19869135.
- ↑ Wang CK, Fang YD, Lin LC, Lin CF, Kuo LC, Chiu FM, Chen CH. Magnetic Resonance Elastography in the Assessment of Acute Effects of Kinesio Taping on Lumbar Paraspinal Muscles. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019 Apr;49(4):1039-1045.
- ↑ Tantawy SA, Abdelbasset WK, Nambi G, Kamel DM. Comparative Study Between the Effects of Kinesio Taping and Pressure Garment on Secondary Upper Extremity Lymphedema and Quality of Life Following Mastectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Integrative Cancer Therapies. January 2019.
- ↑ Wójcik M. The Use of Physical Therapy Procedures in the Treatment of Soft Tissue Injuries in a Horse: A Case Study. J Vet Sci Med Diagn 2017; 6:4.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Kase K, Wallis J, Kase T. Clinical therapeutic applications of the Kinesio taping method. Kinesio 2013, 3rd edition.
- ↑ Gustavo Mendoza. Kinesio effect on cortical brain activity fMRI . Available from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k6WsoxI6nzg&t=27s[last accessed 11/11/2021]
- ↑ Kafa N, Citaker S, Omeroglu S, Peker T, Coskun N, Diker S. Effects of kinesiologic taping on epidermal-dermal distance, pain, oedema and inflammation after experimentally induced soft tissue trauma. Physiother Theory Pract. 2015;31(8):556-61.
- ↑ Lo CM, Wang HB, Dembo M, Wang YL. Cell movement is guided by the rigidity of the substrate. Biophys J. 2000 Jul;79(1):144-52.
- ↑ Hale NA, Yang Y, Rajagopalan P. Cell migration at the interface of a dual chemical-mechanical gradient. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2010 Aug;2(8):2317-24.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Wu W-T, Hong C-Z, Chou L-W. The Kinesio Taping Method for Myofascial Pain Control. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2015; Article ID 950519.
- ↑ Abu-Hijleh MF, Roshier AL, Al-Shboul Q, Dharap AS, Harris PF. The membranous layer of superficial fascia: evidence for its widespread distribution in the body. Surg Radiol Anat. 2006 Dec;28(6):606-19.
- ↑ Ronelle Wood.Fascia Magnified 25x. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uzy8-wQzQMY [last accessed 11/11/2021]
- ↑ Lipinska A, Sliwinski Z, Kiebzak W, Senderek T, Kirenko J. Influence of kinesiotaping application on lymphoedema of an upper limb in women after mastectomy. Polish Journal of Physiotherapy 2007:7;258-269.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Kaze K, Wallis J, Kaze T. Clinical therapeutic applications of the kinesio taping method. Tokyo: Japan, 2003.
- ↑ Kinesio Taping Association International. Kinesio HK:The original from Dr. Kenzo Kaze since 1979. http://www.kinesiotaping.hk/how-to-use-Kinesio-Tapes.html (accessed 13 June 2013).