International Cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Kim Jackson (talk | contribs) m (categorisation) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
== Objective | == Objective == | ||
The International Cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale (ICARS) is an outcome measure that was created in 1997 by the Committee of the World Federation of Neurology with the goal of standardizing the quantification of impairment due to cerebellar ataxia. The scale is scored out of 100 with 19 items and 4 subscales of postural and gait disturbances, limb ataxia, dysarthria, and oculomotor disorders. Higher scores indicate higher levels of impairment. | The International Cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale (ICARS) is an outcome measure that was created in 1997 by the Committee of the World Federation of Neurology with the goal of standardizing the quantification of impairment due to cerebellar ataxia. The scale is scored out of 100 with 19 items and 4 subscales of postural and gait disturbances, limb ataxia, dysarthria, and oculomotor disorders. Higher scores indicate higher levels of impairment. | ||
== Intended Population | == Intended Population == | ||
Clients suffering from cerebellar ataxia. | Clients suffering from cerebellar ataxia. The ICARS has been validated for use in patients with focal cerebellar lesions <ref>Schoch, B; et al. (Nov 2007). "Reliability and validity of ICARS in focal cerebellar lesions". Movement Disorders 22 (15): 2162–2169.</ref> and hereditary spinocerebellar and Friedrich's ataxia. <ref>Schmitz-Hubsch, T; et al. (May 2006). "Reliability and validity of the International Cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale: a study in 156 spinocerebellar ataxia patients". Movement Disorders 21 (5): 699–704</ref> <ref>Storey, E; Tuck, K.; Hester, R.; Hughes, A.; Churchyard, A. (Feb 2004). "Inter-rater reliability of the International Cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale (ICARS)". Movement Disorders 19 (2): 190–192.</ref> | ||
The ICARS has been validated for use in patients with focal cerebellar lesions and hereditary spinocerebellar and Friedrich's ataxia. | |||
Time taken to complete the test - 30 minutes | |||
== Method of Use == | == Method of Use == | ||
The International Cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale (ICARS) (Trouillas et al., 1997) is a 100-point semi-quantitative scale. It is divided into four parts, on the basis of the compartmentalization of cerebellar symptoms (Babinski & Tournay, 1913): | The International Cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale (ICARS) (Trouillas et al., 1997) is a 100-point semi-quantitative scale. It is divided into four parts, on the basis of the compartmentalization of cerebellar symptoms (Babinski & Tournay, 1913): | ||
[[Image:ICARS.JPG|center]] | |||
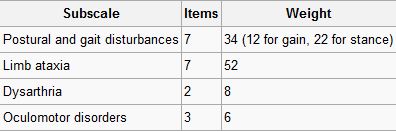
Postural and stance disturbances (subscore: /34) | |||
Limb movement disturbances (subscore: /52) | |||
Speech disorders (subscore: /8) | |||
Oculomotor deficits (subscore: /6) | |||
A. Walking capacities: 10-m test including half-turn, near a wall | Posture and Gait Score (total of scores A to G) | ||
A. Walking capacities: 10-m test including half-turn, near a wall | |||
0 Normal | 0 Normal | ||
1 Almost normal naturally, unable to walk with feet in tandem | |||
2 Walking without support, but abnormal and irregular | |||
3 Walking without support but with considerable staggering; difficulties in half-turn | |||
4 Walking with autonomous support impossible; episodic support of the wall for a 10-m test | |||
5 Walking only possible with one stick | |||
6 Walking only possible with two special sticks or with a stroller | |||
7 Walking only with accompanying person | |||
8 Walking impossible, even with accompanying person (wheelchair)and so on. | |||
PG: 34 Min.: 0 Max.: 100 | |||
Grading for ataxia. Balance assessed using posture and gait (PG) subcomponent | |||
== Reference | == Reference == | ||
Cerebellar Disorders - A Practical Approach to Diagnosis and Management; Mario Ubaldo Manto, 4 - Clinical scales: 53-68 | Cerebellar Disorders - A Practical Approach to Diagnosis and Management; Mario Ubaldo Manto, 4 - Clinical scales: 53-68 | ||
| Line 53: | Line 59: | ||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 21:34, 21 February 2019
Original Editor - Ajay Upadhyay
Top Contributors - Ajay Upadhyay, WikiSysop, George Prudden and Kim Jackson
Objective[edit | edit source]
The International Cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale (ICARS) is an outcome measure that was created in 1997 by the Committee of the World Federation of Neurology with the goal of standardizing the quantification of impairment due to cerebellar ataxia. The scale is scored out of 100 with 19 items and 4 subscales of postural and gait disturbances, limb ataxia, dysarthria, and oculomotor disorders. Higher scores indicate higher levels of impairment.
Intended Population[edit | edit source]
Clients suffering from cerebellar ataxia. The ICARS has been validated for use in patients with focal cerebellar lesions [1] and hereditary spinocerebellar and Friedrich's ataxia. [2] [3]
Time taken to complete the test - 30 minutes
Method of Use[edit | edit source]
The International Cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale (ICARS) (Trouillas et al., 1997) is a 100-point semi-quantitative scale. It is divided into four parts, on the basis of the compartmentalization of cerebellar symptoms (Babinski & Tournay, 1913):
Postural and stance disturbances (subscore: /34) Limb movement disturbances (subscore: /52) Speech disorders (subscore: /8) Oculomotor deficits (subscore: /6)
Posture and Gait Score (total of scores A to G)
A. Walking capacities: 10-m test including half-turn, near a wall
0 Normal 1 Almost normal naturally, unable to walk with feet in tandem 2 Walking without support, but abnormal and irregular 3 Walking without support but with considerable staggering; difficulties in half-turn 4 Walking with autonomous support impossible; episodic support of the wall for a 10-m test 5 Walking only possible with one stick 6 Walking only possible with two special sticks or with a stroller 7 Walking only with accompanying person 8 Walking impossible, even with accompanying person (wheelchair)and so on.
PG: 34 Min.: 0 Max.: 100
Grading for ataxia. Balance assessed using posture and gait (PG) subcomponent
Reference[edit | edit source]
Cerebellar Disorders - A Practical Approach to Diagnosis and Management; Mario Ubaldo Manto, 4 - Clinical scales: 53-68
Evidence[edit | edit source]
High inter-rater reliability (ICC50.95)
High test–re-test reliability (ICC50.97)
Adequate internal consistency(Cronbach’s a50.94)
Good internal structural validity
Links[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
References will automatically be added here, see adding references tutorial.
- ↑ Schoch, B; et al. (Nov 2007). "Reliability and validity of ICARS in focal cerebellar lesions". Movement Disorders 22 (15): 2162–2169.
- ↑ Schmitz-Hubsch, T; et al. (May 2006). "Reliability and validity of the International Cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale: a study in 156 spinocerebellar ataxia patients". Movement Disorders 21 (5): 699–704
- ↑ Storey, E; Tuck, K.; Hester, R.; Hughes, A.; Churchyard, A. (Feb 2004). "Inter-rater reliability of the International Cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale (ICARS)". Movement Disorders 19 (2): 190–192.