Iliocostalis Lumborum: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
postural stabilization of vertebral column<ref name="p3" /> | postural stabilization of vertebral column<ref name="p3" /> | ||
== Clinical Relevance: == | |||
== | == Assessment == | ||
<div class="researchbox"> | |||
=== Palpation === | |||
</div> | |||
=== Power === | |||
=== Length === | |||
== Treatment == | |||
<div class="researchbox"> </div> | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 14:42, 27 June 2018
Original Editor - Oyemi Sillo
Lead Editors - Vidya Acharya, Oyemi Sillo, Kim Jackson, Abbey Wright, Lucinda hampton, Evan Thomas, WikiSysop and 127.0.0.1
Description[edit | edit source]
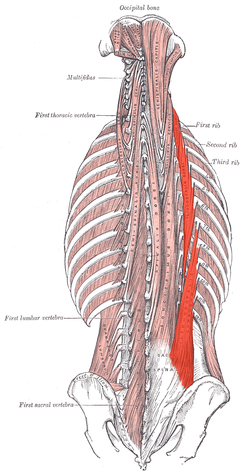
Iliocostalis Lumborum belongs to the lateral column of the Sacrospinalis group of muscles.[1]
Origin[edit | edit source]
Anterior surface of a broad and thick tendon w attached to the medial crest of sacrum, spinous processes of the lumbar vertebrae, 11th and 12th thoracic vertebrae, posterior part of the medial lip of iliac crest, supra-spinous ligament and the lateral crest of sacrum[2].
Insertion[edit | edit source]
By tendons into inferior borders of the angles of the lower 6 or 7 ribs[2][3]
Nerve Supply[edit | edit source]
Dorsal rami of thoracic and lumbar spinal nerves (T7 to L3)[4]
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
Dorsal branches of the lumbar arteries from the aorta. Dorsal branches of the lateral sacral artery from the internal iliac artery.[4]
Action[edit | edit source]
- acting bilaterally, extension and hyperextension of the spine
- acting unilaterally, laterally flexes the spine[3]
- assists as an accessory muscle of expiration, due to its insertion on the ribs[5].
Function[edit | edit source]
postural stabilization of vertebral column[4]
Clinical Relevance:[edit | edit source]
Assessment[edit | edit source]
Palpation[edit | edit source]
Power[edit | edit source]
Length[edit | edit source]
Treatment[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Gray, Henry. Anatomy of the Human Body. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger, 1918; Bartleby.com, 2000. www.bartleby.com/107/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Muscle Testing and Function;4th Edition; Kendall, McCreary, Provance; Page No.138.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/iliocostalis_lumborum_1
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 http://www.anatomyexpert.com/app/structure/5243/
- ↑ Muscles Testing and Function;4th Edition; Kendall, McCreary, Provance; Accessory Muscles of Respiration, Page No.330.