Hip Quadrant Test: Difference between revisions
Oyemi Sillo (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Definition/ description == | == Definition/ description == | ||
The Hip Quadrant test is a passive test that is being applied to asses if there is any damage in structure in the inner and outer quadrant of the hip. The hip quadrant test is also known as the quadrant scour test<ref name=" | The Hip Quadrant test is a passive test that is being applied to asses if there is any damage in structure in the inner and outer quadrant of the hip. The hip quadrant test is also known as the quadrant scour test<ref name="p3">] Peter H. Seidenberg,Jimmy D. Bowen - The Hip and Pelvis in Sports Medicine and Primary Care pg. 33. Peter H. Seidenberg and Jimmy D. Bowen (editors). Springer (publisher)
Evidence level: 5 grade of recommendation: F</ref>. This test is not to be confused to the quadrant test for the lumbar spine.<ref name="p6">Lyle MA, Manes S, McGuinness M, Ziaei S, Iversen MD.Relationship of physical examination findings and self-r eported symptom severity and physical function in patients with degenerative lumbar conditions. Phys Ther. 2005 Feb;85(2):120-33.fckLREvidence level: 2a grade of recommendation: B</ref> <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
== Clinically relevant anatomy == | == Clinically relevant anatomy == | ||
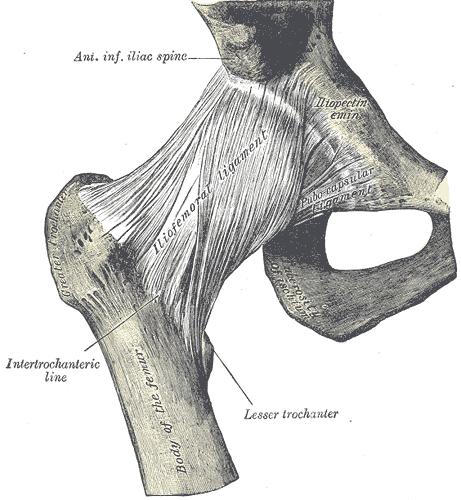
The most important structures of the art. coxae are the fossa acetabuli, facies lunata, labrum acetabuli, lig. transversum acetabuli, caput femoris, lig. ischiofemorale, lig iliofemorale and lig. pubofemorale. The art. Coxae is an articulation sphaeroidea.<ref name=" | The most important structures of the art. coxae are the fossa acetabuli, facies lunata, labrum acetabuli, lig. transversum acetabuli, caput femoris, lig. ischiofemorale, lig iliofemorale and lig. pubofemorale. The art. Coxae is an articulation sphaeroidea.<ref name="p0">Human anatomy atlas Sobotta part 2: lower extremity pg 263 – 272. Bohn Stafleu, Van Loghum
3th print R. Putz and R. Pabst</ref> <ref name="fig. 1">figure 1: http://www.healthbase.com/resources/images/</ref> | ||
[[Image:Anatomy human hip.jpg|frame|center|figure 1]]<br> | [[Image:Anatomy human hip.jpg|frame|center|figure 1]]<br> | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
== Purpose<br> == | == Purpose<br> == | ||
The purpose of the Hip Quadrant test is to determine if there is a nonspecific hip pathology and a chance of ROM. This test does so by completing the ROM from flexion and adduction to flexion and abduction<ref name=" | The purpose of the Hip Quadrant test is to determine if there is a nonspecific hip pathology and a chance of ROM. This test does so by completing the ROM from flexion and adduction to flexion and abduction<ref name="p1">M. Lynn Palmer – Fundamentels of musculoskeletal assesment techniques pg. 305. Second edition, M lynn palmer and Marcia E. Epler. Uppincott Williams and Willens (publisher)
Evidence level: 5 grade of recommendation: F</ref>. This test is also capable to detect early hip degeneration.<ref name="p5">Manning C, Hudson Z. Comparison of hip joint range of motion in professional youth and senior team footballers with age-matched controls: an indication of early degenerative change? Phys Ther Sport. 2009 Feb;10(1):25-9. Epub 2008 Dec 24.fckLREvidence level: 3a grade of recommendation: C</ref> <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
== Technique == | == Technique == | ||
The patient lies supine on the table. The therapist stands on the side of the involved leg. He brings the hip and the knee to 90° flexion, the knee is directed towards the opposite shoulder (figure 1). One hand of the therapist is above the patient’s knee, the other is above the malleolis. Afterwards the therapist puts pressure on the leg by pushing the femur dorsally.<ref name=" | The patient lies supine on the table. The therapist stands on the side of the involved leg. He brings the hip and the knee to 90° flexion, the knee is directed towards the opposite shoulder (figure 1). One hand of the therapist is above the patient’s knee, the other is above the malleolis. Afterwards the therapist puts pressure on the leg by pushing the femur dorsally.<ref name="p7">Thomas A. Souza Differential Diagnosis and Management for the Chiropractor: Protocols and algoritms pg 345. Fourth edition, Thomas A. Souza, DC, DACBSP. Jean and Bartlett publishers (Sanburry, Massachussets).
Evidence level: 5 grade of recommendation: F</ref><ref name="p1" /><ref name="p3" /> | ||
<br>In the first part of the exam the therapist adducts the patient's leg until the pelvis begins to raise off the table. <br><br> | <br>In the first part of the exam the therapist adducts the patient's leg until the pelvis begins to raise off the table. <br><br> | ||
In the second part of the exam the therapist brings the leg of the patient in abduction with the hip still in 90° flexion and goes to abduction until the pelvis almost raises of the table. When he brings the leg to abduction it is important to keep the resistance on the leg and to go to from adduction to abduction in an arch.<ref name=" | In the second part of the exam the therapist brings the leg of the patient in abduction with the hip still in 90° flexion and goes to abduction until the pelvis almost raises of the table. When he brings the leg to abduction it is important to keep the resistance on the leg and to go to from adduction to abduction in an arch.<ref name="p3" /> | ||
<br> {{#ev:youtube|rUO8zeHKOxI}} <br> | <br> {{#ev:youtube|rUO8zeHKOxI}} <br> | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
== Result == | == Result == | ||
The test is considered positive if the patient has any pain. The test is also positive if the therapist can feel any crepitus or if there is a leathery end feeling or if there’s a loss in ROM.<ref name=" | The test is considered positive if the patient has any pain. The test is also positive if the therapist can feel any crepitus or if there is a leathery end feeling or if there’s a loss in ROM.<ref name="p1" /> <br>The test is considered negative if you can go from flexion-adduction to flexion-abduction in an arch, a normal ROM and with a normal end-feeling.<ref name="p1" /><ref name="p3" /> <br><br> | ||
== Dysfunction == | == Dysfunction == | ||
A positive Hip Quadrant test is an indication that there might be arthritis, an osteochrondral defect, avascular necrosis, joint capsule tightness and an acetabular labrum defect<ref name=" | A positive Hip Quadrant test is an indication that there might be arthritis, an osteochrondral defect, avascular necrosis, joint capsule tightness and an acetabular labrum defect<ref name="p4">Mitchell B, McCrory P, Brukner P, O'Donnell J, Colson E, Howells R. Hip joint pathology: clinical presentation and correlation between magnetic resonance arthrography, ultrasound, and arthroscopic findings in 25 consecutive cases. Clin J Sport Med. 2003 May;13(3):152-6.
Evidence level: 2c grade of recommendation: C</ref>. This test also detects if the patients hip can move in the full range of motion.<ref name="p7">Thomas A. Souza Differential Diagnosis and Management for the Chiropractor: Protocols and algoritms pg 345. Fourth edition, Thomas A. Souza, DC, DACBSP. Jean and Bartlett publishers (Sanburry, Massachussets).
Evidence level: 5 grade of recommendation: F</ref><br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 12:43, 6 June 2017
Definition/ description[edit | edit source]
The Hip Quadrant test is a passive test that is being applied to asses if there is any damage in structure in the inner and outer quadrant of the hip. The hip quadrant test is also known as the quadrant scour test[1]. This test is not to be confused to the quadrant test for the lumbar spine.[2]
Clinically relevant anatomy[edit | edit source]
The most important structures of the art. coxae are the fossa acetabuli, facies lunata, labrum acetabuli, lig. transversum acetabuli, caput femoris, lig. ischiofemorale, lig iliofemorale and lig. pubofemorale. The art. Coxae is an articulation sphaeroidea.[3] [4]
Purpose
[edit | edit source]
The purpose of the Hip Quadrant test is to determine if there is a nonspecific hip pathology and a chance of ROM. This test does so by completing the ROM from flexion and adduction to flexion and abduction[5]. This test is also capable to detect early hip degeneration.[6]
Technique[edit | edit source]
The patient lies supine on the table. The therapist stands on the side of the involved leg. He brings the hip and the knee to 90° flexion, the knee is directed towards the opposite shoulder (figure 1). One hand of the therapist is above the patient’s knee, the other is above the malleolis. Afterwards the therapist puts pressure on the leg by pushing the femur dorsally.[7][5][1]
In the first part of the exam the therapist adducts the patient's leg until the pelvis begins to raise off the table.
In the second part of the exam the therapist brings the leg of the patient in abduction with the hip still in 90° flexion and goes to abduction until the pelvis almost raises of the table. When he brings the leg to abduction it is important to keep the resistance on the leg and to go to from adduction to abduction in an arch.[1]
Result[edit | edit source]
The test is considered positive if the patient has any pain. The test is also positive if the therapist can feel any crepitus or if there is a leathery end feeling or if there’s a loss in ROM.[5]
The test is considered negative if you can go from flexion-adduction to flexion-abduction in an arch, a normal ROM and with a normal end-feeling.[5][1]
Dysfunction[edit | edit source]
A positive Hip Quadrant test is an indication that there might be arthritis, an osteochrondral defect, avascular necrosis, joint capsule tightness and an acetabular labrum defect[8]. This test also detects if the patients hip can move in the full range of motion.[7]
Recent Related Research (from Pubmed)[edit | edit source]
References
[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 ] Peter H. Seidenberg,Jimmy D. Bowen - The Hip and Pelvis in Sports Medicine and Primary Care pg. 33. Peter H. Seidenberg and Jimmy D. Bowen (editors). Springer (publisher) Evidence level: 5 grade of recommendation: F
- ↑ Lyle MA, Manes S, McGuinness M, Ziaei S, Iversen MD.Relationship of physical examination findings and self-r eported symptom severity and physical function in patients with degenerative lumbar conditions. Phys Ther. 2005 Feb;85(2):120-33.fckLREvidence level: 2a grade of recommendation: B
- ↑ Human anatomy atlas Sobotta part 2: lower extremity pg 263 – 272. Bohn Stafleu, Van Loghum 3th print R. Putz and R. Pabst
- ↑ figure 1: http://www.healthbase.com/resources/images/
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 M. Lynn Palmer – Fundamentels of musculoskeletal assesment techniques pg. 305. Second edition, M lynn palmer and Marcia E. Epler. Uppincott Williams and Willens (publisher) Evidence level: 5 grade of recommendation: F
- ↑ Manning C, Hudson Z. Comparison of hip joint range of motion in professional youth and senior team footballers with age-matched controls: an indication of early degenerative change? Phys Ther Sport. 2009 Feb;10(1):25-9. Epub 2008 Dec 24.fckLREvidence level: 3a grade of recommendation: C
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Thomas A. Souza Differential Diagnosis and Management for the Chiropractor: Protocols and algoritms pg 345. Fourth edition, Thomas A. Souza, DC, DACBSP. Jean and Bartlett publishers (Sanburry, Massachussets). Evidence level: 5 grade of recommendation: F
- ↑ Mitchell B, McCrory P, Brukner P, O'Donnell J, Colson E, Howells R. Hip joint pathology: clinical presentation and correlation between magnetic resonance arthrography, ultrasound, and arthroscopic findings in 25 consecutive cases. Clin J Sport Med. 2003 May;13(3):152-6. Evidence level: 2c grade of recommendation: C