Hip Pain and Mobility Deficits: Difference between revisions
m ("Aetiology" is added.) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
Hip joint pain is a common clinical problem that can be seen in adulthood at any age or activity level. <ref name=":0">Chamberlain, R. (2021). [https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2021/0115/p81.html Hip pain in adults: evaluation and differential diagnosis.] ''American family physician'', ''103''(2), 81-89.</ref> The purpose of this page is to describe the evidence-based physical therapy practice including diagnosis, assessment and interventions for hip pain in adults. | Hip joint pain is a common clinical problem that can be seen in adulthood at any age or activity level. <ref name=":0">Chamberlain, R. (2021). [https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2021/0115/p81.html Hip pain in adults: evaluation and differential diagnosis.] ''American family physician'', ''103''(2), 81-89.</ref> The purpose of this page is to describe the evidence-based physical therapy practice including diagnosis, assessment and interventions for hip pain in adults. | ||
Hip pain can arise for a variety of reasons, most commonly caused by [[Hip Osteoarthritis|hip osteoarthritis]] (OA). Non-arthritic hip joint pain can arise due to the conditions such as femoroacetabular impingement syndrome (FAIS), developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH), hip instability, acetabular labral tears, osteochondral lesions, loose bodies, and ligamentum teres tears. <ref>Enseki, K. R., Bloom, N. J., Harris-Hayes, M., Cibulka, M. T., Disantis, A., Di Stasi, S., ... & Beattie, P. F. (2023). [https://www.jospt.org/doi/full/10.2519/jospt.2023.0302 Hip Pain and Movement Dysfunction Associated With Nonarthritic Hip Joint Pain: A Revision: Clinical Practice Guidelines Linked to the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health from the Academy of Orthopaedic Physical Therapy and American Academy of Sports Physical Therapy of the American Physical Therapy Association.] ''Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy'', (7), CPG1-CPG70.</ref> | Hip pain can arise for a variety of reasons, most commonly caused by [[Hip Osteoarthritis|hip osteoarthritis]] (OA). Non-arthritic hip joint pain can arise due to the conditions such as femoroacetabular impingement syndrome (FAIS), developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH), hip instability, acetabular labral tears, osteochondral lesions, loose bodies, and ligamentum teres tears. <ref>Enseki, K. R., Bloom, N. J., Harris-Hayes, M., Cibulka, M. T., Disantis, A., Di Stasi, S., ... & Beattie, P. F. (2023). [https://www.jospt.org/doi/full/10.2519/jospt.2023.0302 Hip Pain and Movement Dysfunction Associated With Nonarthritic Hip Joint Pain: A Revision: Clinical Practice Guidelines Linked to the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health from the Academy of Orthopaedic Physical Therapy and American Academy of Sports Physical Therapy of the American Physical Therapy Association.] ''Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy'', (7), CPG1-CPG70.</ref> | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
* Proximal hamstring tendinopathy or tear | * Proximal hamstring tendinopathy or tear | ||
== | ==Diagnostic Procedures== | ||
== | === Anamnesis === | ||
History taking should include: | |||
* Personal history of developmental hip dysplasia | |||
* Slipped capital femoral epiphysis | |||
* Sports activities, and injuries | |||
* Family history of hip problems | |||
* Location and quality of pain | |||
* Aggravating and alleviating factors | |||
* Mechanical symptoms <ref>Wilson, J. J., & Furukawa, M. (2014). [https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2014/0101/p27.html Evaluation of the patient with hip pain]. ''American family physician'', ''89''(1), 27-34.</ref><ref>Kamegaya, M., Saisu, T., Nakamura, J., Murakami, R., Segawa, Y., & Wakou, M. (2011). Drehmann sign and femoro-acetabular impingement in SCFE. ''Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics'', ''31''(8), 853-857.</ref> | |||
==== | === Physical Examination === | ||
* | * Gait analysis: Especially for antalgic or Trendelenburg gait <ref name=":0" /> | ||
* | * Evaluation of the range of motion (including passive ROM) in the hip joint and associated pain <ref name=":0" /> <ref name=":1">Cibulka, M,T., Bloom, N.J., Enseki, K.R., Macdonald, C.W., Woehrle, J., & McDonough, CM. (2017). [https://www.jospt.org/doi/10.2519/jospt.2017.0301 Hip Pain and Mobility Deficits-Hip Osteoarthritis: Revision 2017]. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2017 Jun;47(6):A1-A37. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2017.0301.</ref> | ||
* Strength testing of the muscles overlying the hip joint: Especially the hip abductor muscles <ref name=":0" /><ref name=":1" /> | |||
* Palpation of the painful area <ref name=":0" /> | |||
* Special tests: Flexion, abduction, and external rotation (FABER or Patrick’s) <ref name=":1" /> | |||
==Outcome Measures== | ==Outcome Measures== | ||
Clinicians should use validated outcome measures that include domains of hip pain, body function impairment, activity limitation, and participation restriction to assess outcomes of treatment of hip osteoarthritis | Clinicians should use validated outcome measures that include domains of hip pain, body function impairment, activity limitation, and participation restriction to assess outcomes of treatment of hip osteoarthritis: | ||
Measures to assess hip pain | * Measures to assess hip pain: Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) pain subscale, Brief Pain Inventory (BPI), pressure pain threshold (PPT), pain visual analog scale (VAS). <ref name=":1" /> | ||
* Measure to assess activity limitation and participation restriction: WOMAC physical function subscale, the Hip disability and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (HOOS), Lower Extremity Functional Scale (LEFS), and Harris Hip Score (HHS). <ref name=":1" /> | |||
* To assess activity limitation, participation restrictions, and changes in the patient’s level of function over the episode of care, clinicians should utilize reliable and valid physical performance measures, such as the 6-minute walk test, 30-second chair stand, stair measure, timed up-and-go test, self-paced walk, timed single-leg stance, 4-square step test, and step test. | |||
* 4-square step test, timed single-leg stance test, and the Berg Balance Scale are also recommended to measure balance performance and activities for patients with hip OA especially those with decreased physical function or a high risk of falls because of past history. <ref name=":1" /> | |||
Recommended outcome measures at baseline and at least 1 other follow-up point for patients with with nonarthritic hip joint are listed below: | |||
* To assess the impact of impairments of body function and structure on activity limitations and participation restrictions: International Hip Outcome Tool (iHOT), Copenhagen Hip and Groin Outcome Score (HAGOS), Hip Outcome Score (HOS) ADL, and/or HOS Sports-Related Activities (SRA). | |||
* To assess depression, anxiety, low self-efficacy, and kinesiophobia: patient-reported outcome measure (PROM). | |||
==Management / Interventions== | ==Management / Interventions== | ||
=== Guidelines For Hip Pain Related To [[Hip Osteoarthritis]] === | === Guidelines For Hip Pain Related To [[Hip Osteoarthritis]] === | ||
=== '''Patient Education''' === | |||
Clinicians should provide patient education combined with exercise and/or manual therapy. Education should include teaching activity modification, exercise, supporting weight reduction when overweight, and methods of unloading the arthritic joints. '''(Grade: B)''' | Clinicians should provide patient education combined with exercise and/or manual therapy. Education should include teaching activity modification, exercise, supporting weight reduction when overweight, and methods of unloading the arthritic joints. '''(Grade: B)''' | ||
==== '''Manual Therapy''' ==== | ==== '''Manual Therapy''' ==== | ||
Clinicians should use manual therapy for patients with mild to moderate hip osteoarthritis and impairment of joint mobility, flexibility, and/or pain. Manual therapy may include thrust, nonthrust, and soft tissue mobilization. Doses and duration may range from 1 to 3 times per week over 6 to 12 weeks in patients with mild to moderate hip osteoarthritis. As hip motion improves, clinicians should add exercises including stretching and strengthening to augment and sustain gains in the patient’s range of motion, flexibility, and strength. '''(Grade: A)''' | Clinicians should use manual therapy for patients with mild to moderate hip osteoarthritis and impairment of joint mobility, flexibility, and/or pain. Manual therapy may include thrust, nonthrust, and soft tissue mobilization. Doses and duration may range from 1 to 3 times per week over 6 to 12 weeks in patients with mild to moderate hip osteoarthritis. As hip motion improves, clinicians should add exercises including stretching and strengthening to augment and sustain gains in the patient’s range of motion, flexibility, and strength. '''(Grade: A)'''[[File:Levels of Evidence.jpg|570x570px|thumb|Table 1<ref>Cibulka, M,T., Bloom, N.J., Enseki, K.R., Macdonald, C.W., Woehrle, J., & McDonough, CM. (2017). [https://www.jospt.org/doi/10.2519/jospt.2017.0301 Hip Pain and Mobility Deficits-Hip Osteoarthritis: Revision 2017]. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2017 Jun;47(6):A1-A37. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2017.0301.</ref>]] | ||
==== '''Flexibility, Strengthening, and Endurance Exercise''' ==== | ==== '''Flexibility, Strengthening, and Endurance Exercise''' ==== | ||
Clinicians should use individualized flexibility, strengthening, and endurance exercises to address impairments in hip range of motion, specific muscle weaknesses, and limited thigh (hip) muscle flexibility. For group-based exercise programs, effort should be made to tailor exercises to address patients’ most relevant physical impairments. Dosage and duration of treatment for effect should range from 1 to 5 times per week over 6 to 12 weeks in patients with mild to moderate hip osteoarthritis. '''(Grade: B)''' | Clinicians should use individualized flexibility, strengthening, and endurance exercises to address impairments in hip range of motion, specific muscle weaknesses, and limited thigh (hip) muscle flexibility. For group-based exercise programs, effort should be made to tailor exercises to address patients’ most relevant physical impairments. Dosage and duration of treatment for effect should range from 1 to 5 times per week over 6 to 12 weeks in patients with mild to moderate hip osteoarthritis. '''(Grade: B)''' | ||
| Line 116: | Line 103: | ||
==== '''Weight Loss''' ==== | ==== '''Weight Loss''' ==== | ||
In addition to providing exercise intervention, clinicians should collaborate with physicians, nutritionists, or dietitians to support weight reduction in individuals with hip osteoarthritis who are overweight or obese. '''(Grade: C)''' | In addition to providing exercise intervention, clinicians should collaborate with physicians, nutritionists, or dietitians to support weight reduction in individuals with hip osteoarthritis who are overweight or obese. '''(Grade: C)''' | ||
==Differential Diagnosis== | |||
== Differential Diagnosis == | |||
[[Hip Osteoarthritis|Hip osteoarthritis]]: Moderate anterior or lateral hip pain during weight-bearing activities, morning stiffness less than 1 hour in duration after wakening, hip internal rotation range of motion less than 24° or internal rotation and hip flexion 15° less than the nonpainful side, and/or increased hip pain associated with passive hip internal rotation. <ref name=":1" /> | |||
==Resources == | ==Resources == | ||
* Hip Pain and Mobility Guidelines (Revision 2017): https://www.jospt.org/doi/pdf/10.2519/jospt.2017.0301 | * Hip Pain and Mobility Guidelines (Revision 2017): https://www.jospt.org/doi/pdf/10.2519/jospt.2017.0301 | ||
* Guideline for the Management of Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis, 2nd Ed.: http://www.acsep.org.au/content/Document/guideline-for-the-management-of-knee-and-hip-oa-2nd-edition.pdf | * Guideline for the Management of Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis, 2nd Ed.: http://www.acsep.org.au/content/Document/guideline-for-the-management-of-knee-and-hip-oa-2nd-edition.pdf | ||
* Management of Falls in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Clinical Guidance Statement From the Academy of Geriatric Physical Therapy of the American Physical Therapy Association: https://academic.oup.com/ptj/article/95/6/815/2686335?login=false | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 18:13, 9 July 2023
Original Editors - Tyler Shultz
Top Contributors - Tyler Shultz, Sehriban Ozmen, Amanda Ager, Admin, Evan Thomas, Kim Jackson, Lauren Lopez, WikiSysop and Vidya Acharya
This article or area is currently under construction and may only be partially complete. Please come back soon to see the finished work! (09/07/2023)
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Hip joint pain is a common clinical problem that can be seen in adulthood at any age or activity level. [1] The purpose of this page is to describe the evidence-based physical therapy practice including diagnosis, assessment and interventions for hip pain in adults.
Hip pain can arise for a variety of reasons, most commonly caused by hip osteoarthritis (OA). Non-arthritic hip joint pain can arise due to the conditions such as femoroacetabular impingement syndrome (FAIS), developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH), hip instability, acetabular labral tears, osteochondral lesions, loose bodies, and ligamentum teres tears. [2]
Clinically Relevant Anatomy[edit | edit source]
Aetiology[edit | edit source]
Possible causes of hip joint pain according to the common pain locations are: [1]
Anterior Hip Pain[edit | edit source]
- Referred pain: From intra-abdominal or intrapelvic causes
- Extra-articular: Flexor tendon
- Intra-articular: Femoroacetabular impingement, labral tear, femoral neck stress fracture, avascular necrosis, osteoarthritis, hip fracture
Lateral Hip Pain[edit | edit source]
- Greater trochanteric pain syndrome, including bursitis, gluteus medius tendinopathy or tear, external snapping, or iliotibial band friction
Posterior Hip Pain[edit | edit source]
- Referred pain: From intra-abdominal or intrapelvic causes
- Deep gluteal syndrome
- Ischiofemoral impingement
- Lumbar spine or muscle
- Sacroiliac joint pain
- Proximal hamstring tendinopathy or tear
Diagnostic Procedures[edit | edit source]
Anamnesis[edit | edit source]
History taking should include:
- Personal history of developmental hip dysplasia
- Slipped capital femoral epiphysis
- Sports activities, and injuries
- Family history of hip problems
- Location and quality of pain
- Aggravating and alleviating factors
- Mechanical symptoms [3][4]
Physical Examination[edit | edit source]
- Gait analysis: Especially for antalgic or Trendelenburg gait [1]
- Evaluation of the range of motion (including passive ROM) in the hip joint and associated pain [1] [5]
- Strength testing of the muscles overlying the hip joint: Especially the hip abductor muscles [1][5]
- Palpation of the painful area [1]
- Special tests: Flexion, abduction, and external rotation (FABER or Patrick’s) [5]
Outcome Measures[edit | edit source]
Clinicians should use validated outcome measures that include domains of hip pain, body function impairment, activity limitation, and participation restriction to assess outcomes of treatment of hip osteoarthritis:
- Measures to assess hip pain: Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) pain subscale, Brief Pain Inventory (BPI), pressure pain threshold (PPT), pain visual analog scale (VAS). [5]
- Measure to assess activity limitation and participation restriction: WOMAC physical function subscale, the Hip disability and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (HOOS), Lower Extremity Functional Scale (LEFS), and Harris Hip Score (HHS). [5]
- To assess activity limitation, participation restrictions, and changes in the patient’s level of function over the episode of care, clinicians should utilize reliable and valid physical performance measures, such as the 6-minute walk test, 30-second chair stand, stair measure, timed up-and-go test, self-paced walk, timed single-leg stance, 4-square step test, and step test.
- 4-square step test, timed single-leg stance test, and the Berg Balance Scale are also recommended to measure balance performance and activities for patients with hip OA especially those with decreased physical function or a high risk of falls because of past history. [5]
Recommended outcome measures at baseline and at least 1 other follow-up point for patients with with nonarthritic hip joint are listed below:
- To assess the impact of impairments of body function and structure on activity limitations and participation restrictions: International Hip Outcome Tool (iHOT), Copenhagen Hip and Groin Outcome Score (HAGOS), Hip Outcome Score (HOS) ADL, and/or HOS Sports-Related Activities (SRA).
- To assess depression, anxiety, low self-efficacy, and kinesiophobia: patient-reported outcome measure (PROM).
Management / Interventions[edit | edit source]
Guidelines For Hip Pain Related To Hip Osteoarthritis[edit | edit source]
Patient Education[edit | edit source]
Clinicians should provide patient education combined with exercise and/or manual therapy. Education should include teaching activity modification, exercise, supporting weight reduction when overweight, and methods of unloading the arthritic joints. (Grade: B)
Manual Therapy[edit | edit source]
Clinicians should use manual therapy for patients with mild to moderate hip osteoarthritis and impairment of joint mobility, flexibility, and/or pain. Manual therapy may include thrust, nonthrust, and soft tissue mobilization. Doses and duration may range from 1 to 3 times per week over 6 to 12 weeks in patients with mild to moderate hip osteoarthritis. As hip motion improves, clinicians should add exercises including stretching and strengthening to augment and sustain gains in the patient’s range of motion, flexibility, and strength. (Grade: A)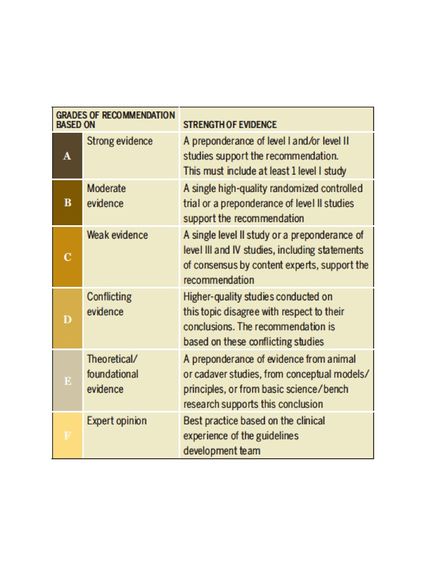
Flexibility, Strengthening, and Endurance Exercise[edit | edit source]
Clinicians should use individualized flexibility, strengthening, and endurance exercises to address impairments in hip range of motion, specific muscle weaknesses, and limited thigh (hip) muscle flexibility. For group-based exercise programs, effort should be made to tailor exercises to address patients’ most relevant physical impairments. Dosage and duration of treatment for effect should range from 1 to 5 times per week over 6 to 12 weeks in patients with mild to moderate hip osteoarthritis. (Grade: B)
Functional, Gait, and Balance Training[edit | edit source]
Clinicians should provide impairment-based functional, gait, and balance training, including the proper use of assistive devices (canes, crutches, walkers), to patients with hip osteoarthritis and activity limitations, balance impairment, and/or gait limitations when associated problems are observed and documented during the history or physical assessment of the patient. (Grade: C)
Clinicians should individualize prescription of therapeutic activities based on the patient’s values, daily life participation, and functional activity needs. (Grade: C)
Modalities[edit | edit source]
Clinicians may use ultrasound (1 MHz; 1 W/cm2 for 5 minutes each to the anterior, lateral, and posterior hip for a total of 10 treatments over a 2-week period) in addition to exercise and hot packs in the short-term management of pain and activity limitation in individuals with hip osteoarthritis. (Grade: B)
Bracing[edit | edit source]
Clinicians should not use bracing as a first line of treatment. A brace may be used after exercise or manual therapies are unsuccessful in improving participation in activities that require turning/pivoting for patients with mild to moderate hip osteoarthritis, especially in those with bilateral hip osteoarthritis.(Grade: F)
Weight Loss[edit | edit source]
In addition to providing exercise intervention, clinicians should collaborate with physicians, nutritionists, or dietitians to support weight reduction in individuals with hip osteoarthritis who are overweight or obese. (Grade: C)
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Hip osteoarthritis: Moderate anterior or lateral hip pain during weight-bearing activities, morning stiffness less than 1 hour in duration after wakening, hip internal rotation range of motion less than 24° or internal rotation and hip flexion 15° less than the nonpainful side, and/or increased hip pain associated with passive hip internal rotation. [5]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- Hip Pain and Mobility Guidelines (Revision 2017): https://www.jospt.org/doi/pdf/10.2519/jospt.2017.0301
- Guideline for the Management of Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis, 2nd Ed.: http://www.acsep.org.au/content/Document/guideline-for-the-management-of-knee-and-hip-oa-2nd-edition.pdf
- Management of Falls in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Clinical Guidance Statement From the Academy of Geriatric Physical Therapy of the American Physical Therapy Association: https://academic.oup.com/ptj/article/95/6/815/2686335?login=false
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Chamberlain, R. (2021). Hip pain in adults: evaluation and differential diagnosis. American family physician, 103(2), 81-89.
- ↑ Enseki, K. R., Bloom, N. J., Harris-Hayes, M., Cibulka, M. T., Disantis, A., Di Stasi, S., ... & Beattie, P. F. (2023). Hip Pain and Movement Dysfunction Associated With Nonarthritic Hip Joint Pain: A Revision: Clinical Practice Guidelines Linked to the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health from the Academy of Orthopaedic Physical Therapy and American Academy of Sports Physical Therapy of the American Physical Therapy Association. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy, (7), CPG1-CPG70.
- ↑ Wilson, J. J., & Furukawa, M. (2014). Evaluation of the patient with hip pain. American family physician, 89(1), 27-34.
- ↑ Kamegaya, M., Saisu, T., Nakamura, J., Murakami, R., Segawa, Y., & Wakou, M. (2011). Drehmann sign and femoro-acetabular impingement in SCFE. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics, 31(8), 853-857.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 Cibulka, M,T., Bloom, N.J., Enseki, K.R., Macdonald, C.W., Woehrle, J., & McDonough, CM. (2017). Hip Pain and Mobility Deficits-Hip Osteoarthritis: Revision 2017. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2017 Jun;47(6):A1-A37. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2017.0301.
- ↑ Cibulka, M,T., Bloom, N.J., Enseki, K.R., Macdonald, C.W., Woehrle, J., & McDonough, CM. (2017). Hip Pain and Mobility Deficits-Hip Osteoarthritis: Revision 2017. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2017 Jun;47(6):A1-A37. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2017.0301.